HDU 1828 Picture(线段树扫描线·周长并)
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝网京东商城女装 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/29 05:40
题意 给你一些矩形的左下和右上的坐标 求这些矩形的周长并
也先来看点图

和面积并类似 求周长并也可以对每条竖边从左往右进行扫描 每次周长增加了多少呢 可以发现y方向上对周长增加的量就是扫描线上线段的总长度的改变量 x方向增加了线段段数 * 2 倍的与下一条竖边间的距离 因为每一段都会对应两个横边
那么我们需要维护线段的总长度len和线段的段数num len和面积并的是一样的 num有点类似区间合并 由子节点更新父节点的时候 先让父节点的num等于两个子节点的num的和 但是当左孩子结点的右端有线段 而其右孩子的左端有线段的时候 这两段是可以连在一起的 父节点的num就要减去1 所以我们还要维护每个区间左端是否有线段lh 右边是否有线段rh
另外求周长并还要注意当两个竖边的x值相等时 要把入边放前面 出边放后面 也就是排序时要注意一下 否则会多加上一些长度
#include <cstdio>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;const int N = 10005, M = N * 4;struct SLine{ int x, y1, y2, flag; SLine() {} SLine(int xx, int a, int b, int f): x(xx), y1(a), y2(b), flag(f) {} bool operator< (const SLine &s) const { if(x == s.x) return flag > s.flag; //有入边出边在一条线上时 要先扫描入边 不然周长可能会多算重叠部分 return x < s.x; }} line[N];int num[M], cnt[M], len[M], y[N];bool lh[M], rh[M];void pushup(int p, int s, int e){ if(cnt[p]) //cnt == 0 时才需要由子节点来更新父节点 { len[p] = y[e] - y[s - 1]; num[p] = lh[p] = rh[p] = 1; } else if(s == e) len[p] = num[p] = lh[p] = rh[p] = 0; else //区间合并 { len[p] = len[p << 1] + len[p << 1 | 1]; num[p] = num[p << 1] + num[p << 1 | 1]; lh[p] = lh[p << 1], rh[p] = rh[p << 1 | 1]; if(rh[p << 1] && lh[p << 1 | 1]) --num[p]; }}void update(int p, int s, int e, int l, int r, int v){ if(l <= s && e <= r) { cnt[p] += v; pushup(p, s, e); return; } int mid = (s + e) >> 1; if(l <= mid) update(p << 1, s, mid, l, r, v); if(r > mid) update(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, e, l, r, v); pushup(p, s, e);}int main(){ int n, m, x1, y1, x2, y2; while(~scanf("%d", &n)) { for(int i = m = 0; i < n; ++i) { scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2); y[m] = y1, y[m + 1] = y2; line[m++] = SLine(x1, y1, y2, 1); line[m++] = SLine(x2, y1, y2, -1); } sort(line, line + m); sort(y, y + m); //离散化 int ans = 0, last = 0, l, r; for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { l = lower_bound(y, y + m, line[i].y1) - y + 1; r = lower_bound(y, y + m, line[i].y2) - y; update(1, 1, m, l, r, line[i].flag); if(i < m - 1) ans += 2 * num[1] * (line[i + 1].x - line[i].x); //横边 ans += abs(len[1] - last); //竖边 last = len[1]; } printf("%d\n", ans); } return 0;}Picture
Problem Description
A number of rectangular posters, photographs and other pictures of the same shape are pasted on a wall. Their sides are all vertical or horizontal. Each rectangle can be partially or totally covered by the others. The length of the boundary of the union of all rectangles is called the perimeter.
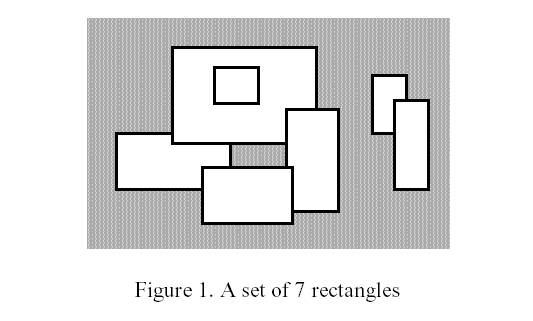
Write a program to calculate the perimeter. An example with 7 rectangles is shown in Figure 1.
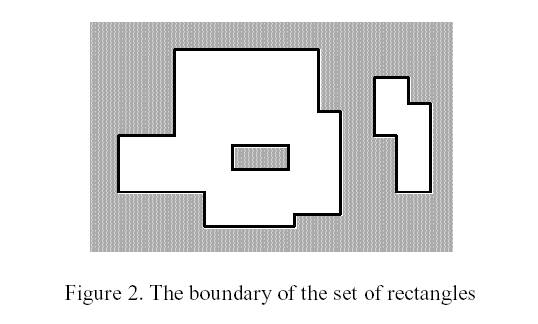
The corresponding boundary is the whole set of line segments drawn in Figure 2.
The vertices of all rectangles have integer coordinates.
Write a program to calculate the perimeter. An example with 7 rectangles is shown in Figure 1.

The corresponding boundary is the whole set of line segments drawn in Figure 2.

The vertices of all rectangles have integer coordinates.
Input
Your program is to read from standard input. The first line contains the number of rectangles pasted on the wall. In each of the subsequent lines, one can find the integer coordinates of the lower left vertex and the upper right vertex of each rectangle. The values of those coordinates are given as ordered pairs consisting of an x-coordinate followed by a y-coordinate.
0 <= number of rectangles < 5000
All coordinates are in the range [-10000,10000] and any existing rectangle has a positive area.
Please process to the end of file.
0 <= number of rectangles < 5000
All coordinates are in the range [-10000,10000] and any existing rectangle has a positive area.
Please process to the end of file.
Output
Your program is to write to standard output. The output must contain a single line with a non-negative integer which corresponds to the perimeter for the input rectangles.
Sample Input
7-15 0 5 10-5 8 20 2515 -4 24 140 -6 16 42 15 10 2230 10 36 2034 0 40 16
Sample Output
228
1 0
- hdu 1828 Picture(线段树&扫描线&周长并)
- HDU 1828 Picture(线段树扫描线·周长并)
- hdu 1828 Picture(线段树扫描线矩形周长并)
- HDU 1828——Picture(线段树+周长并+扫描线)
- poj 1177 || HDU 1828 Picture (线段树扫描线求 图形并的周长)
- hdu 1828 Picture(线段树,扫描线之周长并)
- hdu1828 Picture(扫描线+矩形周长并+线段树)
- hdu1828 Picture (线段树+扫描线)(求周长并)
- HDU1828 Picture(线段树+扫描线求周长并)
- HDU 1828 Picture (线段树扫描线求周长并 区间合并)
- HDU - 1828 Picture (线段树求并周长)
- HDU 1828 Picture(线段树的周长并)
- 【poj1177】Picture(矩形周长并+线段树+扫描线)
- hdu1828-Picture 线段树+扫描线 求周长并
- hdu1828 Picture(线段树+扫描线+矩形周长并)
- hdu 1828线段树扫描线求周长并
- HDU 1828 线段树之扫描线之周长并
- poj-1177 Picture(矩形周长并,线段树+扫描线)
- monkey命令参数列表详解
- 图的存储
- POJ2230 Watchcow(欧拉回路)
- 《深入理解Android 卷III》第七章 深入理解SystemUI
- 几款开源的数据挖掘工具
- HDU 1828 Picture(线段树扫描线·周长并)
- 一些在3D打印机怎么使用中存在的小问题,帮你来解答
- 释伴:Linux 上的 Shebang 符号(#!)
- Java基础——多线程(待续)
- 怎么找一家培训机构来教你3D打印机怎么使用
- jQuery中live绑定的事件与解除绑定
- browser 存储
- xtrabackup原理
- 2016哈工大计算机推免保研工作细则



