Binary Tree Traversals hdu 1710 c++
来源:互联网 发布:三层网络ping 请求超时 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/30 07:50
Binary Tree Traversals
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3320 Accepted Submission(s): 1491
Problem Description
A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
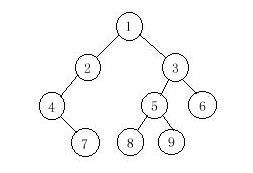
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.

Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating the preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
Output
For each test case print a single line specifying the corresponding postorder sequence.
Sample Input
91 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 64 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
Sample Output
7 4 2 8 9 5 6 3 1
题意:给你一个树的先序和中序,输出后序序列;
思路:递归调用,不断的找出根,输出;
#include<stdio.h>void build_tree(int n,int *a,int *b,int *c){ int *p=b,tt=0; if(n<=0) return; while(1) { if(a[0]==*p) {//找到中序表示中根的位置 break; } else p++; } tt=p-b;//左子树长度; build_tree(tt,a+1,b,c); build_tree(n-tt-1,a+tt+1,b+tt+1,c+tt); c[n-1]=a[0];}int main(){ int n,i; while(~scanf("%d",&n)) { int a[1002],b[1002],c[1002]; for(i=0;i<n;i++){//先序数组 scanf("%d",&a[i]); } for(i=0;i<n;i++){//中序数组 scanf("%d",&b[i]); } build_tree(n,a,b,c); for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){ printf("%d ",c[i]); } printf("%d\n",c[n-1]); } return 0;}
0 0
- HDU 1710-Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU--1710 -- Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu--1710Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- Hdu--1710--Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU-1710-Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu-1710-Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu 1710:Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU-1710-Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU - 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- 相机和相册的调用
- hdu-4946 Area of Mushroom 凸包
- C语言字符串操作--删除子串
- 【 D3.js 入门系列 --- 9.5 】 树状图的制作
- 12个方法去创造你人生中的第二次机会
- Binary Tree Traversals hdu 1710 c++
- uva 11971 - Polygon(连续概率问题)
- ss
- 2014 Multi-University Training Contest 8 题解——by xudyh
- 拼接字符串2
- mysql常用语句总结
- android 蓝牙开发笔记
- Eclipse安装CXF插件开发java web service 集成Spring
- Python要self的理由


