04 Sorting
来源:互联网 发布:c语言字符串格式化 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/08 06:29
题目 1:MaxProductOfThree
A non-empty zero-indexed array A consisting of N integers is given. The product of triplet (P, Q, R) equates to A[P] * A[Q] * A[R] (0 ≤ P < Q < R < N).
For example, array A such that:
A[0] = -3 A[1] = 1 A[2] = 2 A[3] = -2 A[4] = 5 A[5] = 6contains the following example triplets:
- (0, 1, 2), product is −3 * 1 * 2 = −6
- (1, 2, 4), product is 1 * 2 * 5 = 10
- (2, 4, 5), product is 2 * 5 * 6 = 60
Your goal is to find the maximal product of any triplet.
Write a function:
int solution(vector<int> &A);
that, given a non-empty zero-indexed array A, returns the value of the maximal product of any triplet.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [3..100,000];
- each element of array A is an integer within the range [−1,000..1,000].
Complexity:
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(N*log(N));
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(1), beyond input storage (not counting the storage required for input arguments).
#include <algorithm>// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;int solution(vector<int> &A) { // write your code in C++11 int n=A.size(); sort(A.begin(),A.end()); int sum1=A[0]*A[1]*A[n-1]; int sum2=A[n-1]*A[n-2]*A[n-3]; return sum1>sum2?sum1:sum2; }题目 2:Distinct
Write a function
int solution(vector<int> &A);
that, given a zero-indexed array A consisting of N integers, returns the number of distinct values in array A.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [0..100,000];
- each element of array A is an integer within the range [−1,000,000..1,000,000].
For example, given array A consisting of six elements such that:
A[0] = 2 A[1] = 1 A[2] = 1A[3] = 2 A[4] = 3 A[5] = 1the function should return 3, because there are 3 distinct values appearing in array A, namely 1, 2 and 3.
Complexity:
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(N*log(N));
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(N), beyond input storage (not counting the storage required for input arguments).
#include <algorithm>#include <set>// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;int solution(vector<int> &A) { // write your code in C++11 //sort int n=A.size(); sort(A.begin(),A.end()); int count=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { if(i==0||A[i]!=A[i-1]) count++; } return count; //set /* #define FOR(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(int)n;++i) int n=A.size(); set<int> st; FOR(i,n) { st.insert(A[i]); } return st.size(); */}题目 3:Triangle
A zero-indexed array A consisting of N integers is given. A triplet (P, Q, R) is triangular if 0 ≤ P < Q < R < N and:
- A[P] + A[Q] > A[R],
- A[Q] + A[R] > A[P],
- A[R] + A[P] > A[Q].
For example, consider array A such that:
A[0] = 10 A[1] = 2 A[2] = 5 A[3] = 1 A[4] = 8 A[5] = 20Triplet (0, 2, 4) is triangular.
Write a function:
int solution(vector<int> &A);
that, given a zero-indexed array A consisting of N integers, returns 1 if there exists a triangular triplet for this array and returns 0 otherwise.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [0..100,000];
- each element of array A is an integer within the range [−2,147,483,648..2,147,483,647].
Complexity:
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(N*log(N));
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(N), beyond input storage (not counting the storage required for input arguments).
// you can use includes, for example: #include <algorithm>// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.// cout << "this is a debug message" << endl;int solution(vector<int> &A) { // write your code in C++11 int n=A.size(); sort(A.begin(),A.end()); for(int i=0;i<n-2;i++) { if(A[i+2]-A[i+1]<A[i]) return 1; } return 0;}题目 4:NumberOfDiscIntersections
We draw N discs on a plane. The discs are numbered from 0 to N − 1. A zero-indexed array A of N non-negative integers, specifying the radiuses of the discs, is given. The J-th disc is drawn with its center at (J, 0) and radius A[J].
We say that the J-th disc and K-th disc intersect if J ≠ K and the J-th and K-th discs have at least one common point (assuming that the discs contain their borders).
The figure below shows discs drawn for N = 6 and A as follows:
A[0] = 1 A[1] = 5 A[2] = 2 A[3] = 1 A[4] = 4 A[5] = 0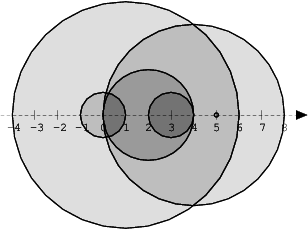
There are eleven (unordered) pairs of discs that intersect, namely:
- discs 1 and 4 intersect, and both intersect with all the other discs;
- disc 2 also intersects with discs 0 and 3.
Write a function:
int solution(vector<int> &A);
that, given an array A describing N discs as explained above, returns the number of (unordered) pairs of intersecting discs. The function should return −1 if the number of intersecting pairs exceeds 10,000,000.
Assume that:
- N is an integer within the range [0..100,000];
- each element of array A is an integer within the range [0..2,147,483,647].
Complexity:
- expected worst-case time complexity is O(N*log(N));
- expected worst-case space complexity is O(N), beyond input storage (not counting the storage required for input arguments).
int solution(vector<int> &A) { // write your code in C++11 int n=A.size(); vector<pair<long,int> > plane; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { plane.push_back(make_pair((long)i-A[i],-1)); plane.push_back(make_pair((long)i+A[i],1)); } sort(plane.begin(),plane.end()); long count=0,allinsert=0; for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++) { if(plane[i].second==-1) { allinsert+=count; if(allinsert>1e7) return -1; count++; } else count--; } return allinsert;}- 04 Sorting
- Sorting
- Sorting:
- Sorting
- Sorting
- Sorting
- Sorting
- Sorting
- GridView sorting
- java sorting
- java sorting
- insert-sorting
- DNA Sorting
- DNA Sorting
- Sorting Algorithms
- DNA Sorting
- DNA Sorting
- DNA Sorting
- epoll 的accept , read, write(重要)
- JavaScript(6) - 数组
- QQ公众号接口使用要求
- Java中实现两变量间的互换
- VS 2013+Qt 5.4.1
- 04 Sorting
- Android项目开发完成以后就要将android项目文件打包成apk文件
- webview的一些操作方法
- 仿QQ聊天界面基本的Fragment用法。
- OAuth2.0微信code获取失败怎么办
- 【开发日记】计算精度
- 对话 Jessica Hamrick:和 Django 的情缘是我前行的动力
- Erlang学习心得
- atlassian conference 安装


