最新EventBus源码详解
来源:互联网 发布:龙虎榜数据查询 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 12:05
Eventbus 的模式图:
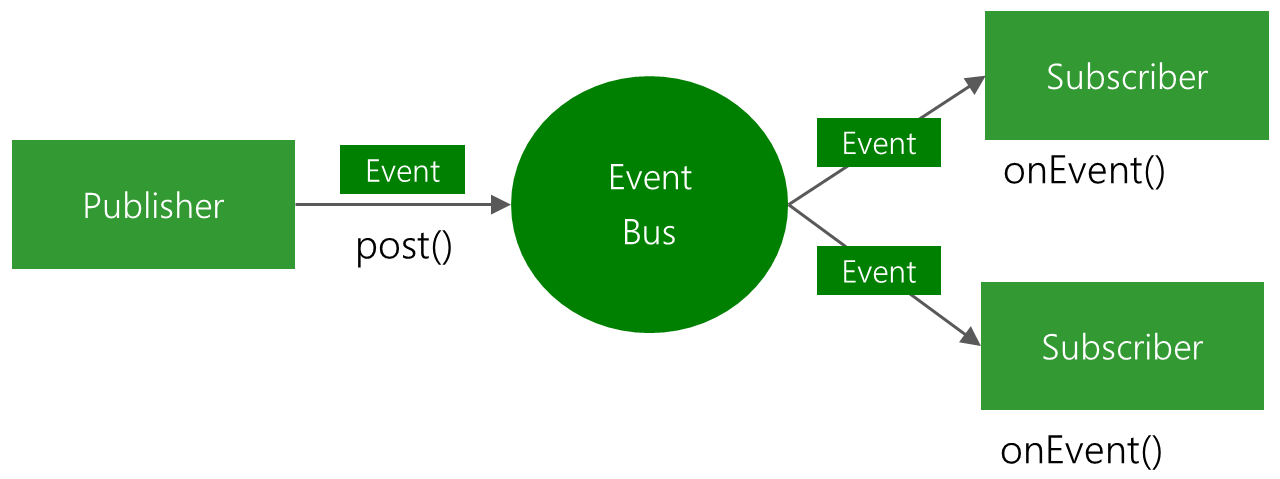
1:getDefault方法,明显看的出来这是单例模式的得到单例对象的方法


/** Convenience singleton for apps using a process-wide EventBus instance. */ public static EventBus getDefault() { if (defaultInstance == null) { synchronized (EventBus.class) { if (defaultInstance == null) { defaultInstance = new EventBus(); } } } return defaultInstance; }2:先来看看register具体实现方法。是的,反射! 对于findSubscriberMethods方法,它里面有一个MethodCache 的HashMap(最新的版本作者改成了ConcurrentHashMap来保证线程安全,)这个HashMap的key是注册类,Value是通过反射得到的Subscribe方法。
private synchronized void register(Object subscriber, boolean sticky, int priority) { List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriber.getClass()); for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) { subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod, sticky, priority); } }3:Subsrcibe 方法:
// 必须在保证线程安全的情况下调用 private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {//得到事件类型,(这个东西就是POST 和 subcribe 想对应的那个类) Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType; Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);//通过Map拿到线程安全的随机访问List CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType); if (subscriptions == null) { subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions); } else { if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) { throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event " + eventType); } }//根据优先级进行插入 int size = subscriptions.size(); for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) { if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) { subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription); break; } }//插入订阅者订阅的消息 List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber); if (subscribedEvents == null) { subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>(); typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents); } subscribedEvents.add(eventType);//拿到SubsriberMethod if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {/*在默认情况下,Subsricb的超类也会被通知,将这个纳入到订阅接受的考虑情况会提高事件的发布效率在这个开关off掉,会提高 20%的事件发布接受效率*/ if (eventInheritance) {/* 这个参数是新版EventBus添加的,这个参数的意义<span style="white-space:pre"></span> 注:因为有很多粘性时间,遍历所有的事件会降低效率 新版的EventBus改变了存储结构 使用了 Class -> List<Class> 的Map结构,*/ Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) { Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey(); if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) { Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue(); checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent); } } } else { Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType); checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent); } } }4:最后看下Post方法:
看一下形式就发现和Handler的实现原理非常类似。Looper,消息队列等等。。
/** Posts the given event to the event bus. */ public void post(Object event) { PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get(); List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue; eventQueue.add(event); if (!postingState.isPosting) { postingState.isMainThread = Looper.getMainLooper() == Looper.myLooper(); postingState.isPosting = true; if (postingState.canceled) { throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset"); } try { while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) { postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState); } } finally { postingState.isPosting = false; postingState.isMainThread = false; } } }最后找到具体实现方法 private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) { switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) { case PostThread: invokeSubscriber(subscription, event); break; case MainThread: if (isMainThread) { invokeSubscriber(subscription, event); } else { mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event); } break; case BackgroundThread: if (isMainThread) { backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event); } else { invokeSubscriber(subscription, event); } break; case Async: asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event); break; default: throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode); } }前面已经说过subscription包含了所有执行需要的东西,大致有:subscriber, subscriberMethod(method, threadMode, eventType), priority;
那么这个方法:第一步根据threadMode去判断应该在哪个线程去执行该方法;
case PostThread。
case MainThread:
首先去判断当前如果是UI线程,则直接调用;否则: mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);把当前的方法加入到队列,然后直接通过handler去发送一个消息,在handler的handleMessage中,去执行我们的方法。说白了就是通过Handler去发送消息,然后执行的。
case BackgroundThread:
如果当前非UI线程,则直接调用;如果是UI线程,则将任务加入到后台的一个队列,最终由Eventbus中的一个线程池去调用
executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();。
case Async:将任务加入到后台的一个队列,最终由Eventbus中的一个线程池去调用;线程池与BackgroundThread用的是同一个。
这么说BackgroundThread和Async有什么区别呢?
BackgroundThread中的任务,一个接着一个去调用,中间使用了一个布尔型变量handlerActive进行的控制。
Async则会动态控制并发。
总结一下:register会把当前类中匹配的方法,通过反射得到存入一个map。Map的键值分别是订阅者和其所有的订阅方法类(这个方法类包含了优先级,执行线程,和EventType等),而post会根据实参去map查找进行反射调用。
0 0
- 最新EventBus源码详解
- EventBus源码详解(一):基本使用
- EventBus源码详解(二):进阶使用
- EventBus详解
- EventBus详解
- EventBus详解
- EventBus详解
- EventBus详解
- EventBus详解
- EventBus详解
- EventBus详解
- Eventbus详解
- EventBus详解
- EventBus 源码解析
- EventBus源码的理解
- EventBus 源码解析
- EventBus 源码解析
- EventBus 源码解析
- LMT LicManager系统对许可证(license)管理创新中的新附加值
- vc字符串特殊字符
- 用javaScript对table的n条记录添加颜色
- LightOJ 1356 Prime Independence(素数筛选法+最大独立集)(Hopcroft-Carp算法)
- iOS程序main函数之前发生了什么
- 最新EventBus源码详解
- 自定义CoordinatorLayout的Behavior(2):实现淘宝和QQ ToolBar透明渐变效果
- Python中列表、元组、占位符的用法
- 一路风景尽收眼底—2015年度总结
- 执行Junit遇到"Launching UTest' has encountered a problem
- 【iOS提高】单例模式在OC的使用
- 线程传参数问题
- Redis配置文件详解
- Git的配置和设置


