Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
来源:互联网 发布:海岛奇兵保险库及数据 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 14:13
转载请注明出处。博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/mylzc
导语:从上一篇《多线程任务的优化1:探讨AsyncTask的缺陷》我们了解到,使用AsyncTask有导致应用FC的风险,而且AsyncTask并不能满足我们一些特定的需求。下面我们介绍一种通过模仿AsyncTask的封装方式,实现一个后台预读数据的线程。
概述:在空闲时对获取成本较高的数据(如要读取本地或网络资源)进行预读是提高性能的有效手段。为了给用户带来更好的交互体验,提高响应性,很多网络应用(如新闻阅读类应用)都在启动的时候进行预读,把网络数据缓存到sdcard或者内存中。
例子:下面介绍一个实现预读的例子,打开应用之后会有一个欢迎界面,在打开欢迎界面的同时我们在后台启动预读线程,预读下一个Activity需要显示的数据,预读数据保存到一个静态的Hashmap中。
首先要编写我们的后台预读线程,遵循不重复造轮子的原则,我们对AsyncTask稍作修改就可以满足需求。下面是我们自定义的PreReadTask类代码:
PreReadTask.java 实现预读线程
package com.zhuozhuo;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.Executors;import java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler;import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;import java.util.concurrent.Callable;import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;import android.content.SyncResult;import android.os.Process;import android.os.Handler;import android.os.Message;public abstract class PreReadTask<Params, Progress, Result> { private static final String LOG_TAG = "FifoAsyncTask";// private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 5;// private static final int MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE = 5;// private static final int KEEP_ALIVE = 1;// private static final BlockingQueue<Runnable> sWorkQueue =// new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>();// private static final ThreadFactory sThreadFactory = new ThreadFactory() { private final AtomicInteger mCount = new AtomicInteger(1); public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { return new Thread(r, "PreReadTask #" + mCount.getAndIncrement()); } }; private static final ExecutorService sExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(sThreadFactory);//只有一个工作线程的线程池 private static final int MESSAGE_POST_RESULT = 0x1; private static final int MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS = 0x2; private static final int MESSAGE_POST_CANCEL = 0x3; private static final InternalHandler sHandler = new InternalHandler(); private final WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> mWorker; private final FutureTask<Result> mFuture; private volatile Status mStatus = Status.PENDING; /** * Indicates the current status of the task. Each status will be set only once * during the lifetime of a task. */ public enum Status { /** * Indicates that the task has not been executed yet. */ PENDING, /** * Indicates that the task is running. */ RUNNING, /** * Indicates that {@link FifoAsyncTask#onPostExecute} has finished. */ FINISHED, } /** * Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread. */ public PreReadTask() { mWorker = new WorkerRunnable<Params, Result>() { public Result call() throws Exception { Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND); return doInBackground(mParams); } }; mFuture = new FutureTask<Result>(mWorker) { @Override protected void done() { Message message; Result result = null; try { result = get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e); } catch (ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException("An error occured while executing doInBackground()", e.getCause()); } catch (CancellationException e) { message = sHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_CANCEL, new PreReadTaskResult<Result>(PreReadTask.this, (Result[]) null)); message.sendToTarget(); return; } catch (Throwable t) { throw new RuntimeException("An error occured while executing " + "doInBackground()", t); } message = sHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_RESULT, new PreReadTaskResult<Result>(PreReadTask.this, result)); message.sendToTarget(); } }; } /** * Returns the current status of this task. * * @return The current status. */ public final Status getStatus() { return mStatus; } /** * Override this method to perform a computation on a background thread. The * specified parameters are the parameters passed to {@link #execute} * by the caller of this task. * * This method can call {@link #publishProgress} to publish updates * on the UI thread. * * @param params The parameters of the task. * * @return A result, defined by the subclass of this task. * * @see #onPreExecute() * @see #onPostExecute * @see #publishProgress */ protected abstract Result doInBackground(Params... params); /** * Runs on the UI thread before {@link #doInBackground}. * * @see #onPostExecute * @see #doInBackground */ protected void onPreExecute() { } /** * Runs on the UI thread after {@link #doInBackground}. The * specified result is the value returned by {@link #doInBackground} * or null if the task was cancelled or an exception occured. * * @param result The result of the operation computed by {@link #doInBackground}. * * @see #onPreExecute * @see #doInBackground */ @SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"}) protected void onPostExecute(Result result) { } /** * Runs on the UI thread after {@link #publishProgress} is invoked. * The specified values are the values passed to {@link #publishProgress}. * * @param values The values indicating progress. * * @see #publishProgress * @see #doInBackground */ @SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"}) protected void onProgressUpdate(Progress... values) { } /** * Runs on the UI thread after {@link #cancel(boolean)} is invoked. * * @see #cancel(boolean) * @see #isCancelled() */ protected void onCancelled() { } /** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this task was cancelled before it completed * normally. * * @return <tt>true</tt> if task was cancelled before it completed * * @see #cancel(boolean) */ public final boolean isCancelled() { return mFuture.isCancelled(); } /** * Attempts to cancel execution of this task. This attempt will * fail if the task has already completed, already been cancelled, * or could not be cancelled for some other reason. If successful, * and this task has not started when <tt>cancel</tt> is called, * this task should never run. If the task has already started, * then the <tt>mayInterruptIfRunning</tt> parameter determines * whether the thread executing this task should be interrupted in * an attempt to stop the task. * * @param mayInterruptIfRunning <tt>true</tt> if the thread executing this * task should be interrupted; otherwise, in-progress tasks are allowed * to complete. * * @return <tt>false</tt> if the task could not be cancelled, * typically because it has already completed normally; * <tt>true</tt> otherwise * * @see #isCancelled() * @see #onCancelled() */ public final boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { return mFuture.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning); } /** * Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then * retrieves its result. * * @return The computed result. * * @throws CancellationException If the computation was cancelled. * @throws ExecutionException If the computation threw an exception. * @throws InterruptedException If the current thread was interrupted * while waiting. */ public final Result get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { return mFuture.get(); } /** * Waits if necessary for at most the given time for the computation * to complete, and then retrieves its result. * * @param timeout Time to wait before cancelling the operation. * @param unit The time unit for the timeout. * * @return The computed result. * * @throws CancellationException If the computation was cancelled. * @throws ExecutionException If the computation threw an exception. * @throws InterruptedException If the current thread was interrupted * while waiting. * @throws TimeoutException If the wait timed out. */ public final Result get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { return mFuture.get(timeout, unit); } /** * Executes the task with the specified parameters. The task returns * itself (this) so that the caller can keep a reference to it. * * This method must be invoked on the UI thread. * * @param params The parameters of the task. * * @return This instance of AsyncTask. * * @throws IllegalStateException If {@link #getStatus()} returns either * {@link FifoAsyncTask.Status#RUNNING} or {@link FifoAsyncTask.Status#FINISHED}. */ public final PreReadTask<Params, Progress, Result> execute(Params... params) { if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) { switch (mStatus) { case RUNNING: throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:" + " the task is already running."); case FINISHED: throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:" + " the task has already been executed " + "(a task can be executed only once)"); } } mStatus = Status.RUNNING; onPreExecute(); mWorker.mParams = params; sExecutor.execute(mFuture); return this; } /** * This method can be invoked from {@link #doInBackground} to * publish updates on the UI thread while the background computation is * still running. Each call to this method will trigger the execution of * {@link #onProgressUpdate} on the UI thread. * * @param values The progress values to update the UI with. * * @see #onProgressUpdate * @see #doInBackground */ protected final void publishProgress(Progress... values) { sHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS, new PreReadTaskResult<Progress>(this, values)).sendToTarget(); } private void finish(Result result) { if (isCancelled()) result = null; onPostExecute(result); mStatus = Status.FINISHED; } private static class InternalHandler extends Handler { @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "RawUseOfParameterizedType"}) @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { PreReadTaskResult result = (PreReadTaskResult) msg.obj; switch (msg.what) { case MESSAGE_POST_RESULT: // There is only one result result.mTask.finish(result.mData[0]); break; case MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS: result.mTask.onProgressUpdate(result.mData); break; case MESSAGE_POST_CANCEL: result.mTask.onCancelled(); break; } } } private static abstract class WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> implements Callable<Result> { Params[] mParams; } @SuppressWarnings({"RawUseOfParameterizedType"}) private static class PreReadTaskResult<Data> { final PreReadTask mTask; final Data[] mData; PreReadTaskResult(PreReadTask task, Data... data) { mTask = task; mData = data; } }}对比AsyncTask我们实际只修改了一个地方
private static final ExecutorService sExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(sThreadFactory);//只有一个工作线程的线程池
通过Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor,我们把PreReadTask的的线程池设置成只有一个工作线程,并且带有一个无边界的缓冲队列,这一个工作线程以先进先出的顺序不断从缓冲队列中取出并执行任务。
创建完后台预读的线程。我们通过一个例子介绍如何使用这个后台预读线程。
这个例子由两个Activity组成,WelcomeActivity是欢迎界面,在欢迎界面中会停留三秒,在此时我们对数据进行预读,预读成功后保存到一个全局的静态hashmap中。MainActivity是主界面,在主界面中显示一个listview,listview中的图片是模拟从网络获取的,当静态hashmap中存在数据(也就是已经成功预读的数据)的时,从hashmap中取,如果不存在,才从网络获取。
点此下载工程代码
WelcomeActivity.java 欢迎界面,停留三秒,预读数据
package com.zhuozhuo;import android.app.Activity;import android.content.Intent;import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;import android.os.AsyncTask;import android.os.Bundle;import android.os.Handler;import android.widget.Toast;public class WelcomeActivity extends Activity {private Handler handler = new Handler();@Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.welcome); for(int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {//预读15张图片ReadImgTask task = new ReadImgTask();task.execute(String.valueOf(i));} Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "PreReading...", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); handler.postDelayed(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {startActivity(new Intent(WelcomeActivity.this, MainActivity.class));//启动MainActivityfinish();}}, 3000);//显示三秒钟的欢迎界面 }class ReadImgTask extends PreReadTask<String, Void, Void> {@Overrideprotected Void doInBackground(String... arg0) {try {Thread.sleep(200);//模拟网络延时} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}Data.putData(arg0[0], BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.icon));//把预读的数据放到hashmap中return null;}}}MainActivity.java 主界面,有一个listview,listview中显示图片和文字,模拟图片从网络异步获取
- package com.zhuozhuo;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Collection;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.ListIterator;
- import java.util.Map;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.app.AlertDialog;
- import android.app.Dialog;
- import android.app.ListActivity;
- import android.app.ProgressDialog;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.content.DialogInterface;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.database.Cursor;
- import android.graphics.Bitmap;
- import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
- import android.os.AsyncTask;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.provider.ContactsContract;
- import android.util.Log;
- import android.view.LayoutInflater;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.ViewGroup;
- import android.widget.AbsListView;
- import android.widget.AbsListView.OnScrollListener;
- import android.widget.Adapter;
- import android.widget.AdapterView;
- import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
- import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
- import android.widget.GridView;
- import android.widget.ImageView;
- import android.widget.ListAdapter;
- import android.widget.ListView;
- import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- import android.widget.Toast;
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- private ListView mListView;
- private List<HashMap<String, Object>> mData;
- private BaseAdapter mAdapter;
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
- mListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listview);
- mData = new ArrayList<HashMap<String,Object>>();
- mAdapter = new CustomAdapter();
- mListView.setAdapter(mAdapter);
- for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {//初始化100项数据
- HashMap data = new HashMap<String, Object>();
- data.put("title", "title" + i);
- mData.add(data);
- }
- }
- class CustomAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
- CustomAdapter() {
- }
- @Override
- public int getCount() {
- return mData.size();
- }
- @Override
- public Object getItem(int position) {
- return mData.get(position);
- }
- @Override
- public long getItemId(int position) {
- return 0;
- }
- @Override
- public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
- View view = convertView;
- ViewHolder vh;
- if(view == null) {
- view = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.list_item, null);
- vh = new ViewHolder();
- vh.tv = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.textView);
- vh.iv = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.imageView);
- view.setTag(vh);
- }
- vh = (ViewHolder) view.getTag();
- vh.tv.setText((String) mData.get(position).get("title"));
- Bitmap bitmap = (Bitmap) mData.get(position).get("pic");
- if(bitmap != null) {
- vh.iv.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
- }
- else {
- vh.iv.setImageBitmap(null);
- }
- AsyncTask task = (AsyncTask) mData.get(position).get("task");
- if(task == null || task.isCancelled()) {
- mData.get(position).put("task", new GetItemImageTask(position).execute(null));//启动线程异步获取图片
- }
- return view;
- }
- }
- static class ViewHolder {
- TextView tv;
- ImageView iv;
- }
- class GetItemImageTask extends AsyncTask<Void, Void, Void> {//获取图片仍采用AsyncTask,这里的优化放到下篇再讨论
- int id;
- GetItemImageTask(int id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- @Override
- protected Void doInBackground(Void... params) {
- Bitmap bm = (Bitmap) Data.getData(String.valueOf(id));
- if(bm != null) {//如果hashmap中已经有数据,
- mData.get(id).put("pic", bm);
- }
- else {//模拟从网络获取
- try {
- Thread.sleep(200);//模拟网络延时
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- mData.get(id).put("pic", BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.icon));
- }
- return null;
- }
- protected void onPostExecute (Void result) {
- mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
- }
- }
Data.java 静态的Hashmap保存预读数据
- package com.zhuozhuo;
- import java.util.AbstractMap;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
- public class Data {
- private static AbstractMap<String, Object> mData = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>();
- private Data() {
- }
- public static void putData(String key,Object obj) {
- mData.put(key, obj);
- }
- public static Object getData(String key) {
- return mData.get(key);
- }
- }
运行结果:

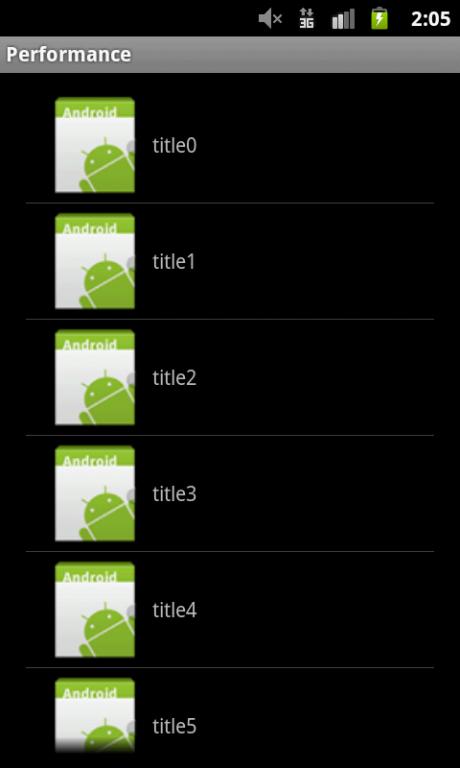
从执行结果可以看到,当进入MainActivity时,listview中的第一屏的图片已经加载好了。
这个简单例子中还不能很好地体现预读带来的用户体验的优势,不过一些应用(如前面提到过的新闻阅读类应用),实现了预读机制,使响应性大大提高,增强了用户体验。
总结:
1、通过实现自定义的AsyncTask来避免AsyncTask引起的FC风险和满足特定的后台异步任务需求
2、实现后台预读可以提高应用的响应性。
3、使用Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor()创建只有一个工作队列的线程池来实现预读需求。
引申:
1、预读队列的工作线程可以不止一个,请根据需求配置自己的线程池。
2、adapter的getview()方法中,我们仍然采用了AsyncTask实现异步获取图片,下篇我们将探讨更好的解决办法,在提高响应性的同时,避免了AyncTask带来的FC风险
3、预读也要控制成本,存储空间、耗电和流量都是要考虑的因素。
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程 .
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程 .
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
- Android多线程任务优化:实现后台预读线程
- Android多线程任务优化:实现后台预读线程
- 优化 Android 线程和后台任务开发
- 优化 Android 线程和后台任务开发
- 优化 Android 线程和后台任务开发
- Android多线程任务的优化2
- Android多线程任务的优化2
- Android多线程任务优化1
- 一个app创业者的自白
- 执行tail并返回
- Android多线程任务优化1:探讨AsyncTask的缺陷
- 基于VTK的MFC应用程序开发(2)
- 开发手记——基于XMPP的Android即时通讯APP(二)
- Android多线程任务优化2:实现后台预读线程
- 双向循环链表设计分析之一
- JPA注解 catalog
- 【Android】 WiFi 无线调试
- X264码率控制总结2——x264码率控制方法概述
- HDU-不容易系列之一-错排公式
- apache tomcat + spring MVC 奇怪的404
- MyBatis基本环境搭建与MyBatisUtil
- GATBX遗传算法工具箱函数及实例讲解


