hdu 1198 农田灌溉 并查集4
来源:互联网 发布:中国万方数据库 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/28 01:34
Farm Irrigation
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 6539 Accepted Submission(s): 2827
Problem Description
Benny has a spacious farm land to irrigate. The farm land is a rectangle, and is divided into a lot of samll squares. Water pipes are placed in these squares. Different square has a different type of pipe. There are 11 types of pipes, which is marked from A to K, as Figure 1 shows.
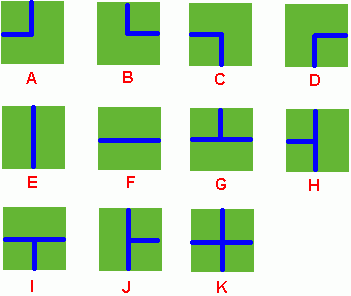
Figure 1
Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC
FJK
IHE
then the water pipes are distributed like
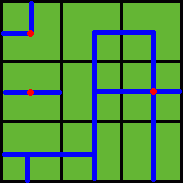
Figure 2
Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.

Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC
FJK
IHE
then the water pipes are distributed like

Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.
Input
There are several test cases! In each test case, the first line contains 2 integers M and N, then M lines follow. In each of these lines, there are N characters, in the range of 'A' to 'K', denoting the type of water pipe over the corresponding square. A negative M or N denotes the end of input, else you can assume 1 <= M, N <= 50.
Output
For each test case, output in one line the least number of wellsprings needed.
Sample Input
2 2DKHF3 3ADCFJKIHE-1 -1
Sample Output
23
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int fa[3000]; //注意不能开小,大于50*50int findfa(int x){ /*if(x==fa[x]) return x; else return fa[x]=findfa(fa[x]); */ while(fa[x]!=x) x=fa[x]; return x;}int unionf(int x,int y){ int fx=findfa(x); int fy=findfa(y); fa[fx]=fy; return 0;}int main(){ int a[12][4]= {{1,0,1,0},{1,0,0,1},{0,1,1,0},{0,1,0,1},{1,1,0,0,},{0,0,1,1},{1,0,1,1},{1,1,1,0}, {0,1,1,1},{1,1,0,1},{1,1,1,1}}; //将每种图形储存在数组中 int m,n,i,j,k,c; while(cin>>m>>n) { if(m==-1&&n==-1) //不用连等 break; int b[60][60]; char b1; for(i=0; i<m; i++) for(j=0; j<n; j++) { cin>>b1; b[i][j]=b1-'A'; } c=m*n; for(i=1; i<=c; i++) fa[i]=i; for(i=0; i<m-1; i++) //比较前m-1行,n-1列 { for(j=0; j<n-1; j++) { if(a[b[i][j]][1]&&a[b[i+1][j]][0]) unionf(i*n+j+1,(i+1)*n+j+1);//a[i][j]的下边,a[i+1][j]的上边都为1,可合并 if(a[b[i][j]][3]&&a[b[i][j+1]][2])//a[i][j]的右边,a[i][j+1]的左边都为1,可合并 unionf(i*n+j+1,i*n+j+2); } } for(i=0; i<m-1; i++) //j=n-1时,即比较最后一列上下块是否可以合并,因为比较上下时有i+1, //右下角块会超出范围 { if(a[b[i][n-1]][1]&&a[b[i+1][n-1]][0]) unionf(i*n+n,(i+1)*n+n); } for(j=0; j<n-1; j++) //i=m-1时,即比较最后一行左右块是否可以合并 { if(a[b[m-1][j]][3]&&a[b[m-1][j+1]][2]) unionf((m-1)*n+j+1,(m-1)*n+j+2); } k=0; for(i=1; i<=c; i++) { if(fa[i]==i) k++; } cout<<k<<endl; } return 0;}优化:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int fa[3000]; //注意不能开小,大于51*51int findfa(int x){ /*if(x==fa[x]) return x; else return fa[x]=findfa(fa[x]); */ while(fa[x]!=x) x=fa[x]; return x;}int unionf(int x,int y){ int fx=findfa(x); int fy=findfa(y); fa[fx]=fy; return 0;}int main(){ int a[12][4]= {{1,0,1,0},{1,0,0,1},{0,1,1,0},{0,1,0,1},{1,1,0,0,},{0,0,1,1},{1,0,1,1},{1,1,1,0}, {0,1,1,1},{1,1,0,1},{1,1,1,1},{0,0,0,0}}; //将每种图形储存在数组中 int m,n,i,j,k,c; while(cin>>m>>n) { if(m==-1&&n==-1) //不用连等 break; int b[60][60]; char b1; for(i=0; i<m; i++) for(j=0; j<n; j++) { cin>>b1; b[i][j]=b1-'A'; } for(i=0; i<=m; i++) b[i][n]=11; for(j=0; j<=n; j++) b[m][j]=11; c=(m+1)*(n+1); for(i=1; i<=c; i++) fa[i]=i; for(i=0; i<m; i++) //比较前m行,n列 { for(j=0; j<n; j++) { if(a[b[i][j]][1]&&a[b[i+1][j]][0]) unionf(i*n+j+1,(i+1)*n+j+1);//a[i][j]的下边,a[i+1][j]的上边都为1,可合并 if(a[b[i][j]][3]&&a[b[i][j+1]][2])//a[i][j]的右边,a[i][j+1]的左边都为1,可合并 unionf(i*n+j+1,i*n+j+2); } } k=0; for(i=1; i<=c; i++) { if(fa[i]==i) k++; } k=k-m-n-1; cout<<k<<endl; } return 0;} 0 0
- hdu 1198 农田灌溉 并查集4
- hdu 1198农田灌溉
- HDU 1198 并查集
- HDU 1198(并查集)
- HDU 1198 并查集
- hdu 1198 并查集
- hdu 1198(并查集 )
- hdu 1198 并查集
- hdu 1198并查集
- hdu 1198 dfs(还是水坑变型题)农田灌溉
- hdu 1198 Farm Irrigation(并查集)
- hdu 1198 并查集应用
- hdu 1198 Farm Irrigation( 并查集)
- HDU 1198 Farm Irrigation(并查集)
- HDU 1198 Farm Irrigation 【并查集】
- HDU 1198Farm Irrigation(并查集)
- HDU 1198(并查集;dfs)
- HDU 1198 Farm Irrigation(并查集)
- Struts2解决乱码方式
- 错误代码: 1064
- 打造一款亿级应用你会碰到哪些问题?
- Java线程
- LINE: run elf in windows
- hdu 1198 农田灌溉 并查集4
- x--与--X的区别
- 林花谢了春红
- uva 769(构造)
- Java垃圾回收器
- Eclipse中的快捷键组合
- Android 解决魅族手机豌豆荚能连上,Eclipse不能识别的问题
- Java JDBC
- iOS控件无法显示的缘由总结


