状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(下)
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝质检报告申請 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/13 00:32
本文由恋花蝶最初发表于http://blog.csdn.net/lanphaday,欢迎转载,但必须保持全文完整,也必须包含本声明。
译者并示取得中文版的翻译授权,翻译本文只是出于研究和学习目的。任何人不得在未经同意的情况下将英文版和中文版用于商业行为,转载本文产生的法律和道德责任由转载者承担,与译者无关。
State-Driven Game Agent Design
状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(下)
Mat Buckland著
赖勇浩(http://blog.csdn.net/lanphaday) 译
原文地址:http://www.ai-junkie.com/architecture/state_driven/tut_state3.html
(续上篇)
状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(上)http://blog.csdn.net/lanphaday/archive/2007/06/24/1664369.aspx
状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(中)http://blog.csdn.net/lanphaday/archive/2007/06/24/1664369.aspx
――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――
Making the State Base Class Reusable
编写可重用的State基类
As the design stands, it’s necessary to create a separate Statebase class for each character type to derive its states from. Instead, let’s make it reusable by turning it into a class template.
作为立足之本,有必要构造一个独立的State基类,以供每一个角色类类型获得自身的状态。我们可以通过类模板来使得它可重用:
template
class State
{
public:
virtual void Enter(entity_type*)=0;
virtual void Execute(entity_type*)=0;
virtual void Exit(entity_type*)=0;
virtual ~State(){}
};
The declaration for a concrete state — using the EnterMineAndDigForNuggetminer state as an example — now looks like this:
下面是Miner类的EnterMineAndDigForNugget状态:
class EnterMineAndDigForNugget : public State
{
public:
/* OMITTED */
};
This, as you will see shortly, makes life easier in the long run.
如你所见,它短小精悍。
Global States and State Blips
全局状态和状态闪动(诚心求更好的译法)
More often than not, when designing finite state machines you will end up with code that is duplicated in every state. For example, in the popular game The Sims by Maxis, a Sim may feel the urge of nature come upon it and have to visit the bathroom to relieve itself. This urge may occur in any state the Sim may be in and at any time. Given the current design, to bestow the gold miner with this type of behavior, duplicate conditional logic would have to be added to every one of his states, or alternatively, placed into the Miner::Updatefunction. While the latter solution is accept- able, it’s better to create a global statethat is called every time the FSM is updated. That way, all the logic for the FSM is contained within the states and not in the agent class that owns the FSM.
通常当设计有限状态机的时候,你最后都会在所有状态中出现重复代码。例如,在Maxis开发的流行游戏《The Sims(第二人生)》中,Sim可以感受到内急等生理需要,必须去洗手间解决。无论Sim在哪里、在什么时间,内急都可能发生。根据当前的设计,给淘金者加上这样一种行为,重复的条件逻辑就可能增加到每一个状态,或者放到Miner::Update函数里。下面介绍一个可接受的解决方案,它增加了一个全局状态——供FSM更新的时候调用。这样,FSM的所有的逻辑都包含在状态内,而不在智能体类的FSM里。
To implement a global state, an additional member variable is required:
实现全局状态,需要增加一个成员变量:
//notice how now that State is a class template we have to declare the entity type
State* m_pGlobalState;
In addition to global behavior, occasionally it will be convenient for an agent to enter a state with the condition that when the state is exited, the agent returns to its previous state. I call this behavior a state blip. For example, just as in The Sims, you may insist that your agent can visit the bathroom at any time, yet make sure it always returns to its prior state. To give an FSM this type of functionality it must keep a record of the previous state so the state blip can revert to it. This is easy to do as all that is required is another member variable and some additional logic in the Miner::ChangeStatemethod.
有时智能体从一个状态进入另一个状态,当它退出这个状态时需要回到它的前一个状态,我将之称为状态闪动。例如就像《The Sims》中你可能必须让你的智能体能够在任何时间进入洗手间,之后再回到之前的状态。要实现这样的功能,就必须记录前一个状态,以便在状态闪动时返回。这可以容易地通过增加成员变量和对Miner::ChangeState方法增加一些额外逻辑来实现。
[译注:状态闪动这一概念的确比较难以理解。所以我画了下面这一张图来帮助理解]

译注图1状态闪动示意图
By now though, to implement these additions, the Minerclass has acquired two extra member variables and one additional method. It has ended up looking something like this (extraneous detail omitted):
到现在,为了完成这些额外功能,Miner类已经增加了两个成员变量和一个方法。它最后看起来就像这样(忽略无关元素):
class Miner : public BaseGameEntity
{
private:
State* m_pCurrentState;
State* m_pPreviousState;
State* m_pGlobalState;
...
public:
void ChangeState(State* pNewState);
void RevertToPreviousState();
...
};
Hmm, looks like it’s time to tidy up a little.
嗯,的确需要整理一下。
Creating a State Machine Class
创建一个状态机类
The design can be made a lot cleaner by encapsulating all the state related data and methods into a state machine class. This way an agent can own an instance of a state machine and delegate the management of current states, global states, and previous states to it.
把所有的状态有关的数据和方法封装到一个状态机类里有利于精简设计。这使智能体能够拥有一个状态机实例并委派它管理当前状态、全局状态和前一个状态。
With this in mind take a look at the following StateMachineclass template.
现在来看看StateMachine模板类。
template
class StateMachine
{
private:
//a pointer to the agent that owns this instance
entity_type* m_pOwner;
State* m_pCurrentState;
//a record of the last state the agent was in
State* m_pPreviousState;
//this state logic is called every time the FSM is updated
State* m_pGlobalState;
public:
StateMachine(entity_type* owner):m_pOwner(owner),
m_pCurrentState(NULL),
m_pPreviousState(NULL),
m_pGlobalState(NULL)
{}
//use these methods to initialize the FSM
void SetCurrentState(State* s){m_pCurrentState = s;}
void SetGlobalState(State* s) {m_pGlobalState = s;}
void SetPreviousState(State* s){m_pPreviousState = s;}
//call this to update the FSM
void Update()const
{
//if a global state exists, call its execute method
if (m_pGlobalState) m_pGlobalState->Execute(m_pOwner);
//same for the current state
if (m_pCurrentState) m_pCurrentState->Execute(m_pOwner);
}
//change to a new state
void ChangeState(State* pNewState)
{
assert(pNewState &&
": trying to change to a null state");
//keep a record of the previous state
m_pPreviousState = m_pCurrentState;
//call the exit method of the existing state
m_pCurrentState->Exit(m_pOwner);
//change state to the new state
m_pCurrentState = pNewState;
//call the entry method of the new state
m_pCurrentState->Enter(m_pOwner);
}
//change state back to the previous state
void RevertToPreviousState()
{
ChangeState(m_pPreviousState);
}
//accessors
State* CurrentState() const{return m_pCurrentState;}
State* GlobalState() const{return m_pGlobalState;}
State* PreviousState() const{return m_pPreviousState;}
//returns true if the current state’s type is equal to the type of the
//class passed as a parameter.
bool isInState(const State& st)const;
};
Now all an agent has to do is to own an instance of a StateMachineand implement a method to update the state machine to get full FSM functionality.
现在所有的智能体都能够拥有一个StateMachine实例,需要做的就是实现一个方法来更新状态机以获得完整的FSM功能。
本文由恋花蝶最初发表于http://blog.csdn.net/lanphaday,欢迎转载,但必须保持全文完整,也必须包含本声明。
译者并示取得中文版的翻译授权,翻译本文只是出于研究和学习目的。任何人不得在未经同意的情况下将英文版和中文版用于商业行为,转载本文产生的法律和道德责任由转载者承担,与译者无关。
The improved Minerclass now looks like this:
新实现的Miner类看起来就是这样的:
class Miner : public BaseGameEntity
{
private:
//an instance of the state machine class
StateMachine* m_pStateMachine;
/* EXTRANEOUS DETAIL OMITTED */
public:
Miner(int id):m_Location(shack),
m_iGoldCarried(0),
m_iMoneyInBank(0),
m_iThirst(0),
m_iFatigue(0),
BaseGameEntity(id)
{
//set up state machine
m_pStateMachine = new StateMachine(this);
m_pStateMachine->SetCurrentState(GoHomeAndSleepTilRested::Instance());
m_pStateMachine->SetGlobalState(MinerGlobalState::Instance());
}
~Miner(){delete m_pStateMachine;}
void Update()
{
++m_iThirst;
m_pStateMachine->Update();
}
StateMachine* GetFSM()const{return m_pStateMachine;}
/* EXTRANEOUS DETAIL OMITTED */
};
Notice how the current and global states must be set explicitly when a StateMachineis instantiated.The class hierarchy is now like that shown in Figure 2.4.
注意StateMachine实例化后如何正确设计当前和全局状态。图2.4是现在的类层次结构图。

Figure 2.4. The updated design
Introducing Elsa
介绍Elsa
To demonstrate these improvements, I’ve created another project: WestWorldWithWoman. In this project, West World has gained another inhabitant, Elsa, the gold miner’s wife. Elsa doesn’t do much; she’s mainly preoccupied with cleaning the shack and emptying her bladder (she drinks way too much cawfee). The state transition diagram for Elsa is shown in Figure 2.5.
为了验证这些改进,我创建了一个新的项目——WestWorldWithWoman。在这个项目里,WestWorld多了一个人物——Elsa,她是淘金者Bob的妻子。Elsa做的事不多,主要是打扫房子和上洗手间(她喝了太多咖啡)。图2.5是Elsa的状态转换图。
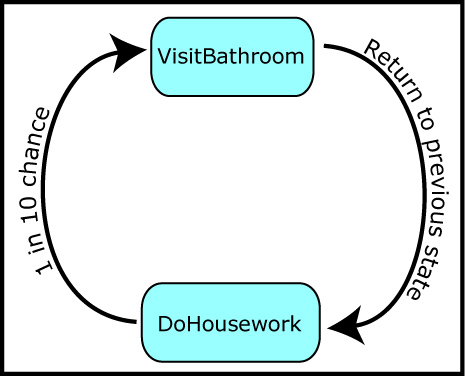
Figure 2.5. Elsa’s state transition diagram. The global state is not shown in the figure because its logic is effectively implemented in any state and never changed.
When you boot up the project into your IDE, notice how the VisitBathroomstate is implemented as a blip state (i.e., it always reverts back to the previous state). Also note that a global state has been defined, WifesGlobalState, which contains the logic required for Elsa’s bathroom visits. This logic is contained in a global state because Elsa may feel the call of nature during any state and at any time.
当你把这个项目导入到你的IDE的时候,注意VisitBathroom状态是如何以状态闪动的形式实现的(也就是它如何返回到前一个状态),同样值得注意的是定义了一个全局状态——WifesGlobalState,它包含了Elsa上洗手间所需的逻辑。在全局状态中包含这一逻辑是因为Elsa可能在任何时候都会感到内急,这是天性,哈哈。
Here is a sample of the output from WestWorldWithWoman.
这里是WestWorldWithWoman项目的输出示例。
Miner Bob: Pickin' up a nugget
Miner Bob: Ah'm leavin' the gold mine with mah pockets full o' sweet gold
Miner Bob: Goin' to the bank. Yes siree
Elsa: Walkin' to the can. Need to powda mah pretty li'l nose
Elsa: Ahhhhhh! Sweet relief!
Elsa: Leavin' the john
Miner Bob: Depositin' gold. Total savings now: 4
Miner Bob: Leavin' the bank
Miner Bob: Walkin' to the gold mine
Elsa: Walkin' to the can. Need to powda mah pretty li'l nose
Elsa: Ahhhhhh! Sweet relief!
Elsa: Leavin' the john
Miner Bob: Pickin' up a nugget
Elsa: Moppin' the floor
Miner Bob: Pickin' up a nugget
Miner Bob: Ah'm leavin' the gold mine with mah pockets full o' sweet gold
Miner Bob: Boy, ah sure is thusty! Walkin' to the saloon
Elsa: Moppin' the floor
Miner Bob: That's mighty fine sippin' liquor
Miner Bob: Leavin' the saloon, feelin' good
Miner Bob: Walkin' to the gold mine
Elsa: Makin' the bed
Miner Bob: Pickin' up a nugget
Miner Bob: Ah'm leavin' the gold mine with mah pockets full o' sweet gold
Miner Bob: Goin' to the bank. Yes siree
Elsa: Walkin' to the can. Need to powda mah pretty li'l nose
Elsa: Ahhhhhh! Sweet relief!
Elsa: Leavin' the john
Miner Bob: Depositin' gold. Total savings now: 5
Miner Bob: Woohoo! Rich enough for now. Back home to mah li'l lady
Miner Bob: Leavin' the bank
Miner Bob: Walkin' home
Elsa: Walkin' to the can. Need to powda mah pretty li'l nose
Elsa: Ahhhhhh! Sweet relief!
Elsa: Leavin' the john
Miner Bob: ZZZZ...
Well, that's it folks. The complexity of the behavior you can create with finite state machines is only limited by your imagination. You don’t have to restrict your game agents to just one finite state machine either. Sometimes it may be a good idea to use two FSMs working in parallel: one to control a character’s movement and one to control the weapon selection, aiming, and firing, for example. It’s even possible to have a state itself contain a state machine. This is known as a hierarchical state machine. For instance, your game agent may have the states Explore, Combat, and Patrol. In turn, the Combat state may own a state machine that manages the states required for combat such as Dodge, ChaseEnemy, and Shoot.
夸张点说,这相当了不起啊。你能够用有限状态机创造非常复杂的行为,到底有多复杂仅受限于你的相像力。你无需限制你的游戏智能体只能有一个有限状态机,有时候你可以使用两个FSM来并行工作:一个控制角色的移动,而另一个控制武器选择、瞄准和开火。你甚至可以创造包含状态机的状态机,即分级状态机。例如你的游戏智能体可能有Explore(探测)、Combat(战斗)和Patrol(逻辑)等状态,而Combat(战斗)状态又可以拥有一个状态机来管理Dodge(躲避)、ChaseEnemy(追逃)和Shoot(射击)等战斗时需要的状态。
本文由恋花蝶最初发表于http://blog.csdn.net/lanphaday,欢迎转载,但必须保持全文完整,也必须包含本声明。
译者并示取得中文版的翻译授权,翻译本文只是出于研究和学习目的。任何人不得在未经同意的情况下将英文版和中文版用于商业行为,转载本文产生的法律和道德责任由转载者承担,与译者无关。
全文完
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(下)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(下)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(下)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(下)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(上)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(上)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(中)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(中)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(中)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(上)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(中)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(上)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(中)
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(上)
- 游戏程序开发:状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(一)
- Yale cas服务器端/客户端环境配置以及其在tomcat服务器下SSL安全协议得部署之完全实现篇
- Mule 1.4对JBPM的集成
- Fedora从2005年到现在的内核缺陷数报表
- Spring2.0和EJB3.0随谈
- VC的预编译机制
- 状态驱动的游戏智能体设计(下)
- 整合Hibernate的EJB架构分析
- 三种快速以太网标准
- Mule - 企业服务总线
- 互联网:从流量经营到服务经营
- 有趣Logo图片: TuxMachines
- “中文问题没商量”之Ant中的中文问题
- vc类与头文件
- 什么是安全套接字层技术


