hdu 1325 Is It A Tree?【并查集】
来源:互联网 发布:mac笔记本配置交换机 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/03 17:41
Is It A Tree?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 19580 Accepted Submission(s): 4392
Problem Description
A tree is a well-known data structure that is either empty (null, void, nothing) or is a set of one or more nodes connected by directed edges between nodes satisfying the following properties.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.
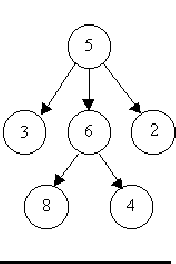
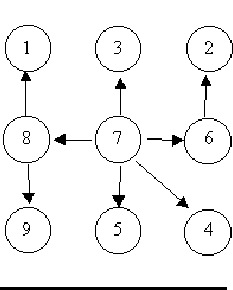
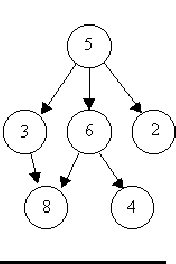
In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.



In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
Input
The input will consist of a sequence of descriptions (test cases) followed by a pair of negative integers. Each test case will consist of a sequence of edge descriptions followed by a pair of zeroes Each edge description will consist of a pair of integers; the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero.
Output
For each test case display the line ``Case k is a tree." or the line ``Case k is not a tree.", where k corresponds to the test case number (they are sequentially numbered starting with 1).
Sample Input
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 45 6 0 08 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 57 4 7 8 7 6 0 03 8 6 8 6 45 3 5 6 5 2 0 0-1 -1
Sample Output
Case 1 is a tree.Case 2 is a tree.Case 3 is not a tree.
图中样例给的树的样例图就是一颗树,不管他是什么树,首先要保证只有一个根节点,也就是说树根只有一个,如果有两个,那就可以叫做森林了、以及,每个点的入度都必须小于等于1,树根的入度是0、另外、树不能成环,保证每一个子节点的父亲只有一个,如果有两个还是不能叫树、了解到这些个内容,我们就可以分块来讨论问题了、
首先是不能自环,自环的条件是什么捏?当我们在找a,b(某两个要连接的点)的祖先的时候,如果他们的祖先相同,说明他们在同一个集合中,如果他们在同一个集合中,并且连接了,那么他们就自环了、
我们这样写就可以了:
if(find(a)==find(b)) ok=1;
然后我们如何判断是否只有一个根呢?
这里代码我提供两种方法,这里直接上完整AC代码一起看~:
#include<stdio.h>//注释掉的地方就是另一种判断是否只有一个根的方法,#include<string.h>using namespace std;int f[1000];//int ff[1000];int vis[1000];int find(int x){ return f[x] == x ? x : (f[x] = find(f[x]));}int main(){ int a,b; int kase=0; while(~scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)) { memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); vis[a]=1; vis[b]=1; for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++) { f[i]=i; // ff[i]=0; } if(a<0&&b<0)break; int ok=0; if(find(a)==find(b)) ok=1; else { f[b]=a; } while(1) { scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); vis[a]=1; vis[b]=1; if(a==0&&b==0)break; else { int aa=find(a); int bb=find(b); if(aa==bb||bb!=b)//如果bb!=b,那么b的入度就大于1了 ok=1; else { f[bb]=f[a]; } } } int cont=0; /* for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++) { if(f[i]==i) continue; else { ff[find(i)]++; } } */ for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++) { if(f[i]==i&&vis[i]==1)//注意这个点一定要出现过才行、 { cont++; } } /* for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++) { if(ff[i]>0) cont++; } */ if(cont>1) { ok=1; } if(ok==1) { printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",++kase); } else { printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",++kase); } }}
0 0
- HDU 1325 Is It A Tree?(并查集)
- hdu 1325 Is It A Tree?(并查集)
- HDU 1325 Is It A Tree? (并查集)
- 【并查集】HDU 1325 Is It A Tree?
- 【并查集】HDU 1325 Is It A Tree?
- HDU 1325 Is It A Tree? 并查集
- hdu 1325 Is It A Tree? 并查集
- HDU 1325 Is It A Tree?(并查集)
- hdu 1325 Is It A Tree?【并查集】
- HDU Problem 1325 Is It A Tree?【并查集】
- 【HDU】-1325-Is It A Tree?(并查集)
- hdu 1325 Is It A Tree?(并查集)
- hdu 1325 Is It A Tree? (并查集)
- hdu 1325 Is It A Tree? (并查集)
- hdu 1325 Is It A Tree? (并查集)
- Is It A Tree? HDU 1325 并查集
- 【并查集】hdu 1325 Is It A Tree? 或 poj 1308 Is It A Tree?
- 【并查集】Is it a tree?
- 获取资源的值
- Oracle学习之常用对象(三)—异常&变量&存储过程
- vim精通
- 常用开发辅助工具推荐
- 设计模式之访问者模式
- hdu 1325 Is It A Tree?【并查集】
- JAVA 冒泡法排序
- 使用python爬取csdn博客访问量
- 【Hibernate系列】(五):关联映射之多对一
- Hdu3231【拓扑排序】
- POJ 3723 Conscription (求最大权森林,kruskal,并查集)
- C#设计模式一句话总结
- 刷题、OJ 1932 母牛的故事
- 请求内容


