HDU 1710 已知前序中序须求后序。
来源:互联网 发布:怎么做淘宝网页设计 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/19 04:04
Binary Tree Traversals
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 5335 Accepted Submission(s): 2470
Problem Description
A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
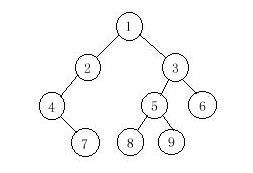
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.

Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating the preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
Output
For each test case print a single line specifying the corresponding postorder sequence.
Sample Input
91 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 64 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
Sample Output
7 4 2 8 9 5 6 3 1
Source
HDU 2007-Spring Programming Contest
Recommend
lcy | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 1708 1707 1709 1512 1251
后序是左右根。
#include <iostream>#include <cmath>#include <algorithm>#include <cstdio>using namespace std;int a[1005];int b[1005];void printf(int begin,int end,int mid){ int i; if(begin>end) return; for(i=begin; i<=end; i++) if(b[i]==a[mid]) break; printf(begin,i-1,mid+1); //中序,先左,后跟,再右。此时i为跟节点,左子树必定在begin到i-1里面。 mid+1是因为前序的左子树为mid+1,此时作为根, printf(i+1,end,mid-begin+i+1);//中序,先左,后跟,再右。此时i为跟节点,右子树必定在i+1到end里面。 同理 cout<<a[mid]; if(mid==1) cout<<endl; else cout<<" ";}int main(){ int n; while(cin>>n) { int i; for(i=1; i<=n; i++) cin>>a[i]; for(i=1; i<=n; i++) cin>>b[i]; printf(1,n,1); } return 0;} 0 0
- HDU 1710 已知前序中序须求后序。
- hdu 1710已知先序中序求后续
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(已知先序中序求后序)
- 已知树的前序和中序求后序 hdu 题目1710 Binary Tree Traversals
- HDU 1710 二叉树的遍历(已知前序和中序求后序)
- hdu 3174 logo (已知角度求点)
- hdu--2504 a,b,c (a,c)=b,已知a,b求c
- HDU 4700 flow Gomory–Hu tree,通过已知最大流构造图形
- 二叉树之已知前序和中序遍历求后序遍历(POJ &&HDU )
- HDU 1102 Constructing Roads [已知路径修好求最小生成树]
- HDU-1698-Just a Hook (区间修改【已知修改后的值】)
- 已知问题
- 已知问题
- 已知先序中序求后序
- 已知中序前序求后序
- 已知前序中序求后序
- 已知中序后序求前序
- 已知前序中序求后序
- Spring BeanFactory
- RabbitMQ理解
- uubntu14.04安装搜狗输入法个人总结
- 摄像机标定示例 First calibration example - Corner extraction, calibration, additional tools
- STL学习笔记--3、迭代器iterator与traits编程
- HDU 1710 已知前序中序须求后序。
- c语言中的read和write函数
- ubuntu 14.04 adb 配置及使用
- zentaophp框架的打印输出
- JS闭包
- INRIA目标检测和定位工具包 INRIA Object Detection and Localization Toolkit
- POJ 2818 Building Block (并查集)(寻找一个元素下面有多少个元素)
- SICP PolySystem
- 为什么叫感知机


