[HDU1693]Eat the Trees
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝达人后台 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/02 02:49
Eat the Trees
Problem Description
Most of us know that in the game called DotA(Defense of the Ancient), Pudge is a strong hero in the first period of the game. When the game goes to end however, Pudge is not a strong hero any more.
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees! 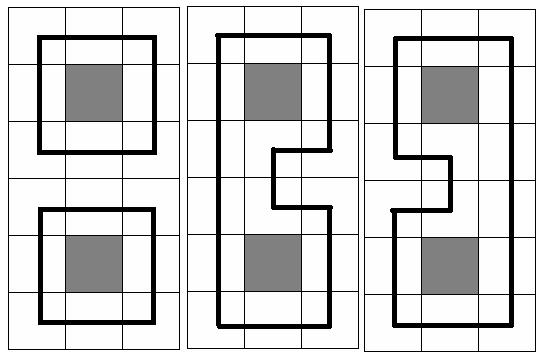
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of the input is the number of the cases. There are no more than 10 cases.
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
Output
For each case, you should print the desired number of ways in one line. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 263 – 1. Use the format in the sample.
Sample Input
2
6 3
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
2 4
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case 1: There are 3 ways to eat the trees.
Case 2: There are 2 ways to eat the trees.
Solution :
轮廓线dp基础题,以01串表示当前轮廓线上插头的状态,逐个格子转移,考虑4种可能的情况即可。
Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;typedef long long ll;typedef pair<int, int> PII;#define rep(i, l, r) for (int i = (l); i <= (r); i++)#define per(i, r, l) for (int i = (r); i >= (l); i--)#define fst first#define sec second#define MS(_) memset(_, 0, sizeof(_))#define PB push_back#define MP make_pairtemplate<typename _T> inline void read(_T &x){ x = 0; bool f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) {if (ch == '-') f = 0; ch = getchar();} while (isdigit(ch)) {x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar();} x = f ? x : -x;}const int N = 22;const int M = 22;const int K = 4444;ll dp[N][M][K];int n, m, mp[N][M];inline void DP(){ MS(dp); dp[0][m][0] = 1ll; int bit = 1<<(m+1); rep(i, 1, n){ rep(k, 0, ((bit>>1)-1)) dp[i][0][k<<1] = dp[i-1][m][k]; rep(j, 1, m) rep(k, 0, bit-1){ int x = 1<<(j-1), y = 1<<j; if (mp[i][j]){ if ((k&x) && (k&y)) dp[i][j][k] += dp[i][j-1][k^x^y]; if (!(k&x) && !(k&y)) dp[i][j][k] += dp[i][j-1][k^x^y]; if ((k&x) && !(k&y)) dp[i][j][k] += dp[i][j-1][k] + dp[i][j-1][k^x^y]; if (!(k&x) && (k&y)) dp[i][j][k] += dp[i][j-1][k] + dp[i][j-1][k^x^y]; }else{ if (!(k&x) && !(k&y)) dp[i][j][k] += dp[i][j-1][k]; else dp[i][j][k] = 0; } } }}int main(){ int T; read(T); rep(cnt, 1, T){ read(n); read(m); rep(i, 1, n) rep(j, 1, m) read(mp[i][j]); DP(); printf("Case %d: There are %lld ways to eat the trees.\n", cnt, dp[n][m][0]); } return 0; }- hdu1693 Eat the Trees
- HDU1693 Eat the Trees
- [HDU1693]Eat the Trees
- [HDU1693]Eat the Trees
- HDU1693 Eat the Trees 题解
- hdu1693 Eat the Trees (插头dp)
- [HDU1693]Eat the Trees && 插头DP
- 【动态规划】[HDU1693] Eat the Trees
- hdu1693 Eat the Trees 插头DP
- hdu1693 Eat the Trees 插头DP
- 【HDU1693】Eat the Trees(插头DP)
- 【HDU1693】Eat the Trees-插头DP
- HDU1693 Eat the Trees(插头dp)
- Eat the Trees hdoj1693
- 【插头DP】Eat the trees
- hdu 1693 Eat the Trees
- hdu 1693 Eat the Trees
- hdu 1693 Eat the Trees
- Apache的Win基本配置
- iOS 中客户端和服务器的 Web Service 网络通信 (2)
- HDU 1505 City Game(DP)
- NSURLSESSION学习笔记
- java基础面试题:你不知道的“= =”
- [HDU1693]Eat the Trees
- iOS开发-归纳总结(下)
- LightOJ - 1086 Jogging Trails(欧拉+状态压缩)
- 遇到问题自己一定要先钻研着解决,不要动不动就去问别人好吧
- 整理 iOS 9 适配中出现的坑(图文)
- 自定义iOS7导航栏背景,标题和返回按钮文字颜色
- android的事件处理
- POJ1003 Hangover
- Hibernate第一课-小应用实践


