Android字符串进阶
来源:互联网 发布:虾囧笑话源码v4.0 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/08 11:20
一、特殊字符的输入
- <string name="welcome_messages">Hello, %1$s! You have %2$d new messages.</string>
- Resources res = getResources();
- String text = String.format(res.getString(R.string.welcome_messages), username, mailCount);
- <string name="welcome">Welcome to <b>Android</b>!</string>
- <string name="welcome_messages">Hello, %1$s! You have <b>%2$d new messages</b>.</string>
- Resources res = getResources();
- String text = String.format(res.getString(R.string.welcome_messages), username, mailCount);
- CharSequence styledText = Html.fromHtml(text);
- String escapedUsername = TextUtil.htmlEncode(username);
- Resources res = getResources();
- String text = String.format(res.getString(R.string.welcome_messages), escapedUsername, mailCount);
- CharSequence styledText = Html.fromHtml(text);
- <string name="welcome_messages">Hello, %1$s! You have <b>%2$d new messages</b>.</string>
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
- Resources rs = getResources();
- mTextView1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
- mTextvView2 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView2);
- String name = new String("<Mike>");
- int count = 12345;
- //未转为html-styled
- format1 = String.format(rs.getString(R.string.welcome_messages), name,count);
- CharSequence styledText1 = Html.fromHtml(format1);
- mTextView1.setText(styledText1);
- //转为html-styled
- format2 = String.format(rs.getString(R.string.welcome_messages), TextUtils.htmlEncode(name),count);
- CharSequence styledText2 = Html.fromHtml(format2);
- mTextvView2.setText(styledText2);
- }
- /**
- * Html-encode the string.
- * @param s the string to be encoded
- * @return the encoded string
- */
- public static String htmlEncode(String s) {
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- char c;
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- c = s.charAt(i);
- switch (c) {
- case '<':
- sb.append("<"); //$NON-NLS-1$
- break;
- case '>':
- sb.append(">"); //$NON-NLS-1$
- break;
- case '&':
- sb.append("&"); //$NON-NLS-1$
- break;
- case '\'':
- sb.append("'"); //$NON-NLS-1$
- break;
- case '"':
- sb.append("""); //$NON-NLS-1$
- break;
- default:
- sb.append(c);
- }
- }
- return sb.toString();
- }
- <plurals name="numberOfSongsAvailable">
- <item quantity="zero">Zero song found.</item>
- <item quantity="one">One song found.</item>
- <item quantity="two">Two song found.</item>
- <item quantity="few">Few song found.</item>
- <item quantity="other">Other song found.</item>
- <item quantity="many">Many song found.</item>
- </plurals>
二、字符及字符串的测量和处理
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
- int count1 = 0;
- Resources res = getResources();
- String songsFound1 = res.getQuantityString(R.plurals.numberOfSongsAvailable, count1, count1);
- TextView textView1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
- textView1.setText(songsFound1);
- int count2 = 1;
- String songsFound2 = res.getQuantityString(R.plurals.numberOfSongsAvailable, count2, count2);
- TextView textView2 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView2);
- textView2.setText(songsFound2);
- int count3 = 2;
- String songsFound3 = res.getQuantityString(R.plurals.numberOfSongsAvailable, count3, count3);
- TextView textView3 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView3);
- textView3.setText(songsFound3);
- int count4 = 3;
- String songsFound4 = res.getQuantityString(R.plurals.numberOfSongsAvailable, count4, count4);
- TextView textView4 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView4);
- textView4.setText(songsFound4);
- int count5 = 4;
- String songsFound5 = res.getQuantityString(R.plurals.numberOfSongsAvailable, count5, count5);
- TextView textView5 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView5);
- textView5.setText(songsFound5);
- int count6 = 1000;
- String songsFound6 = res.getQuantityString(R.plurals.numberOfSongsAvailable, count6, count6);
- TextView textView6 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView6);
- textView6.setText(songsFound6);
- }
- /*
- * 根据要求分割字符串
- */
- public static String[] getLineStrs(String content, Paint paint, float width, float textSize) {
- paint.setTextSize(textSize);//Note1:测量的工具首先需要定义单位
- int index = 0;
- int start = 0;
- int end = 0;
- float textLength = paint.measureText(content);
- int lineNum = (int) Math.ceil(1.5*textLength / width) ;//Note2:计算行数因为判断的不准确,所以增加余量1.5倍,最后处理
- String[] mSplitTextParts = new String[lineNum];
- for (int i = 0; i <= content.length(); i++) {
- end = i;
- float measureLength = paint.measureText(content, start, end);//Note3:[start,end)范围的字符串
- if (measureLength >= width) {
- mSplitTextParts[index] = content.substring(start, end);//Note4:[start,end)范围的字符串
- start = end;
- index++;
- }
- if (end == content.length()) {
- mSplitTextParts[index] = content.substring(start, end);
- return Arrays.copyOf(mSplitTextParts, index);//Note5:因为行数判断的不准确,所以需要清除掉未赋值的null值字符串
- }
- }
- return null;
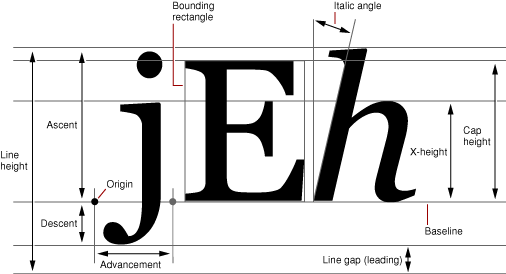
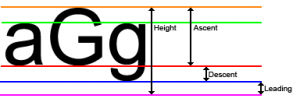
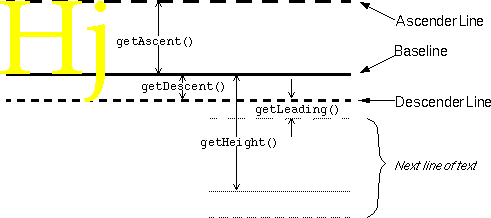
三、字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- public class FontMetricsDemoActivity extends Activity {
- private Canvas canvas;
- /** Called when the activity is first created. */
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
- Paint textPaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
- textPaint.setTextSize( 55);
- textPaint.setColor( Color.WHITE);
- // FontMetrics对象
- FontMetrics fontMetrics = textPaint.getFontMetrics();
- String text = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstu";
- // 计算每一个坐标
- float baseX = 0;
- float baseY = 100;
- float topY = baseY + fontMetrics.top;
- float ascentY = baseY + fontMetrics.ascent;
- float descentY = baseY + fontMetrics.descent;
- float bottomY = baseY + fontMetrics.bottom;
- float leading = baseY + fontMetrics.leading;
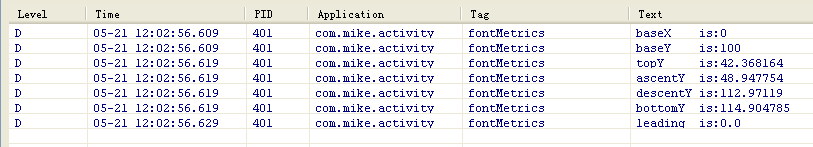
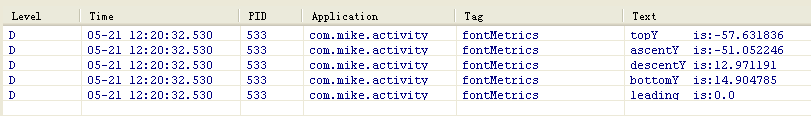
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "baseX is:" + 0);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "baseY is:" + 100);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "topY is:" + topY);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "ascentY is:" + ascentY);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "descentY is:" + descentY);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "bottomY is:" + bottomY);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "leading is:" + leading);
- Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.fontmetrics);
- Bitmap mutableBitmap = bitmap.copy(Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888, true);
- canvas = new Canvas(mutableBitmap);
- // 绘制文本
- canvas.drawText(text, baseX, baseY, textPaint);
- // BaseLine描画
- Paint baseLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
- baseLinePaint.setColor( Color.RED);
- canvas.drawLine(0, baseY, canvas.getWidth(), baseY, baseLinePaint);
- // Base描画
- canvas.drawCircle( baseX, baseY, 5, baseLinePaint);
- // TopLine描画
- Paint topLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
- topLinePaint.setColor( Color.LTGRAY);
- canvas.drawLine(0, topY, canvas.getWidth(), topY, topLinePaint);
- // AscentLine描画
- Paint ascentLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
- ascentLinePaint.setColor( Color.GREEN);
- canvas.drawLine(0, ascentY, canvas.getWidth(), ascentY, ascentLinePaint);
- // DescentLine描画
- Paint descentLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
- descentLinePaint.setColor( Color.YELLOW);
- canvas.drawLine(0, descentY, canvas.getWidth(), descentY, descentLinePaint);
- // ButtomLine描画
- Paint bottomLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
- bottomLinePaint.setColor( Color.MAGENTA);
- canvas.drawLine(0, bottomY, canvas.getWidth(), bottomY, bottomLinePaint);
- ImageView imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imageView1);
- imageView.setImageBitmap(mutableBitmap);
- }
- }
- //test_multiply_lines
- TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
- String textMultiLines = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuabcdefghijklmnopqrstuabcdefghijklmnopqrstuabcdefghijklmnopqrstuabcdefghijklmnopqrstu";
- textView.setTextSize(55);
- textView.setText(textMultiLines);
- FontMetrics fontMetrics2 = textView.getPaint().getFontMetrics();
- // 计算每一个坐标
- float topY = fontMetrics2.top;
- float ascentY = fontMetrics2.ascent;
- float descentY = fontMetrics2.descent;
- float bottomY = fontMetrics2.bottom;
- float leading = fontMetrics2.leading;
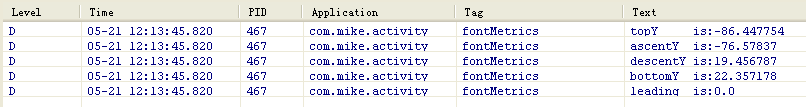
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "topY is:" + topY);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "ascentY is:" + ascentY);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "descentY is:" + descentY);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "bottomY is:" + bottomY);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "leading is:" + leading);
- String text = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstu";
- TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
- textView.setTextSize(55);
- textView.setText(text);
- FontMetrics fontMetrics = textView.getPaint().getFontMetrics();
- // 计算每一个坐标
- float baseX = 0;
- float baseY = 100;
- float topY = baseY + fontMetrics.top;
- float ascentY = baseY + fontMetrics.ascent;
- float descentY = baseY + fontMetrics.descent;
- float bottomY = baseY + fontMetrics.bottom;
- float leading = fontMetrics.leading;
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "topY is:" + fontMetrics.top);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "ascentY is:" + fontMetrics.ascent);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "descentY is:" + fontMetrics.descent);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "bottomY is:" + fontMetrics.bottom);
- Log.d("fontMetrics", "leading is:" + fontMetrics.leading);
本文出自 “小新专栏” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://mikewang.blog.51cto.com/3826268/864801
0 0
- Android字符串进阶
- Android进阶——字符串排序
- 字符串进阶
- Android字符串进阶:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之一(特殊字符的输入)
- Android字符串进阶之一(特殊字符的输入)
- android 进阶
- 进阶Android
- 进阶Android
- Android 进阶
- ANdroid进阶
- Android进阶
- Android进阶
- Android进阶
- Android进阶
- Android 进阶
- 字符串处理函数进阶
- 字符串截取进阶
- CSS清除浮动的4种方法
- Xcode7 使用NSURL发送HTTP请求报错
- R0注入DLL到R3进程
- Spring Security教程外篇(2)---- 乱起八糟的一下东西,自己备用
- 做手机 UI 如何根据手机分辨率在 PS 建画布?
- Android字符串进阶
- 脚本POS规范 笔记
- Oreacl 查询数据出现中文乱码|配置环境变量
- UIScrollView 常用知识点
- Algorithms—208.Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
- 基于PHP的微信公众平台开发(TOKEN验证,消息回复)
- layout_marginTop="-3dp"导致内容被遮挡的问题处理
- HDU 1466 计算直线的交点数 dp晕
- <iOS>多线程GCD