Greenland'sMeltwater May Fertilize Fjords with Phosphorus
来源:互联网 发布:条形码生成器软件下载 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/06 16:39
Greenland'sMeltwater May Fertilize Fjords with Phosphorus
格陵兰冰川融化
fjords是什么意思

n.峡湾,海岸峡江( fjord的名词复数 )
phosphorus是什么意思
n.[化]磷;磷光体
The massive icesheet topping Greenland is losing nearly 300 billion tons a year to melting, according to NASA estimates. And all that melt water means rising seas. But it's also dumping huge amounts of nutrients and minerals into Arctic waters.

topping是什么意思
n.构成顶部的东西;糕点上的装饰配料
dumping是什么意思
n.倾销
v.倾倒( dump的现在分词 );丢下;随便堆放;释放
glaciers是什么意思
n.冰河,冰川( glacier的名词复数 )
据美国航空航天局估计,格陵兰岛表层的巨大冰层正以每年3000亿的速度消失。冰块融化意味着海平面上升。但同时也会有大量的营养物质和矿物会进入北极海域。
"The great thing about glaciers and ice sheets, is that they're these big, very heavy systems, and as they move over rock they grind and crush the rock up."
move over 移开
crush up
粉碎; 揉成一团; 压碎;
Jon Hawkings, a glacial biogeochemist at the University of Bristol in the U.K.
biogeochemical是什么意思
adj.生物地球化学的
"So they expose【all these reactive kind of trace components of the rock lattice】 to【the fresh melt water that's coming in.】 ”
【 trace components】微量成分
【rock lattice】岩石晶格
冰川和冰层的伟大之处在于体积巨大,质量庞大,并且可以移动岩石将岩石击碎。乔恩·霍金是英国布里斯托尔大学的冰川地质学家。“所以岩石中的丰富的微量成分将进入融化的雪水中。”
That meltwater funnels rock dust into Greenland's glacial rivers, where Hawkings and his colleagues took their samples. They found that Greenland's rivers are much richer in phosphorus than previously believed.

融化的冰水将岩石中的尘土过滤,并最终成为格陵兰的冰川河流,而霍金和同事们就在这里进行取样。他们发现,与之前的猜测相比,格陵兰的河流中磷含量非常丰富。
And they estimate that Greenland's glacial rivers may flush some 400,000 tons of phosphorus into ocean waters every year—that's on par with the amount of phosphorous dumped into the ocean by the Mississippi or Amazon rivers. The findings appear in the journal Global Biogeochemical Cycles.

vt. 使齐平;发红,使发亮;用水冲洗;使激动
- 与…同等水平
对此他们估计格陵兰的冰川河每年会把大约40万吨的磷注入海洋——而这一数量与密西西比河或亚马逊河每年的注入量持平。该研究结果发表在《全球生物地球化学循环 》杂志上。
All that extra phosphorus could be fertilizer for ocean life. "It's an essential nutrient for phytoplankton, who are the guys on the bottom of the food chain. So it's really, really important for life. And life can't exist without it."
“所有这些额外的磷将会成为海洋生物的肥料。浮游植物位于食物链的底层,而磷是其重要的营养元素。所以,这些真的很重要,没有它,生命就无法存活。”

And this process—glaciers grinding rocks, then melting and flushing those nutrients to sea—it’s not the first time it's happened. In fact, the authors speculate that during the last extreme ice age—the so-called "snowball Earth,
" some 700 million years ago—all this phosphorus runoff may have caused a bloom in ocean life. A bloom that may have ultimately oxygenated the planet...and paved the way for organisms like us.
runoff是什么意思
n.决胜投票;附加赛;径流
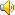

v. 使氧合(oxygenate的过去分词);充氧
冰川研磨岩石这一过程,就会将这些营养物质融化并冲入大海——而这样的事情并不罕见。实际上,作者估计,在过去极端冰河时代——关于7亿年前雪球假说——这些磷径流可能导致海洋生命茂盛。生命旺盛最终导致地球上有氧生物的出现,就为我们人类的产生奠定了基础。
听力原文:
Greenland's Meltwater May Fertilize Fjords with Phosphorus
The massive ice sheet topping Greenland is losing nearly 300 billiontons a year to melting, according to NASA estimates. And all that meltwatermeans rising seas. But it's also dumping huge amounts of nutrients and mineralsinto Arctic waters.
"The great thing about glaciers and ice sheets, is that they'rethese big, very heavy systems, and as they move over rock they grind and crushthe rock up." Jon Hawkings, a glacial biogeochemist at the University ofBristol in the U.K. "So they expose all these reactive kind of tracecomponents of the rock lattice to the fresh meltwater that's coming in.”
That meltwater funnels rock dust into Greenland's glacial rivers,where Hawkings and his colleagues took their samples. They found thatGreenland's rivers are much richer in phosphorus than previously believed. Andthey estimate that Greenland's glacial rivers may flush some 400,000 tons ofphosphorus into ocean waters every year—that’s on par with the amount ofphosphorous dumped into the ocean by the Mississippi or Amazon rivers. Thefindings appear in the journal Global Biogeochemical Cycles.
All that extra phosphorus could be fertilizer for ocean life."It's an essential nutrient for phytoplankton, who are the guys on thebottom of the food chain. So it's really, really important for life. And lifecan't exist without it." And this process—glaciers grinding rocks, thenmelting and flushing those nutrients to sea—it’s not the first time it'shappened. In fact, the authors speculate that during the last extreme iceage—the so-called "snowball Earth," some 700 million years ago—allthis phosphorus runoff may have caused a bloom in ocean life. A bloom that mayhave ultimately oxygenated the planet...and paved the way for organisms likeus.
- Greenland'sMeltwater May Fertilize Fjords with Phosphorus
- 甘思咪哚,肉骨茶,Greenland
- Kerberos authentication may problem with IIS
- May~~~
- May
- ieltsListen was compiled with optimization - stepping may behave oddly; variables may not be availab
- was compiled with optimization - stepping may behave oddly; variables may not be available.
- iOS xcode ‘XXXX’ was compiled with optimization - stepping may behave oddly; variables may not be av
- [app-name] was compiled with optimization - stepping may behave oddly; variables may not be availabl
- ‘XXXX’ was compiled with optimization - stepping may behave oddly; variables may not be available
- xcode 项目 was compiled with optimization -stepping may behave oddly ;variable may not be available
- Unsafe code may only appear if compiling with /unsafe
- Unsafe code may only appear if compiling with /unsafe
- Unsafe code may only appear if compiling with /unsafe
- Unsafe code may only appear if compiling with /unsafe
- Unsafe code may only appear if compiling with /unsafe
- Only no-arg methods may be annotated with @Scheduled
- cron:Only void-returning methods may be annotated with @Scheduled
- Aliyun linux5.7 64位 安装 jdk1.7
- Centos6.5安装Nginx的教程 先安装nginx依赖的库pcre
- httpd+nfs 简单的文件系统共享
- python的time和datetime模块 之 时间形式互转
- servlet 一个simple web project
- Greenland'sMeltwater May Fertilize Fjords with Phosphorus
- aoj2249(最短路)
- node 学习的一些资料收集
- 重构--第一个案例
- 朴素贝叶斯
- 你所不知道的黑客工具之 EK 篇
- 深入理解Android的startservice和bindservice
- spring中使用Quartz任务调度框架
- SharePoint2013 IT Professional - Version Setting


