Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) E. Mike and Geometry Problem (离散化)
来源:互联网 发布:网络调查系统 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/09 15:42
Mike wants to prepare for IMO but he doesn't know geometry, so his teacher gave him an interesting geometry problem. Let's definef([l, r]) = r - l + 1 to be the number of integer points in the segment[l, r] withl ≤ r (say that 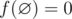 ). You are given two integersn and k andn closed intervals [li, ri] onOX axis and you have to find:
). You are given two integersn and k andn closed intervals [li, ri] onOX axis and you have to find:

In other words, you should find the sum of the number of integer points in the intersection of anyk of the segments.
As the answer may be very large, output it modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Mike can't solve this problem so he needs your help. You will help him, won't you?
The first line contains two integers n andk (1 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of segments and the number of segments in intersection groups respectively.
Then n lines follow, the i-th line contains two integers li, ri( - 109 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 109), describingi-th segment bounds.
Print one integer number — the answer to Mike's problem modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7) in the only line.
3 21 21 32 3
5
3 31 31 31 3
3
3 11 22 33 4
6
In the first example:
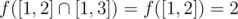 ;
;
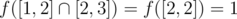 ;
;
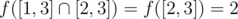 .
.
So the answer is 2 + 1 + 2 = 5.
题意:给你n个数轴上的闭区间,然后任选k个区间求交集,问你所有的这些交集的长度和为多少。
分析:离散化后直接一段一段求它对答案的贡献。
#include <cstdio>#include <queue> #include <vector> #include <cstdio> #include <utility> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f#define MOD 1000000007using namespace std;int tot,n,k,l[200007],r[200007],lin[400007],rout[400007];long long f[200007],g[400007],ans;long long ksm(long long x,long long y){long long ans = 1;while(y){if(y & 1) ans = (ans * x) % MOD;x = x*x % MOD;y>>=1;}return ans;}int main(){cin.sync_with_stdio(false);cin>>n>>k;f[k] = 1ll;for(int i = k+1;i <= n;i++) f[i] = ((f[i-1]*i)% MOD)*ksm(i-k,MOD-2) % MOD;for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {cin>>l[i]>>r[i];g[++tot] = l[i];g[++tot] = ++r[i];}sort(g+1,g+1+tot);for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){lin[lower_bound(g+1,g+1+tot,l[i])-g]++;rout[lower_bound(g+1,g+1+tot,r[i])-g]++; } int now = 0; for(int i = 1;i < tot;i++) { now += lin[i] - rout[i];ans = (ans + (g[i+1]-g[i])*f[now]) % MOD; }cout<<ans<<endl;}- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) E. Mike and Geometry Problem (离散化)
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2)E. Mike and Geometry Problem
- Codeforces 689E Mike and Geometry Problem(离散化+懒标记)
- Codeforces 689E Mike and Geometry Problem【离散化+线段树+组合数】
- Codeforces #361 E. Mike and Geometry Problem 数学
- codeforces 361 div2 E. Mike and Geometry Problem
- Codeforces 689E Mike and Geometry Problem(组合数学)
- Codeforces 689E Mike and Geometry Problem 思维
- Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 2), problem: (A) Mike and Fax
- Codeforces Round #410 (Div. 2) Mike and gcd problem 思维
- Mike and gcd problem Codeforces Round #410 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #371 (Div. 2) E. Sonya and Problem Wihtout a Legend(技巧 + 离散化dp)
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) A. Mike and Cellphone
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) B. Mike and Shortcuts
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) C. Mike and Chocolate Thieves
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) B - Mike and Shortcuts
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) A. Mike and Cellphone
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) B. Mike and Shortcuts
- Xcode 7.2 no matching provisioning profiles found
- SQL select的字段取别名
- HDU.1540 Tunnel Warfare
- Dubbo实例
- Codeforces 208 B Solitaire(记忆化搜索)
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) E. Mike and Geometry Problem (离散化)
- Ubuntu官网论坛再次被黑,又是SQL注入惹的祸
- 机器学习中的数学-线性回归,偏差、方差权衡《2》
- mysql的存储过程
- 关于DropDownList绑定SqlDataSource数据源
- android-createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord
- 4.9.1 练习对于栈的使用,以及栈溢出等问题
- 性能测试-learning loadrunner
- linux系统重启或无故变为只读造成网站无法正常访问的简单临时的做法:


