Java异常处理实例教程
来源:互联网 发布:进职称网络教育学历 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 13:38
1- 异常是什么?
2-异常层次结构
3- 使用try-catch处理异常
4- try-catch-finally
5- 异常绕包
6- RuntimeException和子类
6.1- NullYiibaierException
6.2- ArrayIndexOfBoundException
2-异常层次结构
3- 使用try-catch处理异常
4- try-catch-finally
5- 异常绕包
6- RuntimeException和子类
6.1- NullYiibaierException
6.2- ArrayIndexOfBoundException
1- 什么是异常?
首先,让我们来看看下图的例子:
在这个例子中,存在的错误码由除以0的结果。由于除以0而导致异常: ArithmeticException- HelloException.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception;public class HelloException { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Three"); // This division no problem. int value = 10 / 2; System.out.println("Two"); // This division no problem. value = 10 / 1; System.out.println("One"); // This division has problem, divided by 0. // An error has occurred here. value = 10 / 0; // And the following code will not be executed. System.out.println("Let's go!"); }}运行这个例子,得到的结果是:
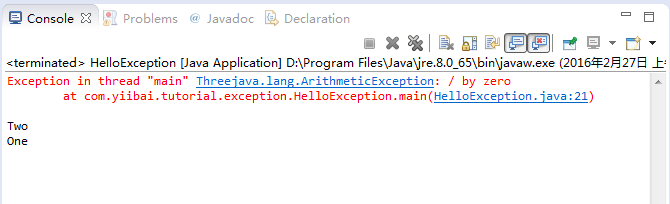

可以看到控制台屏幕上的通知。错误通知是很清楚的,包括代码行的信息。
让我们通过下图中的流程看看下面的程序:
- 程序从(1),(2)至(5)步骤正常运行。
- 在步骤(6)程序除以0。
- 程序跳转出 main 方法后,而(7)代码行还没有被执行。

我们将修改上述实施例的代码。
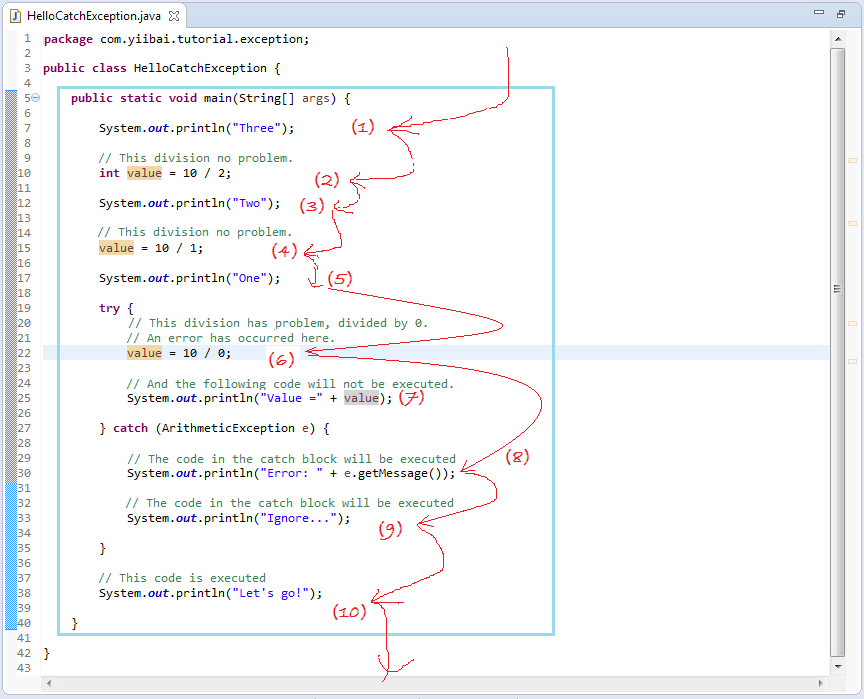
- HelloCatchException.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception;public class HelloCatchException { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Three"); // This division no problem. int value = 10 / 2; System.out.println("Two"); // This division no problem. value = 10 / 1; System.out.println("One"); try { // This division has problem, divided by 0. // An error has occurred here. value = 10 / 0; // And the following code will not be executed. System.out.println("Value =" + value); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { // The code in the catch block will be executed System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage()); // The code in the catch block will be executed System.out.println("Ignore..."); } // This code is executed System.out.println("Let's go!"); }}运行示例结果:
ThreeTwoOneError: / by zeroIgnore...Let's go!
我们将按以下实例图像的流程来解释下面的程序。
- 步骤(1)至(5)是完全正常的。
- 异常发生在步骤(6),除以0出现了问题。
- 它立即跳到catch块执行命令,步骤(7)被跳过。
- 步骤(8),(9)被执行。
- 步骤(10)被执行。
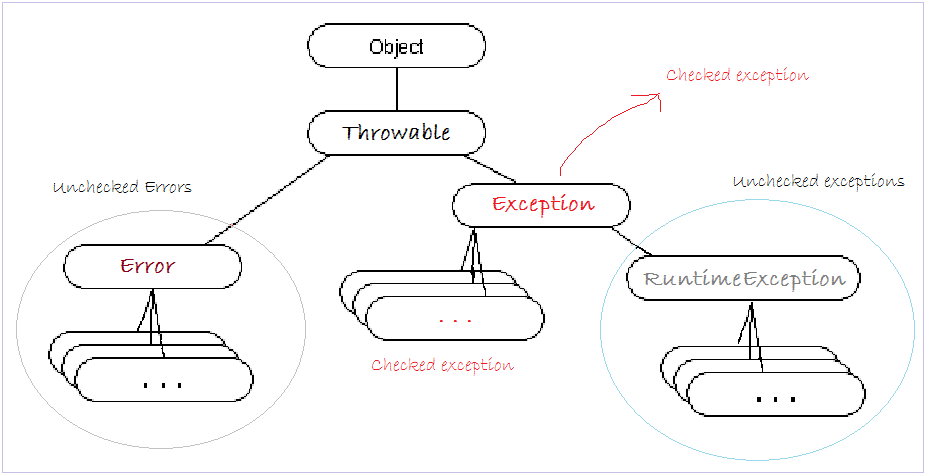
2- 异常层次结构
这是Java异常的分层图的模型。
- 最高的类是:Throwable
- 两个直接子类是 Error 和 Exception。
注意:您的类应该从两个分支:Error或Exception继承,而不是直接从Throwable继承。
Errors
当一个动态链接失败,或在虚拟机的一些其他的“硬”故障发生时,虚拟机引发这个错误。典型的Java程序不捕获错误,所以Java程序都不会抛出任何错误。Exceptions
大多数程序抛出并捕获从Exception类派生的对象。异常指示出现了一个问题,但是这些问题并不是严重系统性问题。你写的大多数程序将会抛出和捕获异常。Exception类在Java包定义了许多子类。这些子类指明不同类型的可能会发生异常。 例如,NegativeArraySizeException表明程序试图创建一个大小为负的数组。
一个导演的子类在Java语言中的特殊含义:RuntimeException.
Runtime Exceptions
RuntimeException类表示Java虚拟机中发生(在运行期间)的异常。运行时异常的一个例子是NullYiibaierException异常,其中,当一种方法试图通过一个空引用来访问对象的成员时就会引发。 NullYiibaierException 可以在任何地方出现某个程序试图取消引用一个对象的引用。经常检查异常捕获的好处远远超过它的成本。由于运行时异常是无所不在的,在试图捕获或指定所有的时间是徒劳的作法(不可读和不可维护的代码), 编译器允许运行时异常去未捕获和指定。
Java包定义几个RuntimeException类。您可以捕获这些异常,就像其他异常。但是并不需要一种方法来指定它抛出运行时异常。此外可以创建自己的RuntimeException子类。 运行时异常 - 下面讨论包含何时以及如何使用运行时异常进行了深入探讨。
3- 使用try-catch处理异常
我们编写从 Exception 继承的类。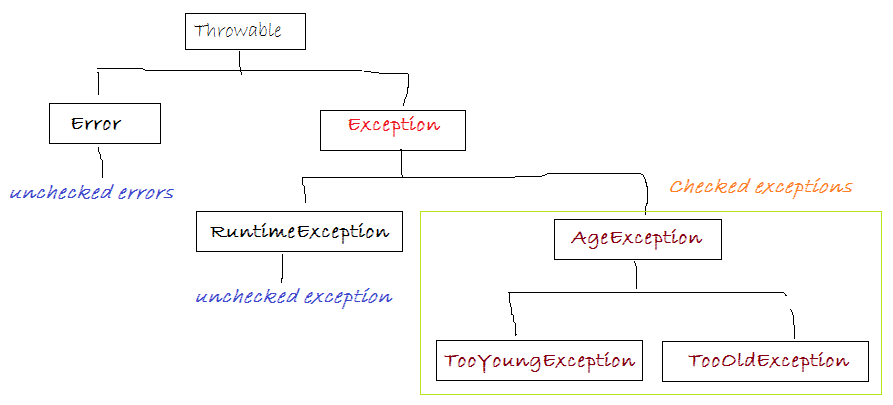
- AgeException.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.basic;public class AgeException extends Exception { public AgeException(String message) { super(message); }}- TooYoungException.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.basic;public class TooYoungException extends AgeException { public TooYoungException(String message) { super(message); }}- TooOldException.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.basic;public class TooOldException extends AgeException { public TooOldException(String message) { super(message); }}以及AgeUtils类检查年龄的检查静态方法。
- AgeUtils.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.basic;public class AgeUtils { // This method checks the age. // If age is less than 18, the method will throw an exception TooYoungException // If age greater than 40, the method will throw an exception TooOldException public static void checkAge(int age) throws TooYoungException, TooOldException { if (age < 18) { // If age is less than 18, an exception will be thrown // This method ends here. throw new TooYoungException("Age " + age + " too young"); } else if (age > 40) { // If age greater than 40, an exception will be thrown. // This method ends here. throw new TooOldException("Age " + age + " too old"); } // If age is between 18-40. // This code will be execute. System.out.println("Age " + age + " OK!"); }}检查异常和未经检查的异常:
- AgeException是Exception,TooOldException的子类和TooYoungException2是 AgeException直接子类,所以它们是“Checked Exception”
- 在AgeUtils.checkAge(int)方法已经抛出异常,需要通过关键字“throws”,列出它们的方法声明。或者可以声明抛出更多的级别。
- 在使用 AgeUtils.checkAge(int) 位置也必须进行处理,以捕获异常,或继续抛出去。

"Checked exception" 是由 "Java Compiler"来检查。
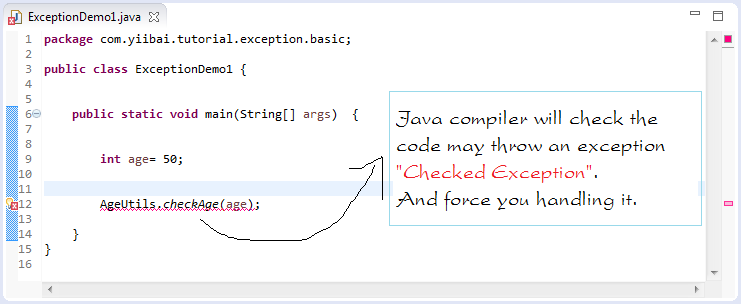
有两个选择:
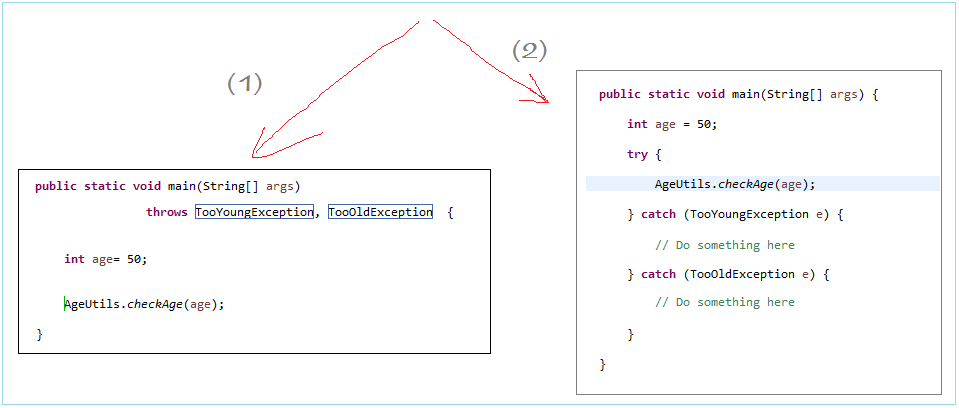

- TryCatchDemo1.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.basic;public class TryCatchDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Start Recruiting ..."); // Check age System.out.println("Check your Age"); int age = 50; try { AgeUtils.checkAge(age); System.out.println("You pass!"); } catch (TooYoungException e) { // Do something here .. System.out.println("You are too young, not pass!"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } catch (TooOldException e) { // Do something here .. System.out.println("You are too old, not pass!"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } }}在下面的例子中,我们将通过父类捕获异常(超Exception类)。
- TryCatchDemo2.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.basic;public class TryCatchDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Start Recruiting ..."); // Check age System.out.println("Check your Age"); int age = 15; try { // Here can throw TooOldException or TooYoungException AgeUtils.checkAge(age); System.out.println("You pass!"); } catch (AgeException e) { // If an exception occurs, type of AgeException // This catch block will be execute System.out.println("Your age invalid, you not pass"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } }}也可以组不同的异常在块中来处理,如果它们对逻辑程序处理是相同的方式。
- TryCatchDemo3.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.basic;public class TryCatchDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Start Recruiting ..."); // Check age System.out.println("Check your Age"); int age = 15; try { // Here can throw TooOldException or TooYoungException AgeUtils.checkAge(age); System.out.println("You pass!"); } catch (TooYoungException | TooOldException e) { // Catch multi exceptions in one block. System.out.println("Your age invalid, you not pass"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } }}4- try-catch-finally
我们已习惯于通过 try-catch 块捕获错误。Try-catch-finally 来完全处理异常。
try { // Do something here} catch (Exception1 e) { // Do something here} catch (Exception2 e) { // Do something here} finally { // Finally block is always executed // Do something here}- TryCatchFinallyDemo.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.basic;public class TryCatchFinallyDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String text = "001234A2"; int value = toInteger(text); System.out.println("Value= " + value); } public static int toInteger(String text) { try { System.out.println("Begin parse text: " + text); // An Exception can throw here (NumberFormatException). int value = Integer.parseInt(text); return value; } catch (NumberFormatException e) { // In the case of 'text' is not a number. // This catch block will be executed. System.out.println("Number format exception " + e.getMessage()); // Returns 0 if NumberFormatException occurs return 0; } finally { System.out.println("End parse text: " + text); } }}这是程序的流程。 finally块无论什么情况下总会被执行。


5- 环绕异常
我们需要一些类参与到这个例子:
- Person: 模拟一个受试者招募到公司的信息:姓名,年龄,性别。
- GenderException: 性别异常。
- ValidateException: 异常评估求职者。
- ValidateUtils: 静态方法类综合评价面试者。
- 如果男性年龄在18-40之间的被认为是有效的。
- Person.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.wrap;public class Person { public static final String MALE = "male"; public static final String FEMALE = "female"; private String name; private String gender; private int age; public Person(String name, String gender, int age) { this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }}- GenderException.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.wrap;// Gender Exception.public class GenderException extends Exception { public GenderException(String message) { super(message); }}ValidateException 类包有其他异常。
- ValidateException.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.wrap;public class ValidateException extends Exception { // Wrap an Exception public ValidateException(Exception e) { super(e); }}- ValidateUtils.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.wrap;import com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.basic.AgeUtils;public class ValidateUtils { public static void checkPerson(Person person) throws ValidateException { try { // Check age. // Valid if between 18-40 // This method can throw TooOldException, TooYoungException. AgeUtils.checkAge(person.getAge()); } catch (Exception e) { // If not valid // Wrap this exception by ValidateException, and throw throw new ValidateException(e); } // If that person is Female, ie invalid. if (person.getGender().equals(Person.FEMALE)) { GenderException e = new GenderException("Do not accept women"); throw new ValidateException(e); } }}- WrapperExceptionDemo.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.wrap;public class WrapperExceptionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // One participant recruitment. Person person = new Person("Marry", Person.FEMALE, 20); try { // Exceptions may occur here. ValidateUtils.checkPerson(person); } catch (ValidateException wrap) { // Get the real cause. // May be TooYoungException, TooOldException, GenderException Exception cause = (Exception) wrap.getCause(); if (cause != null) { System.out.println("Not pass, cause: " + cause.getMessage()); } else { System.out.println(wrap.getMessage()); } } }}6- RuntimeException和子类
RuntimeException类及其子类都是“未检查的例外”。它不是由Java编译器在编译时进行检查。在某些情况下,你可以从这个分支继承编写自己的异常。下面是属于RuntimeException分支一些类(当然,这还不是全部)。
一些处理这种类型异常的例子:
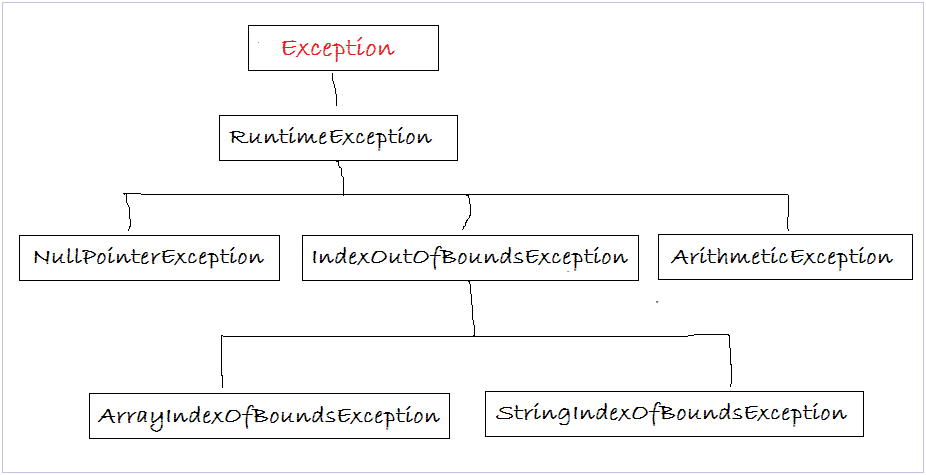

6.1- NullYiibaierException
这是最常见的异常,通常会导致错误在程序中。异常被抛出,当你调用方法或访问一个空对象的字段。
- NullYiibaierExceptionDemo.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.runtime;public class NullYiibaierExceptionDemo { // For example, here is a method that can return null string. public static String getString() { if (1 == 2) { return "1==2 !!"; } return null; } public static void main(String[] args) { // This is an object that references not null. String text1 = "Hello exception"; // Call the method retrieves the string length. int length = text1.length(); System.out.println("Length text1 = " + length); // This is an object that references null. String text2 = getString(); // Call the method retrieves the string length. // NullYiibaierException will occur here. // It is an exception occurs at runtime (type of RuntimeException) // Javac compiler does not force you to use a try-catch block to handle it length = text2.length(); System.out.println("Finish!"); }}运行示例的结果:
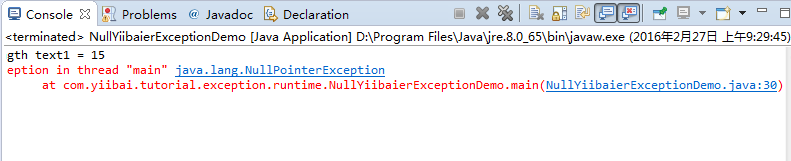

在现实中,像处理其他异常时,可以使用 try-catch 来捕获并处理这个异常。 然而,这是机械的,通常情况下,我们应该检查,以确保在使用它之前,对象不为空值。
您可以更正上面的代码,使其类似于下面的以避免空指针异常:
您可以更正上面的代码,使其类似于下面的以避免空指针异常:
// This is a null object.String text2 = getString();// Check to make sure 'Text2' are not null.// Instead of using try-catch.if (text2 != null) { length = text2.length();}6.2- ArrayIndexOfBoundException
当您试图访问一个无效的索引的数组元素就会发生此异常。例如,一个数组有10个元素可以访问,但您访问的是索引为20的元素。
- ArrayIndexOfBoundsExceptionDemo.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.exception.runtime;public class ArrayIndexOfBoundsExceptionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] strs = new String[] { "One", "Two", "Three" }; // Access to the element has index 0. String str1 = strs[0]; System.out.println("String at 0 = " + str1); // Access to the element has index 5. // ArrayIndexOfBoundsException occur here. String str2 = strs[5]; System.out.println("String at 5 = " + str2); }}为了避免 ArrayIndexOfBoundsException,我们更多的应该是检查数组而不是使用try-catch。
if (strs.length > 5) { String str2 = strs[5]; System.out.println("String at 5 = " + str2);} else { System.out.println("No elements with index 5");} 0 0
- Java异常处理实例教程
- Laravel 中的异常处理器和HTTP异常处理实例教程
- python异常处理实例教程(捕捉异常、错误)
- java 实例教程
- Java2入门与实例教程笔笔记-字符串处理,数组,异常处理
- 【java】java异常处理
- java异常和异常处理
- Java 异常及异常处理
- java异常与异常处理
- Java异常处理-----自定义异常
- Java异常与异常处理
- java异常及异常处理
- Java 异常与异常处理
- Java异常与异常处理
- Java异常及异常处理
- Java异常处理--自定义异常
- JAVA异常之异常处理
- Android图像处理实例教程
- SharedPreferences
- ☆HDU 1024 Max Sum Plus Plus 绝对能看懂得题解(难题,多个子段和的和最大)
- Java String, StringBuffer和StringBuilder实例
- 纯CSS实现多级导航栏。
- groupId Lombok 安装、入门 - 消除冗长的 java 代码
- Java异常处理实例教程
- Java泛型实例
- NKOI 1948 星际转移
- jquery插件搜集
- Java集合框架实例
- Archlinux和windows7双系统启动安装
- Java二进制流
- 多源最短路径算法---Floyd-Warshall
- 高性能Java Web 页面静态化实例


