LeNet、AlexNet、VGG、ZF
来源:互联网 发布:北京java周末班 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/07 20:59
LeNet5
LeNet模型理解
CIFAR10
CIFAR10模型理解简述
AlexNet
Caffe深度学习之图像分类模型AlexNet解读
在imagenet上的图像分类challenge上Alex提出的alexnet网络结构模型赢得了2012届的冠军。要研究CNN类型DL网络模型在图像分类上的应用,就逃不开研究alexnet,这是CNN在图像分类上的经典模型(DL火起来之后)。
在DL开源实现caffe的model样例中,它也给出了alexnet的复现,具体网络配置文件如下 train_val.prototxt
接下来本文将一步步对该网络配置结构中各个层进行详细的解读(训练阶段):
各种layer的operation更多解释可以参考 Caffe Layer Catalogue
从计算该模型的数据流过程中,该模型参数大概5kw+。
- conv1阶段DFD(data flow diagram):

- conv2阶段DFD(data flow diagram):
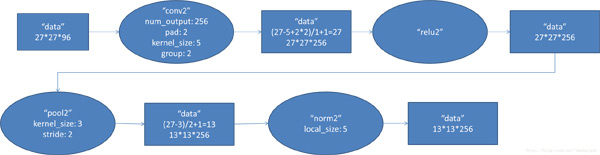
- conv3阶段DFD(data flow diagram):

- conv4阶段DFD(data flow diagram):

- conv5阶段DFD(data flow diagram):

- fc6阶段DFD(data flow diagram):

- fc7阶段DFD(data flow diagram):

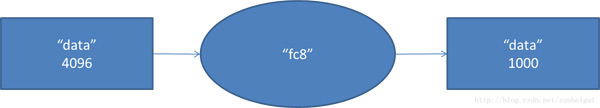
- fc8阶段DFD(data flow diagram):
AlexNet 之结构篇
AlexNet 之算法篇
AlexNet&Imagenet学习笔记
CVPR 2015 之深度学习篇 Part 1 - AlexNet 和 VGG-Net
Alex / OverFeat / VGG 中的卷积参数
import input_datamnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/tmp/data/", one_hot=True)import tensorflow as tf# 定义网络超参数learning_rate = 0.001training_iters = 200000batch_size = 64display_step = 20# 定义网络参数n_input = 784 # 输入的维度n_classes = 10 # 标签的维度dropout = 0.8 # Dropout 的概率# 占位符输入x = tf.placeholder(tf.types.float32, [None, n_input])y = tf.placeholder(tf.types.float32, [None, n_classes])keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.types.float32)# 卷积操作def conv2d(name, l_input, w, b): return tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(l_input, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'),b), name=name)# 最大下采样操作def max_pool(name, l_input, k): return tf.nn.max_pool(l_input, ksize=[1, k, k, 1], strides=[1, k, k, 1], padding='SAME', name=name)# 归一化操作def norm(name, l_input, lsize=4): return tf.nn.lrn(l_input, lsize, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name=name)# 定义整个网络 def alex_net(_X, _weights, _biases, _dropout): # 向量转为矩阵 _X = tf.reshape(_X, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1]) # 卷积层 conv1 = conv2d('conv1', _X, _weights['wc1'], _biases['bc1']) # 下采样层 pool1 = max_pool('pool1', conv1, k=2) # 归一化层 norm1 = norm('norm1', pool1, lsize=4) # Dropout norm1 = tf.nn.dropout(norm1, _dropout) # 卷积 conv2 = conv2d('conv2', norm1, _weights['wc2'], _biases['bc2']) # 下采样 pool2 = max_pool('pool2', conv2, k=2) # 归一化 norm2 = norm('norm2', pool2, lsize=4) # Dropout norm2 = tf.nn.dropout(norm2, _dropout) # 卷积 conv3 = conv2d('conv3', norm2, _weights['wc3'], _biases['bc3']) # 下采样 pool3 = max_pool('pool3', conv3, k=2) # 归一化 norm3 = norm('norm3', pool3, lsize=4) # Dropout norm3 = tf.nn.dropout(norm3, _dropout) # 全连接层,先把特征图转为向量 dense1 = tf.reshape(norm3, [-1, _weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]]) dense1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(dense1, _weights['wd1']) + _biases['bd1'], name='fc1') # 全连接层 dense2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(dense1, _weights['wd2']) + _biases['bd2'], name='fc2') # Relu activation # 网络输出层 out = tf.matmul(dense2, _weights['out']) + _biases['out'] return out# 存储所有的网络参数weights = { 'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 1, 64])), 'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 64, 128])), 'wc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 128, 256])), 'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4*4*256, 1024])), 'wd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, 1024])), 'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024, 10]))}biases = { 'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64])), 'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([128])), 'bc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256])), 'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024])), 'bd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024])), 'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))}# 构建模型pred = alex_net(x, weights, biases, keep_prob)# 定义损失函数和学习步骤cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred, y))optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)# 测试网络correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1), tf.argmax(y,1))accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))# 初始化所有的共享变量init = tf.initialize_all_variables()# 开启一个训练with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) step = 1 # Keep training until reach max iterations while step * batch_size < training_iters: batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) # 获取批数据 sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keep_prob: dropout}) if step % display_step == 0: # 计算精度 acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keep_prob: 1.}) # 计算损失值 loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keep_prob: 1.}) print "Iter " + str(step*batch_size) + ", Minibatch Loss= " + "{:.6f}".format(loss) + ", Training Accuracy= " + "{:.5f}".format(acc) step += 1 print "Optimization Finished!" # 计算测试精度 print "Testing Accuracy:", sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images[:256], y: mnist.test.labels[:256], keep_prob: 1.})VGG
Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition
Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition
Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition(VGG模型)
VGG-16 prototxt
网络结构
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-import chainerfrom chainer import Variableimport chainer.links as Limport chainer.functions as Fclass VGGNet(chainer.Chain): """ VGGNet - It takes (224, 224, 3) sized image as imput """ def __init__(self): super(VGGNet, self).__init__( conv1_1=L.Convolution2D(3, 64, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv1_2=L.Convolution2D(64, 64, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv2_1=L.Convolution2D(64, 128, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv2_2=L.Convolution2D(128, 128, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv3_1=L.Convolution2D(128, 256, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv3_2=L.Convolution2D(256, 256, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv3_3=L.Convolution2D(256, 256, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv4_1=L.Convolution2D(256, 512, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv4_2=L.Convolution2D(512, 512, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv4_3=L.Convolution2D(512, 512, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv5_1=L.Convolution2D(512, 512, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv5_2=L.Convolution2D(512, 512, 3, stride=1, pad=1), conv5_3=L.Convolution2D(512, 512, 3, stride=1, pad=1), fc6=L.Linear(25088, 4096), fc7=L.Linear(4096, 4096), fc8=L.Linear(4096, 1000) ) self.train = False def __call__(self, x, t): h = F.relu(self.conv1_1(x)) h = F.relu(self.conv1_2(h)) h = F.max_pooling_2d(h, 2, stride=2) h = F.relu(self.conv2_1(h)) h = F.relu(self.conv2_2(h)) h = F.max_pooling_2d(h, 2, stride=2) h = F.relu(self.conv3_1(h)) h = F.relu(self.conv3_2(h)) h = F.relu(self.conv3_3(h)) h = F.max_pooling_2d(h, 2, stride=2) h = F.relu(self.conv4_1(h)) h = F.relu(self.conv4_2(h)) h = F.relu(self.conv4_3(h)) h = F.max_pooling_2d(h, 2, stride=2) h = F.relu(self.conv5_1(h)) h = F.relu(self.conv5_2(h)) h = F.relu(self.conv5_3(h)) h = F.max_pooling_2d(h, 2, stride=2) h = F.dropout(F.relu(self.fc6(h)), train=self.train, ratio=0.5) h = F.dropout(F.relu(self.fc7(h)), train=self.train, ratio=0.5) h = self.fc8(h) if self.train: self.loss = F.softmax_cross_entropy(h, t) self.acc = F.accuracy(h, t) return self.loss else: self.pred = F.softmax(h) return self.pred
深度学习常用的Data Set数据集和CNN Model总结
zf net
ZF-net
- LeNet、AlexNet、VGG、ZF
- LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- Lenet、Alexnet 、VGG、 GoogleNet、ResNet模型
- #Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNetInception-ResNet-v2、FractalNet、DenseNet
- Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- CNN五大经典模型:Lenet,Alexnet,Googlenet,VGG,DRL
- 深度学习网络Lenet Alexnet VGG GoogleNet 总结笔记
- #Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- #Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- Deep Learning回顾之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- #Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- #Deep Learning回顾#之LeNet、AlexNet、GoogLeNet、VGG、ResNet
- 卷积神经网络CNN经典模型整理Lenet,Alexnet,Googlenet,VGG,Deep Residual Learning
- pascal下载安装包的请求
- springmvc+mybatis+maven+junit实现网页的增删查改
- spark(RDD之间的基本转换)
- 深入浅出UML类图
- php的tingkphp框架下的前后交互过程
- LeNet、AlexNet、VGG、ZF
- NSNotificationCenter 通知中心
- 动态获取程序的版本名称的方法以及dialog的简单用法以及两种上下文的区别
- 机器学习深度学习开源框架
- C++作业7
- hadoop namenode -format之后datanode无法启动问题
- 深入理解Linux内核 chap 3 进程
- 遗传算法入门到掌握(二)
- 一致性 hash 算法( consistent hashing )


