肤色检测合集
来源:互联网 发布:韩语键盘软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/28 21:05
1 HSV 颜色空间
from: http://blog.csdn.net/onezeros/article/details/5930520
把rgb转换到hsv空间,用h分量 进行识别,像素值在7~29之间 是肤色的几乎全部范围
识别会受到光照的影响。但是整体上准确度是较高的。
在白天 正常的明亮的光照下,效果非常好。
这是我在晚上拍摄的一张图像的处理
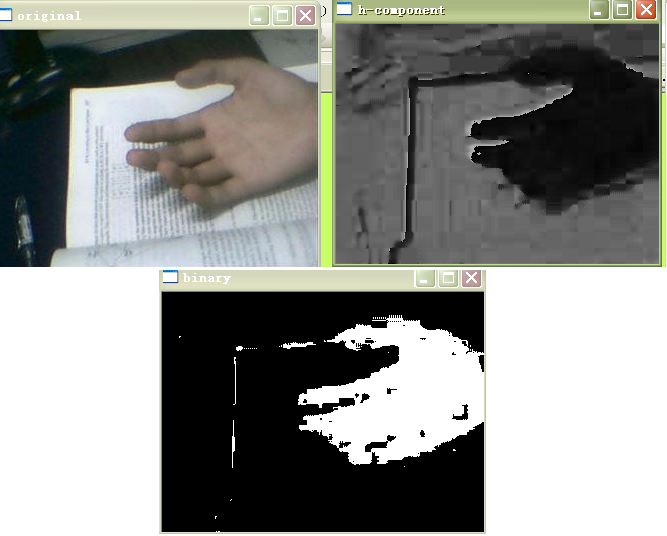
对于不同的环境(主要是光照条件),阈值应相应 变动以提高精确度
程序源码下载 http://download.csdn.net/source/2744062
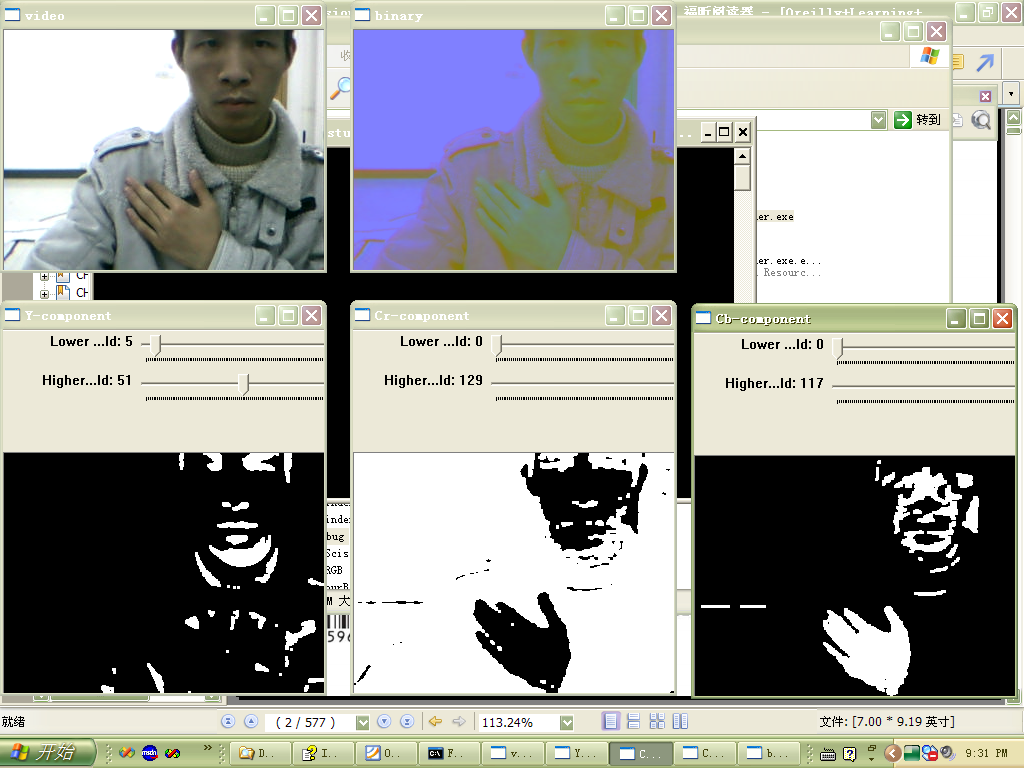
2 YCrCb
源码下下载 http://download.csdn.net/source/2873223
效果图
3 3种模型
今天是地球日,就选了张相关主题的图像做测试
第一种:RGB color space
第二种:RG color space
第三种:Ycrcb之cr分量+otsu阈值化
还有别的一些模型,效果不太好就不贴了
1.rgb model
- // skin region location using rgb limitation
- void SkinRGB(IplImage* rgb,IplImage* _dst)
- {
- assert(rgb->nChannels==3&& _dst->nChannels==3);
- static const int R=2;
- static const int G=1;
- static const int B=0;
- IplImage* dst=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(_dst),8,3);
- cvZero(dst);
- for (int h=0;h<rgb->height;h++) {
- unsigned char* prgb=(unsigned char*)rgb->imageData+h*rgb->widthStep;
- unsigned char* pdst=(unsigned char*)dst->imageData+h*dst->widthStep;
- for (int w=0;w<rgb->width;w++) {
- if ((prgb[R]>95 && prgb[G]>40 && prgb[B]>20 &&
- prgb[R]-prgb[B]>15 && prgb[R]-prgb[G]>15/*&&
- !(prgb[R]>170&&prgb[G]>170&&prgb[B]>170)*/)||//uniform illumination
- (prgb[R]>200 && prgb[G]>210 && prgb[B]>170 &&
- abs(prgb[R]-prgb[B])<=15 && prgb[R]>prgb[B]&& prgb[G]>prgb[B])//lateral illumination
- ) {
- memcpy(pdst,prgb,3);
- }
- prgb+=3;
- pdst+=3;
- }
- }
- cvCopyImage(dst,_dst);
- cvReleaseImage(&dst);
- }
2.rg model
- // skin detection in rg space
- void cvSkinRG(IplImage* rgb,IplImage* gray)
- {
- assert(rgb->nChannels==3&&gray->nChannels==1);
- const int R=2;
- const int G=1;
- const int B=0;
- double Aup=-1.8423;
- double Bup=1.5294;
- double Cup=0.0422;
- double Adown=-0.7279;
- double Bdown=0.6066;
- double Cdown=0.1766;
- for (int h=0;h<rgb->height;h++) {
- unsigned char* pGray=(unsigned char*)gray->imageData+h*gray->widthStep;
- unsigned char* pRGB=(unsigned char* )rgb->imageData+h*rgb->widthStep;
- for (int w=0;w<rgb->width;w++) {
- int s=pRGB[R]+pRGB[G]+pRGB[B];
- double r=(double)pRGB[R]/s;
- double g=(double)pRGB[G]/s;
- double Gup=Aup*r*r+Bup*r+Cup;
- double Gdown=Adown*r*r+Bdown*r+Cdown;
- double Wr=(r-0.33)*(r-0.33)+(g-0.33)*(g-0.33);
- if (g<Gup && g>Gdown && Wr>0.004){
- *pGray=255;
- }else{
- *pGray=0;
- }
- pGray++;
- pRGB+=3;
- }
- }
- }
3.cr+otsu
- // implementation of otsu algorithm
- // author: onezeros#yahoo.cn
- // reference: Rafael C. Gonzalez. Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB
- void cvThresholdOtsu(IplImage* src, IplImage* dst)
- {
- int height=src->height;
- int width=src->width;
- //histogram
- float histogram[256]={0};
- for(int i=0;i<height;i++) {
- unsigned char* p=(unsigned char*)src->imageData+src->widthStep*i;
- for(int j=0;j<width;j++) {
- histogram[*p++]++;
- }
- }
- //normalize histogram
- int size=height*width;
- for(int i=0;i<256;i++) {
- histogram[i]=histogram[i]/size;
- }
- //average pixel value
- float avgValue=0;
- for(int i=0;i<256;i++) {
- avgValue+=i*histogram[i];
- }
- int threshold;
- float maxVariance=0;
- float w=0,u=0;
- for(int i=0;i<256;i++) {
- w+=histogram[i];
- u+=i*histogram[i];
- float t=avgValue*w-u;
- float variance=t*t/(w*(1-w));
- if(variance>maxVariance) {
- maxVariance=variance;
- threshold=i;
- }
- }
- cvThreshold(src,dst,threshold,255,CV_THRESH_BINARY);
- }
- void cvSkinOtsu(IplImage* src, IplImage* dst)
- {
- assert(dst->nChannels==1&& src->nChannels==3);
- IplImage* ycrcb=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(src),8,3);
- IplImage* cr=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(src),8,1);
- cvCvtColor(src,ycrcb,CV_BGR2YCrCb);
- cvSplit(ycrcb,0,cr,0,0);
- cvThresholdOtsu(cr,cr);
- cvCopyImage(cr,dst);
- cvReleaseImage(&cr);
- cvReleaseImage(&ycrcb);
- }
原图像

rgb model

rg model

otsu+cr
4 RGB YCrCb
本文涉及的很多算法,在网络上也有不少同类型的文章,但是肯定的一点就是,很多都是不配代码的,或者所附带的代码都是象征性的,速度慢,不优雅,不具有实用价值,本文努力解决这些问题。
文中各算法出现的顺序并不代表算法的优越性,仅仅是作者随机排布的而已。
2、基于RGB颜色空间的简单阈值肤色识别
在human skin color clustering for face detection一文中提出如下简单的判别算式:
R>95 And G>40 And B>20 And R>G And R>B And Max(R,G,B)-Min(R,G,B)>15 And Abs(R-G)>15
算法非常之简单,同样主要把复杂的判断条件放到后面去判断,能有效的降低程序的执行时间,参考代码:
for (Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++){ Pointer = Scan0 + Y * Stride; SkinP = SkinScan0 + Y * SkinStride; for (X = 0; X < Width; X++) { Blue = *Pointer; Green = *(Pointer + 1); Red = *(Pointer + 2); if (Red > 95 && Green > 40 && Blue > 20 && Red > Blue && Red > Green && Math.Abs(Red - Green) > 15) { if (Blue >= Green) { Max = Blue; Min = Green; } else { Max = Green; Min = Blue; } if (Red > Max) Max = Red; else if (Red < Min) Min = Red; if (Max - Min > 15) *SkinP = 255; } Pointer += 3; SkinP++; }
算法效果:






原图 识别结果图 原图 识别结果图
由上述结果似乎该算法得到了过多的皮肤区域,然后就是算法更喜欢美女一些(^_^)。
3、基于YCbCr颜色空间的简单阈值肤色识别
该算法则更为简单,将图像转换到YCbCr颜色空间,然后按下述计算式判断是否属于皮肤区域:
(Cb > 77 And Cb < 127) And (Cr > 133 And Cr < 173)
关于RGB和YCbCr颜色空间的转换的优化算法,可参考本博客相关文章。
由于当初写这方面的时候没有注明该算法的出处,现在也没从提起了。
代码参考:
for (Y = 0; Y < Height; Y++){ Pointer = Scan0 + Y * Stride; SkinP = SkinScan0 + Y * SkinStride; for (X = 0; X < Width; X++) { Blue = *Pointer; Green = *(Pointer + 1); Red = *(Pointer + 2); Cb = (-176933 * Red - 347355 * Green + 524288 * Blue + 134217728) >> 20; if (Cb > 77 && Cb < 127) { Cr = (524288 * Red - 439026 * Green - 85262 * Blue + 134217728) >> 20; if (Cr > 133 && Cr < 173) *SkinP = 255; } Pointer += 3; SkinP++; }}






原图 识别结果图 原图 识别结果图
误判的区域还是很大的。
还有一种是基于YUV颜色空间进行的肤色识别,似乎也不太准确,可参考http://www.doc88.com/p-97381067005.html。
- 肤色检测合集
- 肤色检测
- 肤色检测
- 肤色检测
- 肤色检测
- 肤色检测
- 肤色检测和人脸检测数据集等链接
- 肤色检测 - OpenCV2.0
- 肤色图像检测
- 肤色检测opencv
- OpenCV肤色检测
- matlab-肤色检测
- OpenCV中的肤色检测
- OpenCV编程->肤色检测
- java 肤色检测
- OpenCV肤色检测
- 利用OpenCV检测肤色
- 肤色检测代码示例
- 使用jQuery制作记住姓名
- Android 开发应该注意的编程规范
- 15个你可能不知道的Axure使用技巧
- C++实验4-穷举法解决组合问题
- MyBatis 中XML映射配置文件
- 肤色检测合集
- (案例2)副本集+分片部署
- Unity3D 物体移动方式总结
- Nginx源代码目录结构
- Redis的三种启动方式
- OC 自定义Cordova插件流程
- POJ 2184 Cow Exhibition
- C# Convert.ToInt32()与int.Parse()的区别
- 属性的set get willSet didSet ?!可空属性







