Mina源码阅读笔记(四)—Mina的连接IoConnector1
来源:互联网 发布:做项目计划软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/06 14:26
上一篇写的是IoAcceptor是服务器端的接收代码,今天要写的是IoConnector,是客户端的连接器。在昨天,我们还留下一些问题没有解决,这些问题今天同样会产生,但是都要等到讲到session的时候才能逐步揭开。先回顾一下问题:
l 我们已经在AbstractPollingIoAcceptor中看到了,mina是将连接(命令)和业务(读写)分不同线程处理的,但是我们还没有看到mina是如何实现对这些线程的管理的。
l 在昨天的最后,我们看到在NioSocketAcceptor中的具体NIO实现,但是我们还没有看到mina是在哪里调用了这些具体操作的。当然这也是mina对连接线程管理的一部分。
这些问题今天也会出现,因为从名字上就能看出,IoConnector和IoAcceptor的构造相差不大,所以在写connector的分析时,主要会从结构和差异上入手,最后再给出昨天没写完的删减版的Acceptor。先回顾一下客户端连接的代码:
01// 创建一个非阻塞的客户端程序02 IoConnector connector = new NioSocketConnector();03 // 设置链接超时时间04 connector.setConnectTimeout(30000);05 // 添加过滤器06 connector.getFilterChain().addLast(07 "codec",08 new ProtocolCodecFilter(new MessageCodecFactory(09 new InfoMessageDecoder(Charset.forName("utf-8")),10 new InfoMessageEncoder(Charset.forName("utf-8")))));11 // 添加业务逻辑处理器类12 connector.setHandler(new ClientHandler());13 IoSession session = null;14 try {15 ConnectFuture future = connector.connect(new InetSocketAddress(16 HOST, PORT));// 创建连接17 future.awaitUninterruptibly();// 等待连接创建完成18 session = future.getSession();// 获得session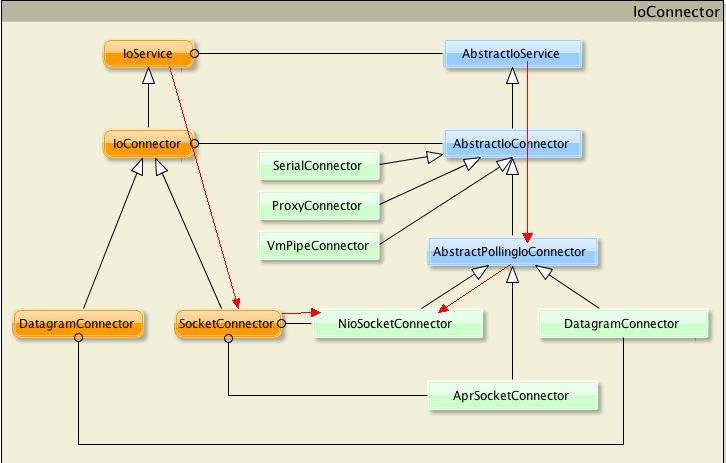
还是先看IoConnector的结构图,图来自mina官网,用XMind绘制的。在写构成之前,我们还是先看一下mina官网对这些connector的介绍:
As we have to use an IoAcceptor for servers, you have to implement the IoConnector. Again, we have many implementation classes :
- NioSocketConnector : the non-blocking Socket transport Connector
- NioDatagramConnector : the non-blocking UDP transport * Connector*
- AprSocketConnector : the blocking Socket transport * Connector*, based on APR
- ProxyConnector : a Connector providing proxy support
- SerialConnector : a Connector for a serial transport
- VmPipeConnector : the in-VM * Connector*
其中,NioSocketConnector是我们最常用到的,proxy方式虽然在mina的源码中也花了大篇幅去撰写,但可惜的是很少有相关的文档,所以学习的成本还挺高的。今天我们主要还是按照上图画的两条路来看NioSocketConnector。
和昨天一样,我们还是从左边的路走起,看interface IoConnector,这个接口主要定义了连接的方法以及socket连接时用到的参数。在mina中通过IoFuture来描述、侦听在IoSession上实现的异步IO操作,所以这IoConnector中的connect方法都返回了一个ConnectFuture实例。
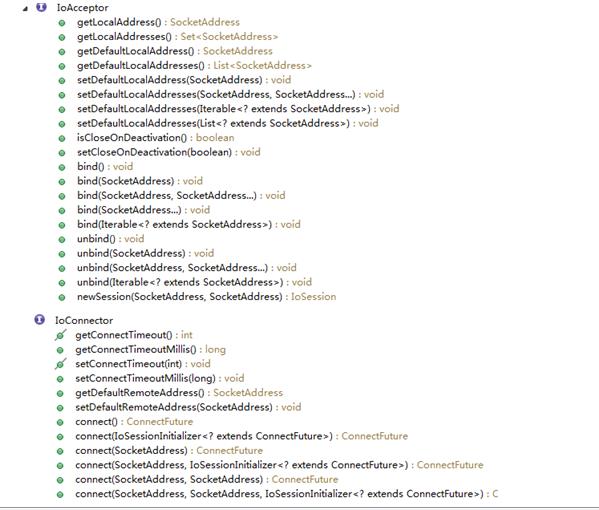
而在SocketConnector接口中的定义中就显得更简单了,它和IoConnector之间也是接口的继承关系,在SocketConnector中就定义了两类方法,一个对远程地址的get和set,一个拿到session的配置。这些都容易理解。
再来看右边,AbstractIoConnector,这个抽象类主要作用就是实现IoConnector里定义的操作,至于他又继承了AbstractIoService,一是为了用到父类(AbstractIoService)的方法,二是为了将那些父类没有实现的方法继续传递下去,让它(AbstractIoConnector)的子类去实现。所以看多了,好多结构也能看明白了,这里我觉得主要要学习的还是接口、抽象类之间的引用关系。
继续看AbstractIoConnector,这个类主要是实现了connect的逻辑操作(封装了连接前后的一些必要执行步骤和check一些状态),具体的连接操作还是让子类去实现,这个和上篇写的AbstractIoAcceptor一模一样,在AbstractIoAcceptor中,主要也是封装了bind的逻辑操作,真正的bind过程是让子类去实现的简单看下代码:
01public final ConnectFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress,02 IoSessionInitializer<? extends ConnectFuture> sessionInitializer) {03 if (isDisposing()) {04 throw new IllegalStateException("The connector has been disposed.");05 }06 07 if (remoteAddress == null) {08 throw new IllegalArgumentException("remoteAddress");09 }10 11 if (!getTransportMetadata().getAddressType().isAssignableFrom(remoteAddress.getClass())) {12 throw new IllegalArgumentException("remoteAddress type: " + remoteAddress.getClass() + " (expected: "13 + getTransportMetadata().getAddressType() + ")");14 }15 16 if (localAddress != null && !getTransportMetadata().getAddressType().isAssignableFrom(localAddress.getClass())) {17 throw new IllegalArgumentException("localAddress type: " + localAddress.getClass() + " (expected: "18 + getTransportMetadata().getAddressType() + ")");19 }20 21 if (getHandler() == null) {22 if (getSessionConfig().isUseReadOperation()) {23 setHandler(new IoHandler() {24 public void exceptionCaught(IoSession session, Throwable cause) throws Exception {25 // Empty handler26 }27 28 public void messageReceived(IoSession session, Object message) throws Exception {29 // Empty handler30 }31 32 public void messageSent(IoSession session, Object message) throws Exception {33 // Empty handler34 }35 36 public void sessionClosed(IoSession session) throws Exception {37 // Empty handler38 }39 40 public void sessionCreated(IoSession session) throws Exception {41 // Empty handler42 }43 44 public void sessionIdle(IoSession session, IdleStatus status) throws Exception {45 // Empty handler46 }47 48 public void sessionOpened(IoSession session) throws Exception {49 // Empty handler50 }51 });52 } else {53 throw new IllegalStateException("handler is not set.");54 }55 }56 57 return connect0(remoteAddress, localAddress, sessionInitializer);58}59 60 61 protected abstract ConnectFuture connect0(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress,62 IoSessionInitializer<? extends ConnectFuture> sessionInitializer);Connect0才是最后具体的操作,而这一步操作在这个类中被没有给出实现。具体实现放在了AbstractPollingIoConnector上。和昨天一样,这些设计都是对称的,我们还是看三点:
l implementing client transport using a polling strategy
l A Executor will be used for running client connection, and an AbstractPollingIoProcessor will be used for processing connected client I/O operations like reading, writing and closing.
l All the low level methods for binding, connecting, closing need to be provided by the subclassing implementation
至于内部的具体实现,那跟acceptor中没什么区别,连使用的工具类都差别不大,这部分就很容易读懂了,只不过一个是bind一个是connect。
最后我们看NioSocketConnector,具体连接的实现类,只有一个成员变量和NioSocketAcceptor一样:
01private volatile Selector selector;02 03 @Override04 protected SocketChannel newHandle(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {05 SocketChannel ch = SocketChannel.open();06 07 int receiveBufferSize = (getSessionConfig()).getReceiveBufferSize();08 if (receiveBufferSize > 65535) {09 ch.socket().setReceiveBufferSize(receiveBufferSize);10 }11 12 if (localAddress != null) {13 ch.socket().bind(localAddress);14 }15 ch.configureBlocking(false);16 return ch;17 }只是需要注意,这里面专门有个内部类来处理selectionkey,将遍历的过程都抽离出来了,这个和我们用NIO的一般写法稍有不同,这样做的好处也是为了复用:
01private static class SocketChannelIterator implements Iterator<SocketChannel> {02 03 private final Iterator<SelectionKey> i;04 05 private SocketChannelIterator(Collection<SelectionKey> selectedKeys) {06 this.i = selectedKeys.iterator();07 }08 09 /**10 * {@inheritDoc}11 */12 public boolean hasNext() {13 return i.hasNext();14 }15 16 /**17 * {@inheritDoc}18 */19 public SocketChannel next() {20 SelectionKey key = i.next();21 return (SocketChannel) key.channel();22 }23 24 /**25 * {@inheritDoc}26 */27 public void remove() {28 i.remove();29 }30 }补一个上篇就应该发的acceptor的阉割版,写这样的东西主要还是为了理清楚结构。我主要是把内容简化了,但是结构都没有变,核心的成员变量也没有少:
起点IoService:
01package org.apache.mina.core.rewrite.service;02 03/**04 * IO Service --handler/processor/acceptor/connector05 *06 * @author ChenHui07 *08 */09public interface IoService {10 /** 添加listener */11 void addListener(IoServiceListener listener);12 13 /** 销毁 */14 void dispose(boolean awaitTermination);15 16 /** 设置handler */17 IoHandler getHandler();18 19 void setHandler(IoHandler handler);20 21 /** 管理session */22 int getManagedSessionCount();23 24 boolean isActive();25}01package org.apache.mina.core.rewrite.service;02 03import java.io.IOException;04import java.net.SocketAddress;05import java.util.Set;06 07/**08 * 注意接口的继承,这里的方法都是新定义的09 * 10 * Acceptor 主要用于:Accepts incoming connection, communicates with clients, and11 * fires events to IoHandler12 *13 * @author ChenHui14 */15public interface IoAcceptor extends IoService {16 17 SocketAddress getLocalAddress();18 19 Set<SocketAddress> getLocalAddresses();20 21 void bind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws IOException;22 23 void bind(Iterable<? extends SocketAddress> localAddresses) throws IOException;24 25 void unbind(SocketAddress localAddress);26 27 28 /**没有写到IoSession 所以暂时不用*/29 //IoSession newSession(SocketAddress remoteAddress,SocketAddress localAddress);30}01package org.apache.mina.rewrite.transport.socket;02 03import java.net.InetSocketAddress;04 05import org.apache.mina.core.rewrite.service.IoAcceptor;06 07public interface SocketAcceptor extends IoAcceptor {08 09 InetSocketAddress getLocalAddress();10 11 void setDefaultLocalAddress(InetSocketAddress localAddress);12 13 public boolean isReuseAddress();14 15 // ...16 17 // SocketSessionConfig getSessionConfig();18}001package org.apache.mina.core.rewrite.service;002 003import java.util.concurrent.Executor;004import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;005import java.util.concurrent.Executors;006import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;007import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;008 009public abstract class AbstractIoService implements IoService {010 011 private static final AtomicInteger id = new AtomicInteger();012 013 private final String threadName;014 015 private final Executor executor;016 017 private final boolean createdExecutor;018 019 private IoHandler handler;020 021 // 用于安全的关闭022 protected final Object disposalLock = new Object();023 024 private volatile boolean disposing;025 026 private volatile boolean disposed;027 028 /**029 *030 * @param param031 * sessionConfig IoSessionConfig032 * @param executor033 * used for handling execution of IO event. can be null034 */035 protected AbstractIoService(Object param, Executor executor) {036 037 // TODO listener & session config038 039 if (executor == null) {040 this.executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();041 createdExecutor = true;042 } else {043 this.executor = executor;044 createdExecutor = false;045 }046 047 threadName = getClass().getSimpleName() + "-" + id.incrementAndGet();048 }049 050 @Override051 public void addListener(IoServiceListener listener) {052 // TODO add listener053 }054 055 /**注意这个不是override来的*/056 protected final void ececuteWorker(Runnable worker, String suffix){057 058 String actualThreadName=threadName;059 if(suffix!=null){060 actualThreadName=actualThreadName+"-"+suffix;061 }062 executor.execute(worker);063 }064 065 @Override066 public void dispose(boolean awaitTermination) {067 if (disposed) {068 return;069 }070 071 synchronized (disposalLock) {072 if (!disposing) {073 disposing = true;074 try {075 /** 真正的关闭方法TODO */076 dispose0();077 } catch (Exception e) {078 e.printStackTrace();079 }080 }081 }082 083 if (createdExecutor) {084 ExecutorService e = (ExecutorService) executor;085 e.shutdown();086 087 if (awaitTermination) {088 try {089 090 e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);091 092 } catch (InterruptedException e1) {093 // 注意异常时的中断处理094 Thread.currentThread().interrupt();095 }096 }097 }098 disposed = true;099 }100 101 protected abstract void dispose0() throws Exception;102 103 @Override104 public IoHandler getHandler() {105 return this.handler;106 }107 108 @Override109 public void setHandler(IoHandler handler) {110 if (handler == null) {111 throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler cannot be null");112 }113 // TODO isActive: when service is active, cannot be set handler114 if(isActive()){115 throw new IllegalStateException("when service is active, cannot be set handler");116 }117 118 this.handler = handler;119 }120 121}- Mina源码阅读笔记(四)—Mina的连接IoConnector1
- Mina源码阅读笔记(四)—Mina的连接IoConnector2
- Mina源码阅读笔记(四)—Mina的连接IoConnector
- Mina源码阅读笔记(三)-Mina的连接IoAccpetor
- Mina源码阅读笔记(三)-Mina的连接IoAccpetor
- Mina源码阅读笔记(三)-Mina的连接IoAccpetor
- Mina源码阅读笔记(三)-Mina的连接IoAccpetor
- Mina源码阅读笔记(五)—Mina对连接的操作IoSession
- Mina源码阅读笔记(五)—Mina对连接的操作IoSession
- Mina源码阅读笔记(五)—Mina对连接的操作IoSession
- Mina源码阅读笔记(五)—Mina对连接的操作IoSession
- Mina源码阅读笔记(六)—Mina异步IO的实现IoFuture
- Mina源码阅读笔记(七)—Mina的拦截器FilterChain
- Mina源码阅读笔记(六)—Mina异步IO的实现IoFuture
- Mina源码阅读笔记(六)—Mina异步IO的实现IoFuture
- Mina源码阅读笔记(七)—Mina的拦截器FilterChain
- Mina源码阅读笔记(八)—Mina拦截器器的末端IoHandler
- Mina源码阅读笔记(二)- IoBuffer的封装
- 学会查看错误日志!!!
- 8086汇编排序(冒泡、选择、快速)
- 设计模式(23)-行为型模式-VISITOR模式
- POJ2983 查分约束系统
- Cross-site scripting with UTF-7
- Mina源码阅读笔记(四)—Mina的连接IoConnector1
- TCP/IP详解卷一 第四章 ARP地址解析协议 第五章 RARP反向地址解析协议
- hdu 1166 敌兵布阵 线段树
- JAVA实现DES加密
- Mina源码阅读笔记(四)—Mina的连接IoConnector2
- Linux平台Makefile文件的编写基础篇
- nutch 1.8与solr 4.8环境搭建
- Python: tkinter实例改名小工具
- poj-1328


