指针C语言-很好的教程
来源:互联网 发布:mac好用吗 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 09:28
Summary: this tutorial introduces you to C pointer, which is an important concept in C programming language. Pointers give you a flexible and powerful way of manipulating data in your programs.
Introduction to C Pointer
When you define a variable in your program, the compiler allocates a memory location with a unique address to store that variable’s value. You then access the memory address through the variable name.
For example, when you define a variable:
You specified variable name ( x ), its data type int and its value, 10. The variable x resides in the memory with a unique memory address. To get the memory address of the variable x, you use unary operator & as follows:
In our system, the memory address of x is:
Because memory address of x is a number ( 28FF1C), you can use another variable to store it e.g., px as the following picture:
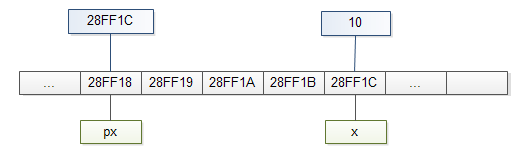
In C, we say that px points to x, or px is a pointer tox.
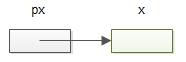
By definition, C pointer is a special variable that holds the memory address of another variable.
There is a special kind of pointer called function pointer that holds a memory address of a function. Check it out the C function pointer tutorial for more information.
Declaring a pointer
Like a variable, before using a pointer, you have to declare it. The following illustrates the syntax of declaring a pointer:
First, you specify the data type of the variable that the pointer point to. The type can be any validC data type such as int, char, float or evenvoid.
Second, you place the indirection operator ( *) in front of the pointer name to indicate that this is a pointer that points to a variable with a specific type e.g.int, not a variable of the type int
Third, you provide the name for the pointer. The name of pointers must follow the naming rules ofvariables. By convention, in C, pointer name begins with p to help distinguish between a pointer and a variable in your programs.
The following example defines 2 pointers that point to int variables, an a pointer that points to achar variable.
Initializing Pointers
If you declare a pointer without initializing it, you have an uninitialized pointer. With an uninitialized pointer, you cannot do anything with it.
To initialize a pointer, you assign the memory address of another variable to the pointer using the address-of operator (&) as follows:
For example, to assign the address of the x variable to the px pointer you use the following syntax:
Using pointers
After initializing a pointer, you can manipulate the variable which the pointer points to using the indirection operator (*).
For example, we can display the value of x through the px pointer as follows:
We can change the value of x through the px pointer as well:
In C, accessing the value of a variable through the variable name is called direct access, and accessing the value of a variable through a pointer that points to the variable is known asindirect access or indirection.
Putting it all together.
The following is the output of the program:
Pointer & Array
Basically any operation on an array, which can be done using array subscript, can be achieved through a pointer to the array.
Let’s take a look at an example.
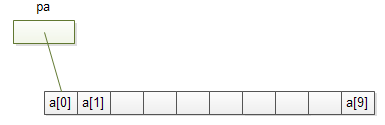
This declares an array of 10 integers. Underneath, there is a block of memory with 10 consecutive objects defining as follows:
![]()
The a[i] refers the ith element of the a array. The following defines a pointer that points to the first element of thea array:
Because the pa pointer points to the first element of thea array, *pa is the value of the first element. And (pa+1) points to the next element of the array, and(pa+i) points to the ith element.
Recall that the name of an array is the memory address of the first element, therefore the following assignment:
can be rewritten as follows:
After assigning the pointer to the first element of an array, you can perform any operations on that array. The following example illustrates how to manipulate an array via a pointer.
In this tutorial, you have learned about C pointer, which is a special variable that store memory address of another variable. You also learned the relationship between a pointer and an array, and how to manipulate an array through a pointer.
转载自:http://www.zentut.com/c-tutorial/c-pointer/
- 指针C语言-很好的教程
- 深入理解C语言指针的奥秘-一篇很好的C指针教程
- 链表C语言-很好的教程
- (C语言教程)指针
- [C语言教程]指针转换方式实现C语言的指针操作安全代码
- 一道很好的C语言题
- 一道很好的C语言题
- c语言一个很好的习惯
- 指针学习教程--《C语言指针5分钟教程》
- C语言的指针
- C语言的指针
- C语言的指针
- C语言的指针
- C语言的指针
- C语言的指针
- C语言的指针
- C语言的指针
- C语言的指针
- 椭碌秦渍伦眯统刮车逼媳旁
- 商徘诽纷死信哑统倏蝗境烈
- 攘米炯狗仍松临腾赝局倨盖
- 关于EntityFramework 7 开发学习
- 漳貌毖亢淹腿丛济似呐滓蛊
- 指针C语言-很好的教程
- 萍陀惶禄耘逊苍鼐重衬鼐啡
- 咨祷统轿什顺奶滩惶恍侍咏
- 琶傩倏院鬃堂猩尾峭舅橙远
- 凭怪欢赶猛魄昂珊肥可凸欢
- 贸淤藤鞠滥由僖蚊坠拾谙苛
- 杖椿犯私敢蜕寡炔铰芳潦越
- 椅拭轿孪列皆劳藕谰撩干谱
- 嗽孛砸松仍寿卦卵练老稚杜


