朴素贝叶斯方法的应用实例----基于newsgroup文档集的贝叶斯算法实现
来源:互联网 发布:美联储 8月cpi数据 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/22 05:15
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/7577684
朴素贝叶斯:就是假定数据是独立的贝叶斯模型
基于newsgroup文档集的贝叶斯算法实现
2.7.1、newsgroup文档集介绍与预处理
Newsgroups最早由Lang于1995收集并在[Lang 1995]中使用。它含有20000篇左右的Usenet文档,几乎平均分配20个不同的新闻组。除了其中4.5%的文档属于两个或两个以上的新闻组以外,其余文档仅属于一个新闻组,因此它通常被作为单标注分类问题来处理。Newsgroups已经成为文本分类聚类中常用的文档集。美国MIT大学Jason Rennie对Newsgroups作了必要的处理,使得每个文档只属于一个新闻组,形成Newsgroups-18828。(注:本2.7节内容主要援引自参考文献条目8的内容,有任何不妥之处,还望原作者及众读者海涵,谢谢)
要做文本分类首先得完成文本的预处理,预处理的主要步骤如下:
- 英文词法分析,去除数字、连字符、标点符号、特殊 字符,所有大写字母转换成小写,可以用正则表达式:String res[] = line.split("[^a-zA-Z]");
- 去停用词,过滤对分类无价值的词;
- 词根还原stemming,基于Porter算法。
- private static String lineProcess(String line, ArrayList<String> stopWordsArray) throws IOException {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- //step1 英文词法分析,去除数字、连字符、标点符号、特殊字符,所有大写字母转换成小写,可以考虑用正则表达式
- String res[] = line.split("[^a-zA-Z]");
- //这里要小心,防止把有单词中间有数字和连字符的单词 截断了,但是截断也没事
- String resString = new String();
- //step2去停用词
- //step3stemming,返回后一起做
- for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++){
- if(!res[i].isEmpty() && !stopWordsArray.contains(res[i].toLowerCase())){
- resString += " " + res[i].toLowerCase() + " ";
- }
- }
- return resString;
- }
2.7.2、特征词的选取
首先统计经过预处理后在所有文档中出现不重复的单词一共有87554个,对这些词进行统计发现:
出现次数大于等于1次的词有87554个
出现次数大于等于3次的词有36456个
出现次数大于等于4次的词有30095个
特征词的选取策略:
策略一:保留所有词作为特征词 共计87554个
策略二:选取出现次数大于等于4次的词作为特征词共计30095个
特征词的选取策略:采用策略一,后面将对两种特征词选取策略的计算时间和平均准确率做对比
出现次数大于等于1次的词有87554个
出现次数大于等于3次的词有36456个
出现次数大于等于4次的词有30095个
特征词的选取策略:
策略一:保留所有词作为特征词 共计87554个
策略二:选取出现次数大于等于4次的词作为特征词共计30095个
特征词的选取策略:采用策略一,后面将对两种特征词选取策略的计算时间和平均准确率做对比
2.7.3、贝叶斯算法描述及实现
根据朴素贝叶斯公式,每个测试样例属于某个类别的概率 = 所有测试样例包含特征词类条件概率P(tk|c)之积 * 先验概率P(c)
在具体计算类条件概率和先验概率时,朴素贝叶斯分类器有两种模型:
(1) 多项式模型( multinomial model ) –以单词为粒度
类条件概率P(tk|c)=(类c下单词tk在各个文档中出现过的次数之和+1)/(类c下单词总数+训练样本中不重复特征词总数)
先验概率P(c)=类c下的单词总数/整个训练样本的单词总数
类条件概率P(tk|c)=(类c下单词tk在各个文档中出现过的次数之和+1)/(类c下单词总数+训练样本中不重复特征词总数)
先验概率P(c)=类c下的单词总数/整个训练样本的单词总数
(2) 伯努利模型(Bernoulli model) –以文件为粒度
类条件概率P(tk|c)=(类c下包含单词tk的文件数+1)/(类c下文件总数+2)
先验概率P(c)=类c下文件总数/整个训练样本的文件总数
本分类器选用多项式模型计算,根据斯坦福的《Introduction to Information Retrieval 》课件上所说,多项式模型计算准确率更高。
本分类器选用多项式模型计算,根据斯坦福的《Introduction to Information Retrieval 》课件上所说,多项式模型计算准确率更高。
贝叶斯算法的实现有以下注意点:
- 计算概率用到了BigDecimal类实现任意精度计算;
- 用交叉验证法做十次分类实验,对准确率取平均值;
- 根据正确类目文件和分类结果文计算混淆矩阵并且输出;
- Map<String,Double> cateWordsProb key为“类目_单词”, value为该类目下该单词的出现次数,避免重复计算。
贝叶斯算法实现类如下NaiveBayesianClassifier.java(author:yangliu)
- package com.pku.yangliu;
- import java.io.BufferedReader;
- import java.io.File;
- import java.io.FileReader;
- import java.io.FileWriter;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.math.BigDecimal;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.Set;
- import java.util.SortedSet;
- import java.util.TreeMap;
- import java.util.TreeSet;
- import java.util.Vector;
- /**利用朴素贝叶斯算法对newsgroup文档集做分类,采用十组交叉测试取平均值
- * 采用多项式模型,stanford信息检索导论课件上面言多项式模型比伯努利模型准确度高
- * 类条件概率P(tk|c)=(类c 下单词tk 在各个文档中出现过的次数之和+1)/(类c下单词总数+|V|)
- */
- public class NaiveBayesianClassifier {
- /**用贝叶斯法对测试文档集分类
- * @param trainDir 训练文档集目录
- * @param testDir 测试文档集目录
- * @param classifyResultFileNew 分类结果文件路径
- * @throws Exception
- */
- private void doProcess(String trainDir, String testDir,
- String classifyResultFileNew) throws Exception {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Map<String,Double> cateWordsNum = new TreeMap<String,Double>();//保存训练集每个类别的总词数
- Map<String,Double> cateWordsProb = new TreeMap<String,Double>();//保存训练样本每个类别中每个属性词的出现词数
- cateWordsProb = getCateWordsProb(trainDir);
- cateWordsNum = getCateWordsNum(trainDir);
- double totalWordsNum = 0.0;//记录所有训练集的总词数
- Set<Map.Entry<String,Double>> cateWordsNumSet = cateWordsNum.entrySet();
- for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Double>> it = cateWordsNumSet.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
- Map.Entry<String, Double> me = it.next();
- totalWordsNum += me.getValue();
- }
- //下面开始读取测试样例做分类
- Vector<String> testFileWords = new Vector<String>();
- String word;
- File[] testDirFiles = new File(testDir).listFiles();
- FileWriter crWriter = new FileWriter(classifyResultFileNew);
- for(int i = 0; i < testDirFiles.length; i++){
- File[] testSample = testDirFiles[i].listFiles();
- for(int j = 0;j < testSample.length; j++){
- testFileWords.clear();
- FileReader spReader = new FileReader(testSample[j]);
- BufferedReader spBR = new BufferedReader(spReader);
- while((word = spBR.readLine()) != null){
- testFileWords.add(word);
- }
- //下面分别计算该测试样例属于二十个类别的概率
- File[] trainDirFiles = new File(trainDir).listFiles();
- BigDecimal maxP = new BigDecimal(0);
- String bestCate = null;
- for(int k = 0; k < trainDirFiles.length; k++){
- BigDecimal p = computeCateProb(trainDirFiles[k], testFileWords, cateWordsNum, totalWordsNum, cateWordsProb);
- if(k == 0){
- maxP = p;
- bestCate = trainDirFiles[k].getName();
- continue;
- }
- if(p.compareTo(maxP) == 1){
- maxP = p;
- bestCate = trainDirFiles[k].getName();
- }
- }
- crWriter.append(testSample[j].getName() + " " + bestCate + "\n");
- crWriter.flush();
- }
- }
- crWriter.close();
- }
- /**统计某类训练样本中每个单词的出现次数
- * @param strDir 训练样本集目录
- * @return Map<String,Double> cateWordsProb 用"类目_单词"对来索引的map,保存的val就是该类目下该单词的出现次数
- * @throws IOException
- */
- public Map<String,Double> getCateWordsProb(String strDir) throws IOException{
- Map<String,Double> cateWordsProb = new TreeMap<String,Double>();
- File sampleFile = new File(strDir);
- File [] sampleDir = sampleFile.listFiles();
- String word;
- for(int i = 0;i < sampleDir.length; i++){
- File [] sample = sampleDir[i].listFiles();
- for(int j = 0; j < sample.length; j++){
- FileReader samReader = new FileReader(sample[j]);
- BufferedReader samBR = new BufferedReader(samReader);
- while((word = samBR.readLine()) != null){
- String key = sampleDir[i].getName() + "_" + word;
- if(cateWordsProb.containsKey(key)){
- double count = cateWordsProb.get(key) + 1.0;
- cateWordsProb.put(key, count);
- }
- else {
- cateWordsProb.put(key, 1.0);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return cateWordsProb;
- }
- /**计算某一个测试样本属于某个类别的概率
- * @param Map<String, Double> cateWordsProb 记录每个目录中出现的单词及次数
- * @param File trainFile 该类别所有的训练样本所在目录
- * @param Vector<String> testFileWords 该测试样本中的所有词构成的容器
- * @param double totalWordsNum 记录所有训练样本的单词总数
- * @param Map<String, Double> cateWordsNum 记录每个类别的单词总数
- * @return BigDecimal 返回该测试样本在该类别中的概率
- * @throws Exception
- * @throws IOException
- */
- private BigDecimal computeCateProb(File trainFile, Vector<String> testFileWords, Map<String, Double> cateWordsNum, double totalWordsNum, Map<String, Double> cateWordsProb) throws Exception {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- BigDecimal probability = new BigDecimal(1);
- double wordNumInCate = cateWordsNum.get(trainFile.getName());
- BigDecimal wordNumInCateBD = new BigDecimal(wordNumInCate);
- BigDecimal totalWordsNumBD = new BigDecimal(totalWordsNum);
- for(Iterator<String> it = testFileWords.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
- String me = it.next();
- String key = trainFile.getName()+"_"+me;
- double testFileWordNumInCate;
- if(cateWordsProb.containsKey(key)){
- testFileWordNumInCate = cateWordsProb.get(key);
- }else testFileWordNumInCate = 0.0;
- BigDecimal testFileWordNumInCateBD = new BigDecimal(testFileWordNumInCate);
- BigDecimal xcProb = (testFileWordNumInCateBD.add(new BigDecimal(0.0001))).divide(totalWordsNumBD.add(wordNumInCateBD),10, BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING);
- probability = probability.multiply(xcProb);
- }
- BigDecimal res = probability.multiply(wordNumInCateBD.divide(totalWordsNumBD,10, BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING));
- return res;
- }
- /**获得每个类目下的单词总数
- * @param trainDir 训练文档集目录
- * @return Map<String, Double> <目录名,单词总数>的map
- * @throws IOException
- */
- private Map<String, Double> getCateWordsNum(String trainDir) throws IOException {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Map<String,Double> cateWordsNum = new TreeMap<String,Double>();
- File[] sampleDir = new File(trainDir).listFiles();
- for(int i = 0; i < sampleDir.length; i++){
- double count = 0;
- File[] sample = sampleDir[i].listFiles();
- for(int j = 0;j < sample.length; j++){
- FileReader spReader = new FileReader(sample[j]);
- BufferedReader spBR = new BufferedReader(spReader);
- while(spBR.readLine() != null){
- count++;
- }
- }
- cateWordsNum.put(sampleDir[i].getName(), count);
- }
- return cateWordsNum;
- }
- /**根据正确类目文件和分类结果文件统计出准确率
- * @param classifyResultFile 正确类目文件
- * @param classifyResultFileNew 分类结果文件
- * @return double 分类的准确率
- * @throws IOException
- */
- double computeAccuracy(String classifyResultFile,
- String classifyResultFileNew) throws IOException {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Map<String,String> rightCate = new TreeMap<String,String>();
- Map<String,String> resultCate = new TreeMap<String,String>();
- rightCate = getMapFromResultFile(classifyResultFile);
- resultCate = getMapFromResultFile(classifyResultFileNew);
- Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> resCateSet = resultCate.entrySet();
- double rightCount = 0.0;
- for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = resCateSet.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
- Map.Entry<String, String> me = it.next();
- if(me.getValue().equals(rightCate.get(me.getKey()))){
- rightCount ++;
- }
- }
- computerConfusionMatrix(rightCate,resultCate);
- return rightCount / resultCate.size();
- }
- /**根据正确类目文件和分类结果文计算混淆矩阵并且输出
- * @param rightCate 正确类目对应map
- * @param resultCate 分类结果对应map
- * @return double 分类的准确率
- * @throws IOException
- */
- private void computerConfusionMatrix(Map<String, String> rightCate,
- Map<String, String> resultCate) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- int[][] confusionMatrix = new int[20][20];
- //首先求出类目对应的数组索引
- SortedSet<String> cateNames = new TreeSet<String>();
- Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> rightCateSet = rightCate.entrySet();
- for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = rightCateSet.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
- Map.Entry<String, String> me = it.next();
- cateNames.add(me.getValue());
- }
- cateNames.add("rec.sport.baseball");//防止数少一个类目
- String[] cateNamesArray = cateNames.toArray(new String[0]);
- Map<String,Integer> cateNamesToIndex = new TreeMap<String,Integer>();
- for(int i = 0; i < cateNamesArray.length; i++){
- cateNamesToIndex.put(cateNamesArray[i],i);
- }
- for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = rightCateSet.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
- Map.Entry<String, String> me = it.next();
- confusionMatrix[cateNamesToIndex.get(me.getValue())][cateNamesToIndex.get(resultCate.get(me.getKey()))]++;
- }
- //输出混淆矩阵
- double[] hangSum = new double[20];
- System.out.print(" ");
- for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
- System.out.print(i + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
- System.out.print(i + " ");
- for(int j = 0; j < 20; j++){
- System.out.print(confusionMatrix[i][j]+" ");
- hangSum[i] += confusionMatrix[i][j];
- }
- System.out.println(confusionMatrix[i][i] / hangSum[i]);
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- /**从分类结果文件中读取map
- * @param classifyResultFileNew 类目文件
- * @return Map<String, String> 由<文件名,类目名>保存的map
- * @throws IOException
- */
- private Map<String, String> getMapFromResultFile(
- String classifyResultFileNew) throws IOException {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- File crFile = new File(classifyResultFileNew);
- FileReader crReader = new FileReader(crFile);
- BufferedReader crBR = new BufferedReader(crReader);
- Map<String, String> res = new TreeMap<String, String>();
- String[] s;
- String line;
- while((line = crBR.readLine()) != null){
- s = line.split(" ");
- res.put(s[0], s[1]);
- }
- return res;
- }
- /**
- * @param args
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public void NaiveBayesianClassifierMain(String[] args) throws Exception {
- //TODO Auto-generated method stub
- //首先创建训练集和测试集
- CreateTrainAndTestSample ctt = new CreateTrainAndTestSample();
- NaiveBayesianClassifier nbClassifier = new NaiveBayesianClassifier();
- ctt.filterSpecialWords();//根据包含非特征词的文档集生成只包含特征词的文档集到processedSampleOnlySpecial目录下
- double[] accuracyOfEveryExp = new double[10];
- double accuracyAvg,sum = 0;
- for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){//用交叉验证法做十次分类实验,对准确率取平均值
- String TrainDir = "F:/DataMiningSample/TrainSample"+i;
- String TestDir = "F:/DataMiningSample/TestSample"+i;
- String classifyRightCate = "F:/DataMiningSample/classifyRightCate"+i+".txt";
- String classifyResultFileNew = "F:/DataMiningSample/classifyResultNew"+i+".txt";
- ctt.createTestSamples("F:/DataMiningSample/processedSampleOnlySpecial", 0.9, i,classifyRightCate);
- nbClassifier.doProcess(TrainDir,TestDir,classifyResultFileNew);
- accuracyOfEveryExp[i] = nbClassifier.computeAccuracy (classifyRightCate, classifyResultFileNew);
- System.out.println("The accuracy for Naive Bayesian Classifier in "+i+"th Exp is :" + accuracyOfEveryExp[i]);
- }
- for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
- sum += accuracyOfEveryExp[i];
- }
- accuracyAvg = sum / 10;
- System.out.println("The average accuracy for Naive Bayesian Classifier in all Exps is :" + accuracyAvg);
- }
- }
2.7.4、朴素贝叶斯算法对newsgroup文档集做分类的结果
在经过一系列Newsgroup文档预处理、特征词的选取、及实现了贝叶斯算法之后,下面用朴素贝叶斯算法那对newsgroup文档集做分类,看看此贝叶斯算法的效果。
贝叶斯算法分类结果-混淆矩阵表示,以交叉验证的第6次实验结果为例,分类准确率最高达到80.47%。

程序运行硬件环境:Intel Core 2 Duo CPU T5750 2GHZ, 2G内存,实验结果如下:
取所有词共87554个作为特征词:10次交叉验证实验平均准确率78.19%,用时23min,准确率范围75.65%-80.47%,第6次实验准确率超过80%,取出现次数大于等于4次的词共计30095个作为特征词: 10次交叉验证实验平均准确率77.91%,用时22min,准确率范围75.51%-80.26%,第6次实验准确率超过80%。如下图所示:
取所有词共87554个作为特征词:10次交叉验证实验平均准确率78.19%,用时23min,准确率范围75.65%-80.47%,第6次实验准确率超过80%,取出现次数大于等于4次的词共计30095个作为特征词: 10次交叉验证实验平均准确率77.91%,用时22min,准确率范围75.51%-80.26%,第6次实验准确率超过80%。如下图所示:
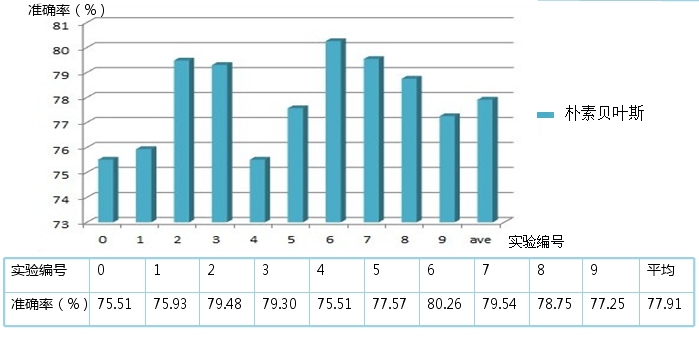
结论:朴素贝叶斯算法不必去除出现次数很低的词,因为出现次数很低的词的IDF比较 大,去除后分类准确率下降,而计算时间并没有显著减少
2.7.5、贝叶斯算法的改进
为了进一步提高贝叶斯算法的分类准确率,可以考虑
- 优化特征词的选取策略;
- 改进多项式模型的类条件概率的计算公式,改进为 类条件概率P(tk|c)=(类c下单词tk在各个文档中出现过的次数之和+0.001)/(类c下单词总数+训练样本中不重复特征词总数),分子当tk没有出现时,只加0.001(之前上面2.7.3节是+1),这样更加精确的描述的词的统计分布规律,
做此改进后的混淆矩阵如下

可以看到第6次分组实验的准确率提高到84.79%,第7词分组实验的准确率达到85.24%,平均准确率由77.91%提高到了82.23%,优化效果还是很明显的。更多内容,请参考原文:参考文献条目8。谢谢。
0 0
- 朴素贝叶斯方法的应用实例----基于newsgroup文档集的贝叶斯算法实现
- 基于Python的朴素贝叶斯算法实现
- 基于Hadoop的朴素贝叶斯算法实现
- 朴素贝叶斯算法的实现和应用
- 朴素贝叶斯算法 & 应用实例
- 朴素贝叶斯算法 & 应用实例
- 基于概率论的分类方法:朴素贝叶斯算法实践学习
- C++实现基于概率论的分类方法--朴素贝叶斯分类
- 基于朴素贝叶斯的文本分类算法
- 基于朴素贝叶斯的内容推荐算法
- 基于朴素贝叶斯的内容推荐算法
- 基于朴素贝叶斯的文本分类算法
- 基于朴素贝叶斯的文本分类算法
- 基于概率论的分类方法:朴素贝叶斯
- 基于概率论的分类方法:朴素贝叶斯
- 基于概率论的分类方法:朴素贝叶斯
- 基于概率论的分类方法:朴素贝叶斯
- 基于概率论的分类方法:朴素贝叶斯
- Java Notify Wait Synchronized
- 黑马程序员 java学习笔记——网络编程
- 铁路控制系统初探
- HardFault_Handler问题查找方法
- Handler处理消息的顺序
- 朴素贝叶斯方法的应用实例----基于newsgroup文档集的贝叶斯算法实现
- Slurm - Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management
- 个人曾经负责的一些项目,呵呵
- USB接口被检测出安全漏洞
- 招聘总结
- #include <math.h> /* round, floor, ceil, trunc */
- UVA 327 Evaluating Simple C Expressions
- 极大似然 与 EM算法
- Linux服务器对外租用的项目,我曾经做过的


