spring security 转
来源:互联网 发布:关于开关电源的软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/06 11:01
开篇说明
最近工作有权限控制的需求,所以看了一下spring的security,它提供了很好的安全服务;
参考文章:http://peiquan.blog.51cto.com/7518552/1384168 ;
在这里我使用第三种权限控制方法,即将用户,权限,资源使用数据库存储,并自定义过滤器,在配置文件里进行相应配置。
二、数据准备
--权限表
CREATE TABLE `authorities` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`authority` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`uid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, //用户id
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ;
INSERT INTO `authorities` VALUES ('1', 'ROLE_ADMIN', '1');
INSERT INTO `authorities` VALUES ('2', 'ROLE_USER', '2');
--用户表(密码为123,这里已加密)
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
`enabled` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
INSERT INTO `users` VALUES ('1', 'admin', 86888061b399e74e30eeead8c7aab922, '1');
INSERT INTO `users` VALUES ('2', 'user', '368703df04cc8d60e2f494a5c244e45a', '1');
--资源表
CREATE TABLE `demo_resources` (
`id` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`resource_name` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`resource_type` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`resource_content` varchar(200) NOT NULL,
`resource_desc` varchar(200) NOT NULL,
`enabled` int(2) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `resource_name` (`resource_name`),
KEY `resource_name_2` (`resource_name`)
);
INSERT INTO `demo_resources` VALUES ('1', '所有资源', 'requesturl', '/**', '所有页面', '1');
INSERT INTO `demo_resources` VALUES ('2', '管理员资源', 'requesturl', '/admin.jsp', '进入管理员页面', '1');
INSERT INTO `demo_resources` VALUES ('3', 'user资源', 'requesturl', '/', 'user能进入首页', '1');
--资源与权限关联表
CREATE TABLE `resource_authority` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`rid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, //资源id
`aid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, //权限id
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
INSERT INTO `resource_authority` VALUES ('1', '1', '1');
INSERT INTO `resource_authority` VALUES ('2', '2', '1');
INSERT INTO `resource_authority` VALUES ('3', '3', '2');
上面的数据说明:
1) admin角色的用户能够访问所有资源(/**,当然我加/admin.jsp这个有点多余,不过没关系) ;
2) user角色的用户只能进入首页(/);
三、security配置
<http pattern="/login.jsp" security="none" /> <http auto-config="true" access-denied-page="/403.jsp"> <form-login login-page="/login.jsp" /> <!-- 自定义filter --> <custom-filter before="FILTER_SECURITY_INTERCEPTOR" ref="securityInterceptorFilter" /> </http> <!-- 配置认证管理器 --> <authentication-manager alias="authenticationManager"> <authentication-provider user-service-ref='userDetailsService'> <!-- 用户加密解密类 --> <password-encoder hash="md5"> <salt-source user-property="username"/> </password-encoder> </authentication-provider> </authentication-manager> <beans:bean id="userDetailsService" class="com.springmvc.security.impl.SpringMvcUserDetailsServiceImpl" /> <!-- PasswordEncoder 密码接口 --> <beans:bean id="passwdEcoder" class="org.springframework.security.authentication.encoding.Md5PasswordEncoder"/> <!-- 元数据提供接口 --> <beans:bean id="springMvcInvocationSecurityMetadataSource" class="com.springmvc.security.impl.SpringMvcInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceImpl" > </beans:bean> <!-- 权限抉择接口 --> <beans:bean id="accessDecisionManager" class="com.springmvc.security.impl.DemoAccessDecisionManager"/> <!-- 自定义过滤器 --> <beans:bean id="securityInterceptorFilter" class="com.springmvc.security.impl.DemoSecurityInterceptor"> <beans:property name="securityMetadataSource" ref="springMvcInvocationSecurityMetadataSource"/><!-- FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource 接口实现类 --> <beans:property name="authenticationManager" ref="authenticationManager"/><!-- 鉴定管理类 --> <beans:property name="accessDecisionManager" ref="accessDecisionManager"/><!-- AccessDecisionManager 接口实现类 --> </beans:bean>四、功能说明
1) springMvcInvocationSecurityMetadataSource
服务器启动时,会将数据库中所有权限和资源提取出来,放在一个map里,等用户登录到该系统时,就会使用到map,从而判断该用户是否有这个权限。
public class SpringMvcInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceImpl implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory .getLogger(SpringMvcInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceImpl.class); private SecurityServiceInf securityService; @Autowired public SpringMvcInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceImpl( SecurityServiceInf securityService) { this.securityService = securityService; initResources(); } // 所有的资源和权限的映射就存在这里 private HashMap<RequestMatcher, Collection<ConfigAttribute>> requestMap = new HashMap<RequestMatcher, Collection<ConfigAttribute>>(); private Collection<ConfigAttribute> allAttribute = new HashSet<ConfigAttribute>(); /** * 初始化所有的资源,这个会在容器运行的时候的构造方法里调用 */ private void initResources() { logger.debug("init SecurityMetadataSource load all resources"); // 读取所有的资源,和资源相关联的的权限 // 读取所有权限点 Collection<AuthorityEntity> allAuthority = securityService .getAllAuthority(); logger.debug("start to convert AUthortiyEntity to SercurityConfig"); for (AuthorityEntity authEntity : allAuthority) { String authString = authEntity.getAuthority(); logger.debug("add authroity named:[" + authString + "]"); SecurityConfig attrConfig = new SecurityConfig(authString); allAttribute.add(attrConfig); } // 读取所有资源 Collection<ResourceEntity> allResources = securityService .findAllResources(); // 循环所有资源 for (ResourceEntity resourceEntiry : allResources) { // 按照资源查询和资源相关的权限点 Collection<AuthorityEntity> authEntities = securityService .getAuthorityByResource(resourceEntiry.getId()); // 把此关系保存到requestMap里 // 获取资源 String resourceContent = resourceEntiry.getResourceContent(); // 把url资源转化为一个spring的工具类,请求匹配器类 logger.debug("add new requestmatcher with [" + resourceContent + "]"); RequestMatcher matcher = new AntPathRequestMatcher(resourceContent); // 循环权限 定义一个权限的集合,和此资源对应起来,添加到HashMap里 Collection<ConfigAttribute> array = new ArrayList<ConfigAttribute>( authEntities.size()); for (AuthorityEntity auth : authEntities) { // 转化权限对象为SecurityConfig SecurityConfig securityConfig = new SecurityConfig( auth.getAuthority()); array.add(securityConfig); } requestMap.put(matcher, array); } } /** * 根据资源获取需要的权限名称 */ @Override public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object) throws IllegalArgumentException { logger.debug("get resource " + object + " authority"); // 把对象转化为请求 final HttpServletRequest request = ((FilterInvocation) object) .getRequest(); // 循环整个Map 看看有没有可以匹配的,如果有匹配的就立刻返回 Collection<ConfigAttribute> attrHashMap = new HashSet<ConfigAttribute>(); for (Map.Entry<RequestMatcher, Collection<ConfigAttribute>> entry : requestMap .entrySet()) { if (entry.getKey().matches(request)) { logger.debug("request matches :" + request.getRequestURL()); attrHashMap.addAll(entry.getValue()); } } if (attrHashMap.size() > 0) { // 如果有匹配的就转成ArrayList,然后返回list Collection<ConfigAttribute> attr = new ArrayList<ConfigAttribute>( attrHashMap); return attr; } logger.debug("request no matches"); return Collections.emptyList(); } /** * 获取所有权限点 */ @Override public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() { return this.allAttribute; } @Override public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return true; }}requestMap里的数据如下:

2) userDetailsService
当用户登录时,会使用输入的用户信息,与数据库中的比较,用户名错误或密码错误,都会有相应的提示(下面会有介绍),都正确的话,会返回一个user实体。
public class SpringMvcUserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsServiceInf { @Autowired private DemoAuthorityRepository authRepository; @Autowired private UserRepository demoUserReposiroty; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { // 读取用户 UsersEntity userEntity = demoUserReposiroty.findByName(username); // 读取权限 Collection<GrantedAuthority> auths = new ArrayList<GrantedAuthority>(); // 这里需要从数据库里读取所有的权限点 Collection<com.springmvc.model.AuthorityEntity> aes = authRepository .getAuthorityByUser(userEntity.getId()); for (AuthorityEntity ae : aes) { auths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(ae.getAuthority())); } User user = new User(userEntity.getUsername(), userEntity.getPassword(), true, true, true, true, auths); return user; }}3) accessDecisionManager
判断当前用户是否拥有访问该资源的权限。
public class DemoAccessDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager { @Override public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException { if (null == configAttributes) { return; } Iterator<ConfigAttribute> cons = configAttributes.iterator(); while (cons.hasNext()) { ConfigAttribute ca = cons.next(); String needRole = ((SecurityConfig) ca).getAttribute(); // gra 为用户所被赋予的权限,needRole为访问相应的资源应具有的权限 for (GrantedAuthority gra : authentication.getAuthorities()) { if (needRole.trim().equals(gra.getAuthority().trim())) { return; } } } throw new AccessDeniedException("没有权限"); } @Override public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return true; } @Override public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return true; }}五、权限控制
1) 登录
若使用security默认的登录页,则登录时的错误提示信息是在spring-security-core包下面的messages.properties等;
但是一般我们使用自己的登录页,上面security.xml已配置了登陆页的路径login.jsp,那么提示信息就得自己配置了,可以自定义message_zh_CN.properties,放在根路径下的message包里,然后这样配置:
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8" /> <property name="basenames"> <list> <value>classpath:message/message</value> </list> </property> </bean>message_zh_CN.properties信息如下:
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials=\u5BC6\u7801\u4E0D\u6B63\u786Esecurity默认提示:坏的凭证,这里是'密码不正确',当然你可以改成任何提示信息;
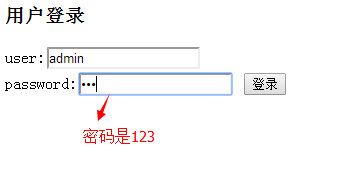
若登录时用户名错误,返回的信息是no entity found....
下面使用错误密码登录,提示信息如下:

比较密文的代码如下:
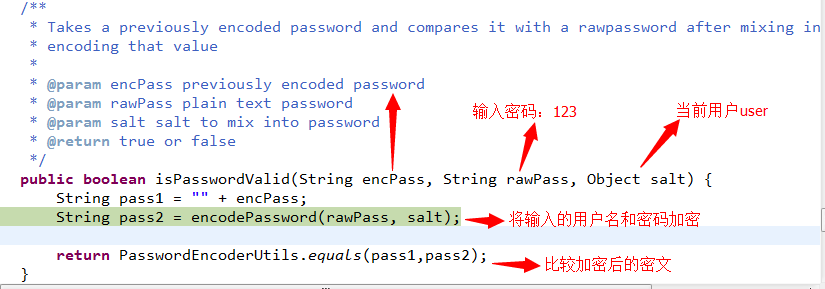
2) 登录成功后,访问资源
i. 使用admin账号登录,然后访问admin.jsp


ii. 使用user账号登录,然后访问admin.jsp


可以看到,user无权访问admin.jsp。
ok,只要权限和资源关系配置好,security会帮我们自动拦截,实现权限控制。
- spring security 转
- Spring Security about DelegatingFilterProxy【转】
- 玩转Spring Boot 使用Spring security
- Spring Security
- Spring Security
- spring security
- spring security
- spring security
- spring security
- spring security
- spring security
- spring security
- spring security
- spring security
- Spring Security
- spring security
- spring-security
- Spring Security
- 多线程编程与同步控制(Java与C)
- 【详解】更新整个maven工程及相关底层并再运行的记录
- asp.net 母版页使用详解
- dos批处理:列出指定目录下所有文件
- Linux环境Tomcat运行报错java.lang.OutOfMemoryError
- spring security 转
- 用于web类库代码的单元测试
- Qt之认识JSON
- 串的模式匹配算法---RK
- 手机页面页脚代码
- [Java]Java工程师成神之路
- CPU affinity
- 有一个本地文件的路径或者文件的名字,计算文件的大小
- iOS---取出字符串中的数字


