torch学习
来源:互联网 发布:数据黑产吧 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/22 17:34
torch是一个基于LuaJIT的科学计算框架。
详情见 http://torch.ch/
安装torch
参考http://torch.ch/docs/getting-started.html
在terminal中输入以下命令即可:
git clone https://github.com/torch/distro.git ~/torch --recursivecd ~/torch; bash install-deps;./install.sh其中install-deps用于安装LuaJIT和Torch所需的依赖包,而install.sh用于安装LuaJIT和LuaRocks并用LuaRocks安装torch。
运行torch
在terminal中输入th即可。
运行文件输入dofile "file.lua"即可。
在terminal中运行lua文件则输入
th file.lua使用torch例子
网站提供很多相关例子在Cheatsheet中:https://github.com/torch/torch7/wiki/Cheatsheet
下面是一个使用导数和梯度下降求二次函数最小值的例子,参考http://torch.ch/docs/five-simple-examples.html
定义一个正定二次型
require 'torch'torch.manualSeed(1234)N = 5-- 创建一个随机的N x N矩阵AA = torch.rand(N, N)-- 把A变成对称A = A*A:t()-- 把A变成正定A:add(0.001, torch.eye(N))-- 创建一个随机向量bb = torch.rand(N)-- 创建一个二次型函数function J(x) return 0.5*x:dot(A*x)-b:dot(x)end-- 输出某一随机点的函数值print(J(torch.rand(N)))输出该二次型函数的最小值
显然该二次型函数在
xs = torch.inverse(A)*bprint(string.format('J(x^*) = %g', J(xs)))样例输出:
J(x^*) = -3.13684使用梯度下降来求最小值
-- J(x)的梯度function dJ(x) return A*x-bendx = torch.rand(N)lr = 0.01for i=1,20000 do x = x - dJ(x)*lr -- 输出每次迭代的目标函数值 print(string.format('at iter %d J(x) = %f', i, J(x)))end样例输出:
...at iter 19995 J(x) = -3.135664at iter 19996 J(x) = -3.135664at iter 19997 J(x) = -3.135665at iter 19998 J(x) = -3.135665at iter 19999 J(x) = -3.135665at iter 20000 J(x) = -3.135666使用optim包
默认已经安装了optim包,如果没安装,可以使用luarocks install optim安装。
do local neval = 0 function JdJ(x) local Jx = J(x) neval = neval + 1 print(string.format('after %d evaluations J(x) = %f', neval, Jx)) return Jx, dJ(x) endendrequire 'optim'state = { verbose = true, maxIter = 100}x = torch.rand(N)optim.cg(JdJ, x, state)样例输出:
...after 120 evaluation J(x) = -3.136835after 121 evaluation J(x) = -3.136836after 122 evaluation J(x) = -3.136837after 123 evaluation J(x) = -3.136838after 124 evaluation J(x) = -3.136840after 125 evaluation J(x) = -3.136838可视化图表
可视化图表需要使用gnuplot包,同理默认已安装。可使用luarocks install gnuplot安装。
evaluations = {}time = {}timer = torch.Timer()neval = 0function JdJ(x) local Jx = J(x) neval = neval + 1 print(string.format('after %d evaluations, J(x) = %f', neval, Jx)) table.insert(evaluations, Jx) table.insert(time, timer:time().real) return Jx, dJ(x)end-- 使用梯度下降求最小值state = { verbose = true, maxIter = 100}x0 = torch.rand(N)cgx = x0:clone()timer:reset()optim.cg(JdJ, cgx, state)-- 保存时间和值cgtime = torch.Tensor(time)cgevaluations = torch.Tensor(evaluations)-- 使用随机梯度下降求最小值evaluations = {}time = {}neval = 0state = { lr = 0.1}-- 使用同样的初始值x = x0:clone()timer:reset()for i=1,1000 do optim.sgd(JdJ, x, state) table.insert(evaluations, Jx)endsgdtime = torch.Tensor(time)sgdevaluations = torch.Tensor(evaluations)-- 输出可视化图表到plot.pngrequire 'gnuplot'gnuplot.pngfigure('plot.png')gnuplot.plot( {'CG', cgtime, cgevaluations, '-'}, {'SGD', sgdtime, sgdevaluations, '-'})gnuplot.xlabel('time (s)')gnuplot.ylabel('J(x)')gnuplot.plotflush()输出图像大致如下
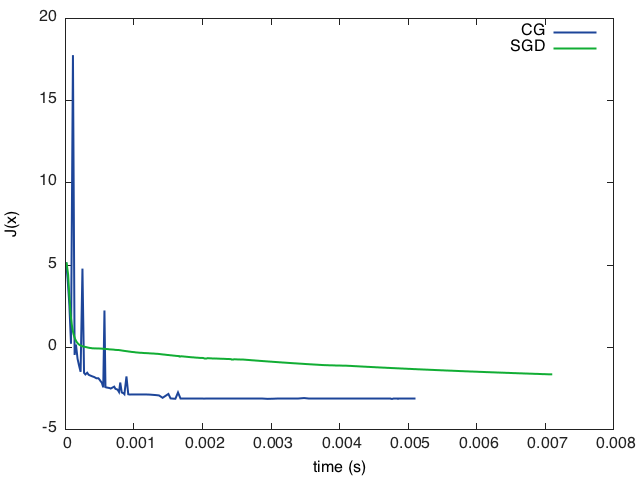
0 0
- torch学习
- torch学习(一) torch使用
- torch学习笔记
- torch学习笔记
- torch学习资料
- Torch深度学习入门
- Torch学习(二)
- torch学习笔记<一>
- Torch学习笔记
- Torch学习笔记
- Torch学习笔记
- Torch学习笔记
- Torch学习笔记
- torch学习资料整理
- Torch深度学习入门
- torch深度学习教程
- torch:LUA编程学习
- Torch学习资料
- 为Qtcreator 编译的程序添加管理员权限
- 第十四周项目—阅读并运行程序,解释程序执行得到的结果(2)
- 自定义之类微信底部渐变栏
- php编程安全指南
- 20位活跃在Github上的国内技术大牛
- torch学习
- Android Studio 混淆代码
- Apache服务器最新版下载、安装及配置(win版
- Android调用系统分享直接抵达微信
- 杂的文
- Codeforces Round #352 (Div. 2) A.Summer Camp
- 安装win7、windows server 2012 出现无法配置在此计算机硬件上运行 解决方案
- 初学java反射机制
- 使用logstash+elasticsearch+kibana快速搭建日志平台


