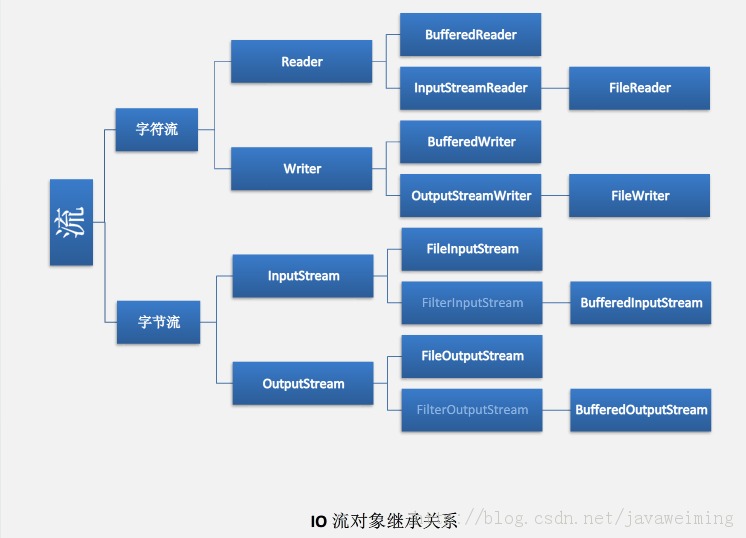
java读取文件及文件流
来源:互联网 发布:cydia软件源 sim 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/20 00:48
java读取文件或是文件流的代码,涵盖了读取jar文件中的文件流,网络文件流等,有些读取方式为了防止编码转换带来的问题,采取了动态byte[]的方式读取,源码如下 :
imp
imp
imp
imp
imp
imp
public class Util ...{
public Util() ...{
}
/** *//**
* 读取源文件内容
* @param filename String 文件路径
* @throws IOException
* @return byte[] 文件内容
*/
public static byte[] readFile(String filename) throws IOException ...{
File file =new File(filename);
if(filename==null || filename.equals(""))
...{
throw new NullPointerException("无效的文件路径");
}
long len = file.length();
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int)len];
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
int r = bufferedInputStream.read( bytes );
if (r != len)
throw new IOException("读取文件不正确");
bufferedInputStream.close();
return bytes;
}
/** *//**
* 将数据写入文件
* @param da
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void writeFile(byte[] da
File file =new File(filename);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
bufferedOutputStream.write(da
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
/** *//**
* 从jar文件里读取class
* @param filename String
* @throws IOException
* @return byte[]
*/
public byte[] readFileJar(String filename) throws IOException ...{
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream=new BufferedInputStream(getClass().getResource(filename).openStream());
int len=bufferedInputStream.available();
byte[] bytes=new byte[len];
int r=bufferedInputStream.read(bytes);
if(len!=r)
...{
bytes=null;
throw new IOException("读取文件不正确");
}
bufferedInputStream.close();
return bytes;
}
/** *//**
* 读取网络流,为了防止中文的问题,在读取过程中没有进行编码转换,而且采取了动态的byte[]的方式获得所有的byte返回
* @param bufferedInputStream BufferedInputStream
* @throws IOException
* @return byte[]
*/
public byte[] readUrlStream(BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream) throws IOException ...{
byte[] bytes = new byte[100];
byte[] bytecount=null;
int n=0;
int ilength=0;
while((n=bufferedInputStream.read(bytes))>=0)
...{
if(bytecount!=null)
ilength=bytecount.length;
byte[] tempbyte=new byte[ilength+n];
if(bytecount!=null)
...{
System.arraycopy(bytecount,0,tempbyte,0,ilength);
}
System.arraycopy(bytes,0,tempbyte,ilength,n);
bytecount=tempbyte;
if(n<bytes.length)
break;
}
return bytecount;
}
}
1、按字节读取文件内容
2、按字符读取文件内容
3、按行读取文件内容
4、随机读取文件内容
/**
* 以字节为单位读取文件,常用于读二进制文件,如图片、声音、影像等文件。
*/
public static void readFileByBytes(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
InputStream in = null;
try {
System.out.println("以字节为单位读取文件内容,一次读一个字节:");
// 一次读一个字节
in = new FileInputStream(file);
int tempbyte;
while ((tempbyte = in.read()) != -1) {
System.out.write(tempbyte);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
try {
System.out.println("以字节为单位读取文件内容,一次读多个字节:");
// 一次读多个字节
byte[] tempbytes = new byte[100];
int byteread = 0;
in = new FileInputStream(fileName);
ReadFromFile.showAvailableBytes(in);
// 读入多个字节到字节数组中,byteread为一次读入的字节数
while ((byteread = in.read(tempbytes)) != -1) {
System.out.write(tempbytes, 0, byteread);
}
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 以字符为单位读取文件,常用于读文本,数字等类型的文件
*/
public static void readFileByChars(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
Reader reader = null;
try {
System.out.println("以字符为单位读取文件内容,一次读一个字节:");
// 一次读一个字符
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
int tempchar;
while ((tempchar = reader.read()) != -1) {
// 对于windows下,\r\n这两个字符在一起时,表示一个换行。
// 但如果这两个字符分开显示时,会换两次行。
// 因此,屏蔽掉\r,或者屏蔽\n。否则,将会多出很多空行。
if (((char) tempchar) != '\r') {
System.out.print((char) tempchar);
}
}
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
System.out.println("以字符为单位读取文件内容,一次读多个字节:");
// 一次读多个字符
char[] tempchars = new char[30];
int charread = 0;
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName));
// 读入多个字符到字符数组中,charread为一次读取字符数
while ((charread = reader.read(tempchars)) != -1) {
// 同样屏蔽掉\r不显示
if ((charread == tempchars.length)
&& (tempchars[tempchars.length - 1] != '\r')) {
System.out.print(tempchars);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < charread; i++) {
if (tempchars[i] == '\r') {
continue;
} else {
System.out.print(tempchars[i]);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 以行为单位读取文件,常用于读面向行的格式化文件
*/
public static void readFileByLines(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
System.out.println("以行为单位读取文件内容,一次读一整行:");
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String tempString = null;
int line = 1;
// 一次读入一行,直到读入null为文件结束
while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) {
// 显示行号
System.out.println("line " + line + ": " + tempString);
line++;
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 随机读取文件内容
*/
public static void readFileByRandomAccess(String fileName) {
RandomAccessFile randomFile = null;
try {
System.out.println("随机读取一段文件内容:");
// 打开一个随机访问文件流,按只读方式
randomFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "r");
// 文件长度,字节数
long fileLength = randomFile.length();
// 读文件的起始位置
int beginIndex = (fileLength > 4) ? 4 : 0;
// 将读文件的开始位置移到beginIndex位置。
randomFile.seek(beginIndex);
byte[] bytes = new byte[10];
int byteread = 0;
// 一次读10个字节,如果文件内容不足10个字节,则读剩下的字节。
// 将一次读取的字节数赋给byteread
while ((byteread = randomFile.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.write(bytes, 0, byteread);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (randomFile != null) {
try {
randomFile.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 显示输入流中还剩的字节数
*/
private static void showAvailableBytes(InputStream in) {
try {
System.out.println("当前字节输入流中的字节数为:" + in.available());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String fileName = "C:/temp/newTemp.txt";
ReadFromFile.readFileByBytes(fileName);
ReadFromFile.readFileByChars(fileName);
ReadFromFile.readFileByLines(fileName);
ReadFromFile.readFileByRandomAccess(fileName);
}
}
5、将内容追加到文件尾部
/**
* A方法追加文件:使用RandomAccessFile
*/
public static void appendMethodA(String fileName, String content) {
try {
// 打开一个随机访问文件流,按读写方式
RandomAccessFile randomFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "rw");
// 文件长度,字节数
long fileLength = randomFile.length();
//将写文件指针移到文件尾。
randomFile.seek(fileLength);
randomFile.writeBytes(content);
randomFile.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* B方法追加文件:使用FileWriter
*/
public static void appendMethodB(String fileName, String content) {
try {
//打开一个写文件器,构造函数中的第二个参数true表示以追加形式写文件
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(fileName, true);
writer.write(content);
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String fileName = "C:/temp/newTemp.txt";
String content = "new append!";
//按方法A追加文件
AppendToFile.appendMethodA(fileName, content);
AppendToFile.appendMethodA(fileName, "append end. \n");
//显示文件内容
ReadFromFile.readFileByLines(fileName);
//按方法B追加文件
AppendToFile.appendMethodB(fileName, content);
AppendToFile.appendMethodB(fileName, "append end. \n");
//显示文件内容
ReadFromFile.readFileByLines(fileName);
}
}
- java读取文件及文件流
- java读取文件及文件流
- java读取文件及文件流
- java读取文件及文件流
- JAVA 读取文件及反编译
- java读取文件夹文件及操作
- java读取Properties文件及赋值
- java读取.properties文件及文件复制(通道)
- java IO流 读取文件 && 文件复制
- java读取文件-字符流读取方式
- Java IO流读取文件
- Java IO流读取文件
- Java IO流读取文件
- Java IO 流读取文件
- Java IO流读取文件
- Java IO流读取文件
- Java文件字符流读取
- java读取资源文件--使用文件流的方式读取
- cocos2d-x中shader的使用
- android studio module无法删除
- 【SSH快速进阶】——Spring IOC容器注入的几种方式
- 称砝码--软件测试
- UVA 11827 Maximum GCD ungetc函数将ch字符重新退到输入流
- java读取文件及文件流
- bzoj4196(树链剖分)
- vim操作详解
- 【9906】装箱问题
- 缩小浏览器窗口延迟执行代码
- MySQL数据库学习笔记(四)----MySQL聚合函数、控制流程函数(含navicat软件的介绍)
- java之Treeset
- web端测试和移动端测试的区别
- Cpp环境【POJ3320】Jessica's Reading Problem 洁西卡的复习计划