LBP纹理特征
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝美工练手 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/30 02:04
局部二进制模式(Local binary patterns,LBP)最早是作为一种有有效的纹理描述算子提出的,由于其对图像局部纹理特征的卓越描绘能力而获得了非常广泛的应用。LBP特征具有很强的分类能力(Highly Discriminative)、较高的计算效率并且对于单调的灰度变化具有不变性。LBP方法在1994年首先由T. Ojala, M.Pietikäinen, 和 D. Harwood 提出,是一个计算机视觉中用于图像特征分类的重要方法,后来LBP方法与HOG特征分类器联合使用,改善了一些数据集上的检测效果。
(1)基本LBP
下图给出了一个基本的LBP算子,应用LBP算子的过程类似于滤波过程中的模板操作。逐行扫描图像,对于图像中的每一个像素点,以该点的灰度作为阈值,对周围3X3的8邻域进行二值化,按照一定的顺序将二值化的结果组成一个8位二进制数,以此二进制数的值(0~255)作为该点的响应。
例如,对下图中的3X3区域的中心点,以其灰度值68作为阈值,对其8邻域进行二值化,并且从左上点开始按照顺时针方向(具体的顺序可以任意,只要统一即可)将二值化的结果组成一个二进制数10001011,即十进制的139,作为中心点的响应。
在整个逐行扫描过程结束后,会得到一个LBP响应图像,这个响应图像的直方图被称为LBP统计直方图,或LBP直方图,它常常被作为后续识别工作的特征,因此也被称为LBP特征。
LBP的主要思想是以某一点与其邻域像素的相对灰度作为响应,正是这种相对机制使得LBP算子对于单调的灰度变化具有不变性。人脸图像常常会受到光照因素的影响而产生灰度变化,但在一个局部区域内,这种变化常常可以被视为是单调的,因此LBP在光照不均的人脸识别应用中也取得了很好的效果。
(2)圆形邻域LBP算子
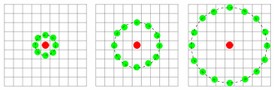
基本LBP算子可以被进一步推广为使用不同大小和形状的邻域。采用圆形的邻域并结合双线性插值运算可以获得任意半径和任意数目的邻域像素点。
如下图, 应用LBP算法的三个邻域示例所示)进行顺时针或逆时针的比较,如果中心像素值比该邻点大,则将邻点赋值为1,否则赋值为0,这样每个点都会获得一个8位二进制数(通常转换为十进制数)。然后计算每个cell的直方图,即每个数字(假定是十进制数)出现的频率(也就是一个关于每一个像素点是否比邻域内点大的一个二进制序列进行统计),然后对该直方图进行归一化处理。最后将得到的每个cell的统计直方图进行连接,就得到了整幅图的LBP纹理特征,然后便可利用SVM或者其他机器学习算法进行分类了。
(3)MATLAB实现
一共有三个m文件,一个是lbp.m, 存放主要的lbp算法,一个是getmapping,用以做算法的辅助函数,一个是cont.m。
1.lbp.m
%LBP returns the local binary pattern image or LBP histogram of an image.% J = LBP(I,R,N,MAPPING,MODE) returns either a local binary pattern% coded image or the local binary pattern histogram of an intensity% image I. The LBP codes are computed using N sampling points on a % circle of radius R and using mapping table defined by MAPPING. % See the getmapping function for different mappings and use 0 for% no mapping. Possible values for MODE are% 'h' or 'hist' to get a histogram of LBP codes% 'nh' to get a normalized histogram% Otherwise an LBP code image is returned.%% J = LBP(I) returns the original (basic) LBP histogram of image I%% J = LBP(I,SP,MAPPING,MODE) computes the LBP codes using n sampling% points defined in (n * 2) matrix SP. The sampling points should be% defined around the origin (coordinates (0,0)).%% Examples% --------% I=imread('rice.png');% mapping=getmapping(8,'u2'); % H1=LBP(I,1,8,mapping,'h'); %LBP histogram in (8,1) neighborhood% %using uniform patterns% subplot(2,1,1),stem(H1);%% H2=LBP(I);% subplot(2,1,2),stem(H2);%% SP=[-1 -1; -1 0; -1 1; 0 -1; -0 1; 1 -1; 1 0; 1 1];% I2=LBP(I,SP,0,'i'); %LBP code image using sampling points in SP% %and no mapping. Now H2 is equal to histogram% %of I2.function result = lbp(varargin) % image,radius,neighbors,mapping,mode)% Version 0.3.3% Authors: Marko Heikkil?and Timo Ahonen% Changelog% Version 0.3.2: A bug fix to enable using mappings together with a% predefined spoints array% Version 0.3.1: Changed MAPPING input to be a struct containing the mapping% table and the number of bins to make the function run faster with high number% of sampling points. Lauge Sorensen is acknowledged for spotting this problem.% Check number of input arguments.error(nargchk(1,5,nargin));image=varargin{1};d_image=double(image);if nargin==1 spoints=[-1 -1; -1 0; -1 1; 0 -1; -0 1; 1 -1; 1 0; 1 1]; neighbors=8; mapping=0; mode='h';endif (nargin == 2) && (length(varargin{2}) == 1) error('Input arguments');endif (nargin > 2) && (length(varargin{2}) == 1) radius=varargin{2}; neighbors=varargin{3}; spoints=zeros(neighbors,2); % Angle step. a = 2*pi/neighbors; for i = 1:neighbors spoints(i,1) = -radius*sin((i-1)*a); spoints(i,2) = radius*cos((i-1)*a); end if(nargin >= 4) mapping=varargin{4}; if(isstruct(mapping) && mapping.samples ~= neighbors) error('Incompatible mapping'); end else mapping=0; end if(nargin >= 5) mode=varargin{5}; else mode='h'; endendif (nargin > 1) && (length(varargin{2}) > 1) spoints=varargin{2}; neighbors=size(spoints,1); if(nargin >= 3) mapping=varargin{3}; if(isstruct(mapping) && mapping.samples ~= neighbors) error('Incompatible mapping'); end else mapping=0; end if(nargin >= 4) mode=varargin{4}; else mode='h'; end end% Determine the dimensions of the input image.[ysize xsize] = size(image);miny=min(spoints(:,1));maxy=max(spoints(:,1));minx=min(spoints(:,2));maxx=max(spoints(:,2));% Block size, each LBP code is computed within a block of size bsizey*bsizexbsizey=ceil(max(maxy,0))-floor(min(miny,0))+1;bsizex=ceil(max(maxx,0))-floor(min(minx,0))+1;% Coordinates of origin (0,0) in the blockorigy=1-floor(min(miny,0));origx=1-floor(min(minx,0));% Minimum allowed size for the input image depends% on the radius of the used LBP operator.if(xsize < bsizex || ysize < bsizey) error('Too small input image. Should be at least (2*radius+1) x (2*radius+1)');end% Calculate dx and dy;dx = xsize - bsizex;dy = ysize - bsizey;% Fill the center pixel matrix C.C = image(origy:origy+dy,origx:origx+dx);d_C = double(C);bins = 2^neighbors;% Initialize the result matrix with zeros.result=zeros(dy+1,dx+1);%Compute the LBP code imagefor i = 1:neighbors y = spoints(i,1)+origy; x = spoints(i,2)+origx; % Calculate floors, ceils and rounds for the x and y. fy = floor(y); cy = ceil(y); ry = round(y); fx = floor(x); cx = ceil(x); rx = round(x); % Check if interpolation is needed. if (abs(x - rx) < 1e-6) && (abs(y - ry) < 1e-6) % Interpolation is not needed, use original datatypes N = image(ry:ry+dy,rx:rx+dx); D = N >= C; else % Interpolation needed, use double type images ty = y - fy; tx = x - fx; % Calculate the interpolation weights. w1 = roundn((1 - tx) * (1 - ty),-6); w2 = roundn(tx * (1 - ty),-6); w3 = roundn((1 - tx) * ty,-6) ; % w4 = roundn(tx * ty,-6) ; w4 = roundn(1 - w1 - w2 - w3, -6); % Compute interpolated pixel values N = w1*d_image(fy:fy+dy,fx:fx+dx) + w2*d_image(fy:fy+dy,cx:cx+dx) + ...w3*d_image(cy:cy+dy,fx:fx+dx) + w4*d_image(cy:cy+dy,cx:cx+dx); N = roundn(N,-4); D = N >= d_C; end % Update the result matrix. v = 2^(i-1); result = result + v*D;end%Apply mapping if it is definedif isstruct(mapping) bins = mapping.num; for i = 1:size(result,1) for j = 1:size(result,2) result(i,j) = mapping.table(result(i,j)+1); end endendif (strcmp(mode,'h') || strcmp(mode,'hist') || strcmp(mode,'nh')) % Return with LBP histogram if mode equals 'hist'. result=hist(result(:),0:(bins-1)); if (strcmp(mode,'nh')) result=result/sum(result); endelse %Otherwise return a matrix of unsigned integers if ((bins-1)<=intmax('uint8')) result=uint8(result); elseif ((bins-1)<=intmax('uint16')) result=uint16(result); else result=uint32(result); endendendfunction x = roundn(x, n)error(nargchk(2, 2, nargin, 'struct'))validateattributes(x, {'single', 'double'}, {}, 'ROUNDN', 'X')validateattributes(n, ... {'numeric'}, {'scalar', 'real', 'integer'}, 'ROUNDN', 'N')if n < 0 p = 10 ^ -n; x = round(p * x) / p;elseif n > 0 p = 10 ^ n; x = p * round(x / p);else x = round(x);endend2.getmapping.m
%GETMAPPING returns a structure containing a mapping table for LBP codes.% MAPPING = GETMAPPING(SAMPLES,MAPPINGTYPE) returns a% structure containing a mapping table for% LBP codes in a neighbourhood of SAMPLES sampling% points. Possible values for MAPPINGTYPE are% 'u2' for uniform LBP% 'ri' for rotation-invariant LBP% 'riu2' for uniform rotation-invariant LBP.%% Example:% I=imread('rice.tif');% MAPPING=getmapping(16,'riu2');% LBPHIST=lbp(I,2,16,MAPPING,'hist');% Now LBPHIST contains a rotation-invariant uniform LBP% histogram in a (16,2) neighbourhood.%function mapping = getmapping(samples,mappingtype)% Version 0.2% Authors: Marko Heikkil?, Timo Ahonen and Xiaopeng Hong% Changelog% 0.1.1 Changed output to be a structure% Fixed a bug causing out of memory errors when generating rotation% invariant mappings with high number of sampling points.% Lauge Sorensen is acknowledged for spotting this problem.% Modified by Xiaopeng HONG and Guoying ZHAO% Changelog% 0.2% Solved the compatible issue for the bitshift function in Matlab% 2012 & highermatlab_ver = ver('MATLAB');matlab_ver = str2double(matlab_ver.Version);if matlab_ver < 8 mapping = getmapping_ver7(samples,mappingtype);else mapping = getmapping_ver8(samples,mappingtype);endendfunction mapping = getmapping_ver7(samples,mappingtype)disp('For Matlab version 7.x and lower');table = 0:2^samples-1;newMax = 0; %number of patterns in the resulting LBP codeindex = 0;if strcmp(mappingtype,'u2') %Uniform 2 newMax = samples*(samples-1) + 3; for i = 0:2^samples-1 j = bitset(bitshift(i,1,samples),1,bitget(i,samples)); %rotate left numt = sum(bitget(bitxor(i,j),1:samples)); %number of 1->0 and %0->1 transitions %in binary string %x is equal to the %number of 1-bits in %XOR(x,Rotate left(x)) if numt <= 2 table(i+1) = index; index = index + 1; else table(i+1) = newMax - 1; end endendif strcmp(mappingtype,'ri') %Rotation invariant tmpMap = zeros(2^samples,1) - 1; for i = 0:2^samples-1 rm = i; r = i; for j = 1:samples-1 r = bitset(bitshift(r,1,samples),1,bitget(r,samples)); %rotate %left if r < rm rm = r; end end if tmpMap(rm+1) < 0 tmpMap(rm+1) = newMax; newMax = newMax + 1; end table(i+1) = tmpMap(rm+1); endendif strcmp(mappingtype,'riu2') %Uniform & Rotation invariant newMax = samples + 2; for i = 0:2^samples - 1 j = bitset(bitshift(i,1,samples),1,bitget(i,samples)); %rotate left numt = sum(bitget(bitxor(i,j),1:samples)); if numt <= 2 table(i+1) = sum(bitget(i,1:samples)); else table(i+1) = samples+1; end endendmapping.table=table;mapping.samples=samples;mapping.num=newMax;endfunction mapping = getmapping_ver8(samples,mappingtype)disp('For Matlab version 8.0 and higher');table = 0:2^samples-1;newMax = 0; %number of patterns in the resulting LBP codeindex = 0;if strcmp(mappingtype,'u2') %Uniform 2 newMax = samples*(samples-1) + 3; for i = 0:2^samples-1 i_bin = dec2bin(i,samples); j_bin = circshift(i_bin',-1)'; %circularly rotate left numt = sum(i_bin~=j_bin); %number of 1->0 and %0->1 transitions %in binary string %x is equal to the %number of 1-bits in %XOR(x,Rotate left(x)) if numt <= 2 table(i+1) = index; index = index + 1; else table(i+1) = newMax - 1; end endendif strcmp(mappingtype,'ri') %Rotation invariant tmpMap = zeros(2^samples,1) - 1; for i = 0:2^samples-1 rm = i; r_bin = dec2bin(i,samples); for j = 1:samples-1 r = bin2dec(circshift(r_bin',-1*j)'); %rotate left if r < rm rm = r; end end if tmpMap(rm+1) < 0 tmpMap(rm+1) = newMax; newMax = newMax + 1; end table(i+1) = tmpMap(rm+1); endendif strcmp(mappingtype,'riu2') %Uniform & Rotation invariant newMax = samples + 2; for i = 0:2^samples - 1 i_bin = dec2bin(i,samples); j_bin = circshift(i_bin',-1)'; numt = sum(i_bin~=j_bin); if numt <= 2 table(i+1) = sum(bitget(i,1:samples)); else table(i+1) = samples+1; end endendmapping.table=table;mapping.samples=samples;mapping.num=newMax;end%C computes the VAR descriptor.% J = CONT(I,R,N,LIMS,MODE) returns either a rotation invariant local % variance (VAR) image or a VAR histogram of the image I. The VAR values % are determined for all pixels having neighborhood defined by the input % arguments. The VAR operator calculates variance on a circumference of % R radius circle. The circumference is discretized into N equally spaced% sample points. Function returns descriptor values in a continuous form or% in a discrete from if the quantization limits are defined in the argument% LIMS. %% Examples% --------%% im = imread('rice.png');% c = cont(im,4,16); % d = cont(im,4,16,1:500:2000);%% figure% subplot(121),imshow(c,[]), title('VAR image')% subplot(122),imshow(d,[]), title('Quantized VAR image')function result = cont(varargin) % Version: 0.1.0% Check number of input arguments.error(nargchk(1,5,nargin));image=varargin{1};d_image=double(image);if nargin==1 spoints=[-1 -1; -1 0; -1 1; 0 -1; -0 1; 1 -1; 1 0; 1 1]; neighbors=8; lims=0; mode='i';endif (nargin > 2) && (length(varargin{2}) == 1) radius=varargin{2}; neighbors=varargin{3}; spoints=zeros(neighbors,2); lims=0; mode='i'; % Angle step. a = 2*pi/neighbors; for i = 1:neighbors spoints(i,1) = -radius*sin((i-1)*a); spoints(i,2) = radius*cos((i-1)*a); end if(nargin >= 4 && ~ischar(varargin{4})) lims=varargin{4}; end if(nargin >= 4 && ischar(varargin{4})) mode=varargin{4}; end if(nargin == 5) mode=varargin{5}; endendif (nargin == 2) && ischar(varargin{2}) mode=varargin{2}; spoints=[-1 -1; -1 0; -1 1; 0 -1; -0 1; 1 -1; 1 0; 1 1]; neighbors=8; lims=0;end% Determine the dimensions of the input image.[ysize xsize] = size(image);miny=min(spoints(:,1));maxy=max(spoints(:,1));minx=min(spoints(:,2));maxx=max(spoints(:,2));% Block size, each LBP code is computed within a block of size bsizey*bsizexbsizey=ceil(max(maxy,0))-floor(min(miny,0))+1;bsizex=ceil(max(maxx,0))-floor(min(minx,0))+1;% Coordinates of origin (0,0) in the blockorigy=1-floor(min(miny,0));origx=1-floor(min(minx,0));% Minimum allowed size for the input image depends% on the radius of the used LBP operator.if(xsize < bsizex || ysize < bsizey) error('Too small input image. Should be at least (2*radius+1) x (2*radius+1)');end% Calculate dx and dy;dx = xsize - bsizex;dy = ysize - bsizey;%Compute the local contrastfor i = 1:neighbors y = spoints(i,1)+origy; x = spoints(i,2)+origx; % Calculate floors and ceils for the x and y. fy = floor(y); cy = ceil(y); fx = floor(x); cx = ceil(x); % Use double type images ty = y - fy; tx = x - fx; % Calculate the interpolation weights. w1 = (1 - tx) * (1 - ty); w2 = tx * (1 - ty); w3 = (1 - tx) * ty ; w4 = tx * ty ; % Compute interpolated pixel values N = w1*d_image(fy:fy+dy,fx:fx+dx) + w2*d_image(fy:fy+dy,cx:cx+dx) + ... w3*d_image(cy:cy+dy,fx:fx+dx) + w4*d_image(cy:cy+dy,cx:cx+dx); % Compute the variance using on-line algorithm % ( http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algorithms_for_calculating_variance#On-line_algorithm ). if i == 1 MEAN=zeros(size(N)); DELTA=zeros(size(N)); M2=zeros(size(N)); end DELTA=N-MEAN; MEAN=MEAN+DELTA/i; M2=M2+DELTA.*(N-MEAN); end% Compute the variance matrix.% Optional estimate for variance:% VARIANCE_n=M2/neighbors;result=M2/(neighbors-1);% Quantize if LIMS is givenif lims [q r s]=size(result); quant_vector=q_(result(:),lims); result=reshape(quant_vector,q,r,s); if strcmp(mode,'h') % Return histogram result=hist(result, length(lims)-1); end endif strcmp(mode,'h') && ~lims % Return histogram %epoint = round(max(result(:))); result=hist(result(:),0:1:1e4);endendfunction indx = q_(sig,partition)[nRows, nCols] = size(sig);indx = zeros(nRows, nCols);for i = 1 : length(partition) indx = indx + (sig > partition(i));endend%%LBP_test.mImg=imread('lena.jpg');I=rgb2gray(Img);mapping=getmapping(8,'u2'); H1=LBP(I,1,8,mapping,'h'); %LBP histogram in (8,1) neighborhood %using uniform patternssubplot(2,1,1),stem(H1);H2=LBP(I);subplot(2,1,2),stem(H2);SP=[-1 -1; -1 0; -1 1; 0 -1; -0 1; 1 -1; 1 0; 1 1];I2=LBP(I,SP,0,'i'); %LBP code image using sampling points in SP %and no mapping. Now H2 is equal to histogram of I2.% show the imagesfigure, imshow(I);title('Input Image');figure, imshow(I2);title('Result of LBP');- LBP纹理特征
- LBP纹理特征
- LBP纹理特征
- 纹理特征-LBP
- LBP纹理特征
- LBP纹理特征
- 纹理特征-LBP
- LBP纹理特征
- LBP纹理特征
- LBP纹理特征研究
- LBP纹理特征提取
- LBP纹理特征
- 【计算机视觉】LBP纹理特征
- 纹理特征提取 及LBP纹理特征matlab实现
- 纹理特征-LBP的扩展DLBP
- 纹理特征-LBP的扩展DLBP
- 纹理特征-LBP的扩展VLBP
- 纹理分类(一)全局特征LBP
- 在IE、fixfox、chrome等浏览器中ajax提交成功后,打开新标签页面被浏览器拦截问题
- 使用dir()、readdir()和glob()遍历目录及测试性能 http://blog.csdn.net/hpy1165331898/article/details/44918879
- 大众点评2015笔试题(答案)
- 学习队列 总结
- 多态、抽象、接口
- LBP纹理特征
- HTTP协议中POST和GET的区别
- utf-8 unicode 各种编码的区别与联系
- Selenium2(JAVA) Web自动化测试实战 电子书百度阅读正式上架 欢迎试读购买
- PAT Basic 1034 有理数四则运算(20)
- DataBase
- poj 2377 最小生成树(kruskal算法)
- HDU 5437 Alisha’s Party
- hdu 5024 Wang Xifeng's Little Plot(搜索)






