【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 689B Mike and Shortcuts (最短路+spfa)
来源:互联网 发布:002175 东方网络 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 10:30
【CF简介】
提交链接:CF 689B
题面:
Recently, Mike was very busy with studying for exams and contests. Now he is going to chill a bit by doing some sight seeing in the city.
City consists of n intersections numbered from1 ton. Mike starts walking from his house located at the intersection number1 and goes along some sequence of intersections. Walking from intersection numberi to intersection j requires|i - j| units of energy. Thetotal energy spent by Mike to visit a sequence of intersectionsp1 = 1, p2, ..., pk is equal to units of energy.
units of energy.
Of course, walking would be boring if there were no shortcuts. A shortcut is a special path that allows Mike walking from one intersection to another requiring only1 unit of energy. There are exactlyn shortcuts in Mike's city, the ith of them allows walking from intersectioni to intersectionai (i ≤ ai ≤ ai + 1) (but not in the opposite direction), thus there is exactly one shortcut starting at each intersection. Formally, if Mike chooses a sequencep1 = 1, p2, ..., pk then for each1 ≤ i < k satisfyingpi + 1 = api andapi ≠ pi Mike will spendonly 1 unit of energy instead of|pi - pi + 1| walking from the intersectionpi to intersectionpi + 1. For example, if Mike chooses a sequencep1 = 1, p2 = ap1, p3 = ap2, ..., pk = apk - 1, he spends exactly k - 1 units of total energy walking around them.
Before going on his adventure, Mike asks you to find the minimum amount of energy required to reach each of the intersections from his home. Formally, for each1 ≤ i ≤ n Mike is interested in finding minimum possible total energy of some sequencep1 = 1, p2, ..., pk = i.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of Mike's city intersection.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an(i ≤ ai ≤ n ,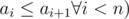 , describing shortcuts of Mike's city, allowing to walk from intersectioni to intersection ai using only1 unit of energy. Please note that the shortcuts don't allow walking in opposite directions (fromai toi).
, describing shortcuts of Mike's city, allowing to walk from intersectioni to intersection ai using only1 unit of energy. Please note that the shortcuts don't allow walking in opposite directions (fromai toi).
In the only line print n integers m1, m2, ..., mn, wheremi denotes the least amount of total energy required to walk from intersection1 to intersectioni.
32 2 3
0 1 2
51 2 3 4 5
0 1 2 3 4
74 4 4 4 7 7 7
0 1 2 1 2 3 3
In the first sample case desired sequences are:
1: 1; m1 = 0;
2: 1, 2; m2 = 1;
3: 1, 3; m3 = |3 - 1| = 2.
In the second sample case the sequence for any intersection 1 < i is always 1, i and mi = |1 - i|.
In the third sample case — consider the following intersection sequences:
1: 1; m1 = 0;
2: 1, 2; m2 = |2 - 1| = 1;
3: 1, 4, 3; m3 = 1 + |4 - 3| = 2;
4: 1, 4; m4 = 1;
5: 1, 4, 5; m5 = 1 + |4 - 5| = 2;
6: 1, 4, 6; m6 = 1 + |4 - 6| = 3;
7: 1, 4, 5, 7; m7 = 1 + |4 - 5| + 1 = 3.
题意:
给定一张图,有n个节点(1<=n<=200000),任意两个节点的距离为这两点的序号之差绝对值。且每个点都会有一个捷径,通过该捷径到达对应点的代价为1,求每个点到点1的最小距离。
解题:
刚开始看到这题肯定是懵逼的,这么大的图,没办法存。但是这题很有特殊性,任意两点间距离已知,且为序号差,同时如果不算捷径的话,除1以外的其他节点直接到节点1的距离和通过他的前继到达节点1的距离是一样的,利用这个特殊性,我们就可以省去大部分边,只保留1->2->3->....->n的边和捷径,这样大致只有40000条边,采用SPFA求解即可。
注意点:
1.捷径是单向的,节点间的路是双向的。
2.部分捷径是通往自身的,可以直接省略。
代码:
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <queue>#define maxn 200010#define inf 0x3f3f3f3fusing namespace std;struct edge{int fm,to,val;}store[maxn*3];queue <int> qe;int cnt=0,head[maxn],next[maxn*3],vis[maxn];int dist[maxn];void addedge(int fm,int to,int val){ next[cnt]=head[fm]; head[fm]=cnt; store[cnt].fm=fm; store[cnt].to=to; store[cnt].val=val; cnt++;}void spfa(){ int cur,tmp; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); qe.push(1); vis[1]=1; while(!qe.empty()) { cur=qe.front(); qe.pop(); vis[cur]=0; for(int i=head[cur];~i;i=next[i]) { tmp=dist[store[i].fm]+store[i].val; if(tmp<dist[store[i].to]) { dist[store[i].to]=tmp; // 队列中保留一个更新即可 if(!vis[store[i].to]) qe.push(store[i].to); } } }}int main(){int n,tmp;memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));scanf("%d",&n);memset(dist,inf,sizeof(dist));dist[1]=0;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d",&tmp); if(tmp!=i) addedge(i,tmp,1);}for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){addedge(i-1,i,1);addedge(i,i-1,1);} spfa();printf("%d",dist[1]);for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)printf(" %d",dist[i]);printf("\n");return 0;}- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 689B Mike and Shortcuts (最短路+spfa)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 689C Mike and Chocolate Thieves (二分)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 216B Forming Teams (图论)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 701B Cells Not Under Attack (分析)
- CodeForces 689B Mike and Shortcuts(SPFA)
- CodeForces 689 B. Mike and Shortcuts(SPFA)
- Codeforces #361 (Div. 2)B-Mike and Shortcuts(spfa最短路)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 615B Longtail Hedgehog (DFS/拓扑排序)
- 【打CF,学算法——二星级】CodeForces 689A Mike and Cellphone (模拟)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】Codeforces 9C Hexadecimal's Numbers (解法汇总)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 550D Regular Bridge (构造)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 645C Enduring Exodus (二分+贪心)
- B. Mike and Shortcuts(cf#361)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 2) C. Gerald's Hexagon
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 567D One-Dimensional Battle Ships (二分)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】Codeforces 698A Vacations (动态规划)
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 701C They Are Everywhere
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】Codeforces 704A Thor (模拟)
- [mtk lcd]调试问题总结
- Eclipse中jsp、js文件编辑时,卡死现象解决汇总
- php 的aes加密
- Android多媒体MediaStore运用
- pc端软件与移动app的区别是什么?
- 【打CF,学算法——三星级】CodeForces 689B Mike and Shortcuts (最短路+spfa)
- volatile关键字简介
- unity调取windows保存或读取窗口
- hibernate执行hql查询出现java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: antlr.collections.AST.getLine()I之解法
- PullToRefreshListView addHeadView的正确姿势
- STM32 ——端口复用和重映射
- [mtk]按power键亮屏速度慢问题
- 几何画板对象进行删除和拖动的技巧
- domain的一些理解


