STL系列之六 set与hash_set
来源:互联网 发布:层次聚类 python 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/17 23:45
set和hash_set是STL中比较重要的容器,有必要对其进行深入了解。在STL中,set是以红黑树(RB-tree)作为底层数据结构的,hash_set是以Hash table(哈希表)作为底层数据结构的。set可以在时间复杂度为O(logN)情况下插入、删除和查找数据。hash_set操作的时间复杂度则比较复杂,这取决于哈希函数和哈希表的负载情况。下面列出set和hash_set的常用函数: 
set和hase_set的更多函数请查阅MSDN。
set的使用范例如下(hash_set类似):
// by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )#include <set>#include <ctime>#include <cstdio>using namespace std;int main(){ printf("--set使用 by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows ) --\n\n"); const int MAXN = 15; int a[MAXN]; int i; srand(time(NULL)); for (i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i) a[i] = rand() % (MAXN * 2); set<int> iset; set<int>::iterator pos; //插入数据 insert()有三种重载 iset.insert(a, a + MAXN); //当前集合中个数 最大容纳数据量 printf("当前集合中个数: %d 最大容纳数据量: %d\n", iset.size(), iset.max_size()); //依次输出 printf("依次输出集合中所有元素-------\n"); for (pos = iset.begin(); pos != iset.end(); ++pos) printf("%d ", *pos); putchar('\n'); //查找 int findNum = MAXN; printf("查找 %d是否存在-----------------------\n", findNum); pos = iset.find(findNum); if (pos != iset.end()) printf("%d 存在\n", findNum); else printf("%d 不存在\n", findNum); //在最后位置插入数据,如果给定的位置不正确,会重新找个正确的位置并返回该位置 pos = iset.insert(--iset.end(), MAXN * 2); printf("已经插入%d\n", *pos); //删除 iset.erase(MAXN); printf("已经删除%d\n", MAXN); //依次输出 printf("依次输出集合中所有元素-------\n"); for (pos = iset.begin(); pos != iset.end(); ++pos) printf("%d ", *pos); putchar('\n'); return 0;}运行结果如下: 
下面试下在set中使用类(结构体也可以类似这样做)。这个类很简单,只有一个成员变量,及设置和获取这个成员变量的成员函数。
//在set中使用类要重载‘<’并实现拷贝构造函数// by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )#include <set>#include <ctime>#include <cstdio>using namespace std;class Node{public: Node(int nAge = 0) { m_nAge = nAge; } Node(const Node &na) //拷贝构造函数 { m_nAge = na.GetAge(); } int GetAge() { return m_nAge; }private: int m_nAge;};//不能写成类的成员函数inline bool operator < (const Node &na, const Node &nb) { return na.GetAge() < nb.GetAge();}int main(){ int i; set<Node> nset; for (i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i) nset.insert(Node(i)); return 0;}编译,直接报了3个错误!!1个在拷贝构造函数,2个在operator<()函数。如下图所示: 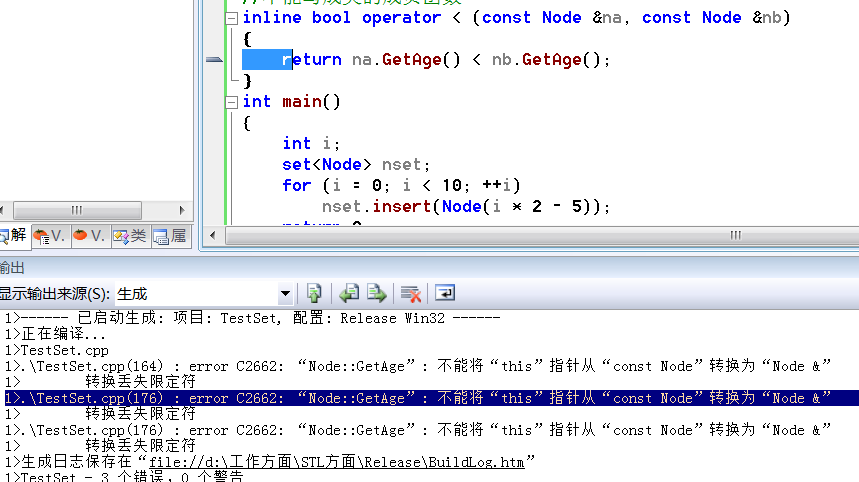
3个错误都是一样的:
error C2662: “Node::GetAge”: 不能将“this”指针从“const Node”转换为“Node &” 转换丢失限定符
这是怎么回事呀?分析下,拷贝构造函数与operator<()函数出错,错误都指向了GetAge()函数,有点古怪,比较下它们与GetAge()函数,可以发现最大的不同点在于这2个函数都用到了const而GetAge()函数没有使用const。难道是这个导致报错了吗?先给GetAge()函数加个const看看,如下:
int GetAge() const //增加这个const { returnm_nAge; }再编译,不报错了。再查下资料,原因如下——因为那2个函数都使用了const修饰的对象,但GetAge()没有加上const以保证它不修改对象,编译器认为这种写法是不安全的,所以就毫不犹豫报了个错误。
这种错误如果不亲身体会下,到笔试面试时很可能写了个错误程序而自己还处于一无所知中(死在这些小细节上最不值得)。另外,如果使用VC6.0则不会提示详细的错误信息——“转换丢失限定符”。
STL还为set提供了一些集合运算的函数,如交集set_intersection()、并集set_union()、差集set_difference()和对称差集set_symmetric_difference()。这些就不详细介绍了,有兴趣可以自己动手试一试。
下面开始对set和hash_set作个性能测试(Win7 +VS2008Release下)。
测试代码如下:
// by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )#include <set>#include <hash_set>#include <iostream>#include <ctime>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>using namespace std;using namespace stdext; //hash_set// MAXN个数据 MAXQUERY次查询const int MAXN = 10000, MAXQUERY = 5000000;int a[MAXN], query[MAXQUERY];void PrintfContainertElapseTime(char *pszContainerName, char *pszOperator, long lElapsetime){ printf("%s 的%s操作 用时 %d毫秒\n", pszContainerName, pszOperator, lElapsetime);}int main(){ printf("set VS hash_set 性能测试 数据容量 %d个 查询次数 %d次\n", MAXN, MAXQUERY); const int MAXNUM = MAXN * 4; const int MAXQUERYNUM = MAXN * 4; printf("容器中数据范围 [0, %d) 查询数据范围[0, %d)\n", MAXNUM, MAXQUERYNUM); printf("--by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows ) --\n\n"); //随机生成在[0, MAXNUM)范围内的MAXN个数 int i; srand(time(NULL)); for (i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i) a[i] = (rand() * rand()) % MAXNUM; //随机生成在[0, MAXQUERYNUM)范围内的MAXQUERY个数 srand(time(NULL)); for (i = 0; i < MAXQUERY; ++i) query[i] = (rand() * rand()) % MAXQUERYNUM; set<int> nset; hash_set<int> nhashset; clock_t clockBegin, clockEnd; //insert printf("-----插入数据-----------\n"); clockBegin = clock(); nset.insert(a, a + MAXN); clockEnd = clock(); printf("set中有数据%d个\n", nset.size()); PrintfContainertElapseTime("set", "insert", clockEnd - clockBegin); clockBegin = clock(); nhashset.insert(a, a + MAXN); clockEnd = clock(); printf("hash_set中有数据%d个\n", nhashset.size()); PrintfContainertElapseTime("hase_set", "insert", clockEnd - clockBegin); //find printf("-----查询数据-----------\n"); int nFindSucceedCount, nFindFailedCount; nFindSucceedCount = nFindFailedCount = 0; clockBegin = clock(); for (i = 0; i < MAXQUERY; ++i) if (nset.find(query[i]) != nset.end()) ++nFindSucceedCount; else ++nFindFailedCount; clockEnd = clock(); PrintfContainertElapseTime("set", "find", clockEnd - clockBegin); printf("查询成功次数: %d 查询失败次数: %d\n", nFindSucceedCount, nFindFailedCount); nFindSucceedCount = nFindFailedCount = 0; clockBegin = clock(); for (i = 0; i < MAXQUERY; ++i) if (nhashset.find(query[i]) != nhashset.end()) ++nFindSucceedCount; else ++nFindFailedCount; clockEnd = clock(); PrintfContainertElapseTime("hash_set", "find", clockEnd - clockBegin); printf("查询成功次数: %d 查询失败次数: %d\n", nFindSucceedCount, nFindFailedCount); return 0;}在数据容量100万,查询次数500万时,程序运行结果如下: 
由于查询的失败次数太多,这次将查询范围变小使用再测试下: 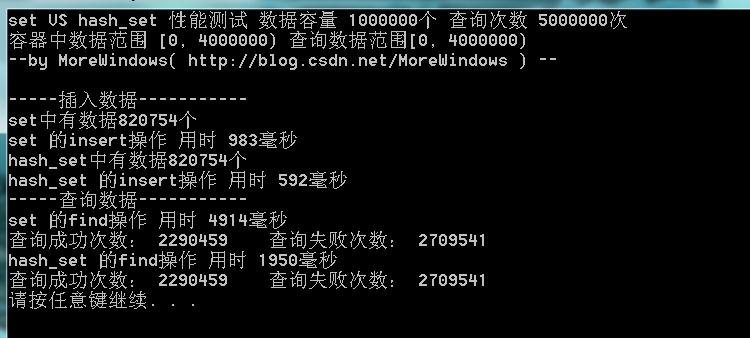
由于结点过多,80多万个结点,set的红黑树树高约为19(2^19=524288,2^20=1048576),查询起来还是比较费时的。hash_set在时间性能上比set要好一些,并且如果查询成功的几率比较大的话,hash_set会有更好的表现。想知道为什么hash_set会有优良的性能表现,请看继集——《STL系列之九 探索hash_set》。
注1 MSDN上讲set的erase()是有返回值的,但在VS2008中查看set的源代码,erase()函数的三个重载版本中,有二个返回值都为void即无返回值,另一个返回size_type。 可以通过http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/8h4a3515(v=VS.90).aspx查看MSDN上对set的erase()说明。
http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/7029587
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六:set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- STL系列set与hash_set
- STL之set与hash_set
- STL之set和hash_set
- STL—— set与hash_set
- STL——set与hash_set
- 几种网页弹出层的实现
- coreseek(sphinx)错误:WARNING: attribute 'id' not found - IGNORING原因及解决方法
- 支持向量机:Kernel II
- hibernate泛型Dao,让持久层简洁起来
- CompletionService
- STL系列之六 set与hash_set
- nova 9.24会议纪要
- UI26_编程总结
- 正则化与反问题
- Entity Framework - 理清关系 - 基于外键关联的单向一对一关系
- rdlc 报表
- redis-cli 命令选项--raw中文输出
- Django——Xadmin中添加显示图片函数
- 回归,梯度下降


