ACM--dyx--steps--5.1.3--Is It A Tree?
来源:互联网 发布:程序员杂志订阅 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/14 12:16
Is It A Tree?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s): 872 Accepted Submission(s): 282Problem Description
A tree is a well-known data structure that is either empty (null, void, nothing) or is a set of one or more nodes connected by directed edges between nodes satisfying the following properties.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.
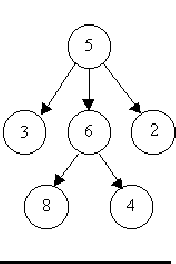
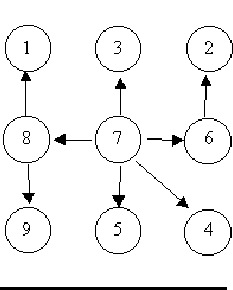
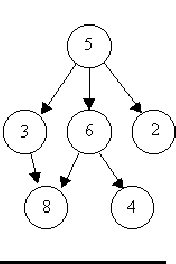
In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.



In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
Input
The input will consist of a sequence of descriptions (test cases) followed by a pair of negative integers. Each test case will consist of a sequence of edge descriptions followed by a pair of zeroes Each edge description will consist of a pair of integers; the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero.
Output
For each test case display the line ``Case k is a tree.\\\\\\\" or the line ``Case k is not a tree.\\\\\\\", where k corresponds to the test case number (they are sequentially numbered starting with 1).
Sample Input
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 45 6 0 08 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 57 4 7 8 7 6 0 03 8 6 8 6 45 3 5 6 5 2 0 0-1 -1
Sample Output
Case 1 is a tree.Case 2 is a tree.Case 3 is not a tree.
Source
North Central North America 1997
Recommend
Ignatius.L
#include<iostream>using namespace std;/*首先作为一棵树应该具备以下几种条件;1,空树也是一棵树;2,作为树不能有环;3,在子节点当中不能出现重新指向祖先节点的情况;4,节点本身不能指向自己:5,除了根节点的入度为0,其他节点的入度全为1;*/const int N=100009;struct node{ int vis,deg,root;};node dyx[N];//代表当前节点的上一个节点;int find(int x){ int r; r=x; while(dyx[r].root!=r) { r=dyx[r].root; } return r;}void mix(int a,int b){ //合并根节点; int RootA=find(a); int RootB=find(b); if(RootA==RootB) return ; dyx[a].root=b;}void set(){ //对dyx[N]进行初始化: for(int i=1;i<N;i++) { dyx[i].vis=0;//代表访问的状态; dyx[i].root=i; dyx[i].deg=0;//节点的入度为0; }}int main(){ int n,m;//输入的两个节点; bool flag=true; int Ti=1;//记录数据组数 set(); while(cin>>n>>m&&n>=0&&m>=0) { //确定非树; if(!flag&&m!=0&&n!=0) continue; //如果输入的两个数字均等于0,则进行全部节点的判断; if(n==0&&m==0) { int root_num=0;//一棵树的根节点只能有一个; for(int j=1;j<N;j++) { if(dyx[j].vis&&dyx[j].root==j) root_num++; if(dyx[j].deg>1) { flag=false;//一棵树的入度不能超过1; break; } } if(root_num>1) flag=false; if(flag) cout<<"Case "<<Ti++<<" is a tree."<<endl; else cout<<"Case "<<Ti++<<" is not a tree."<<endl; flag=true;//还原状态; set(); continue; } if(m!=n&&find(m)==find(n)) { //出现环; flag=false; } else { dyx[m].vis=1; dyx[n].vis=1; dyx[m].deg++; mix(m,n); } } return 0;} 0 0
- ACM--dyx--steps--5.1.3--Is It A Tree?
- ACM--steps--dyx--5.1.5--Code Lock
- ACM--steps--dyx--1.2.1
- ACM--steps--dyx--1.2.2--
- ACM--steps--dyx--5.1.2--小希的迷宫
- ACM--steps--dyx--5.1.4--find the most comfortable road
- ACM--steps--dyx--1.3.3--Tian Ji -- The Horse Racing
- ACM--steps--dyx--1.2.4--Buildings
- ACM--steps--dyx--1.2.6--Quicksum
- ACM--steps--dyx--1.2.7--Lowest Bit
- ACM--steps----dyx--1.2.8--AC Me
- ACM-steps--dyx--1.3.4--百步穿杨
- ACM--steps--dyx--2.1.1--最小公倍数
- ACM--dyx--steps--3.1.8--Queuing
- ACM--steps--dyx--2.3.2--Exponentiation
- ACM--steps--dyx--Hat's Fibonacci
- 杭电acm oj 1325 Is It A Tree?
- HDOJ 1325 Is It A Tree? 杭电 ACM
- Training a deep autoencoder or a classifier on MNIST digits_之调试运行与理解
- 黑马程序员——IO流2:字符流
- 最大公约数问题
- MFC控件移动
- 要读的专业书籍 2015.5.27更新
- ACM--dyx--steps--5.1.3--Is It A Tree?
- 编程之美2015资格赛 C 基站选址 (数学)
- chrome浏览器频频崩溃,如何解决?
- Android 关于NDK Clang3.4 编译可执行文件无法启动的问题
- 网口扫盲一:网卡初步认识
- java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver完美解决方案
- 迅雷与迅雷看看播放器使用体验(一)
- java用for循环打印九九乘法表
- MySQL在忘记root密码的时候


