Java正则表达式实例教程
来源:互联网 发布:打谱软件overture下载 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/25 18:10
1- 正则表达式
1.1- 概述
正则表达式定义了一个字符串搜索模式。正则表达式可以用于搜索,编辑和处理文本。由正则表达式定义的模式可在任何匹配一次或多次,或不为给定的字符串。正则表达式的缩写是regex。
1.2- 支持的语言
正则表达式在大多数编程语言中都有支持,例如,Java和Perl,Groovy等等。不幸的每种语言支持正则表达式略有不同。
2- 编写正则表达式规则
No正则表达式
描述1.匹配任何字符
2^regex找到必须在行头的匹配的正则
3regex$找到必须在行的末尾匹配的正则
4[abc]集定义,可以匹配字母a或b或c
5[abc][vz]集定义,可以匹配a或b或c后跟v或z
6[^abc]当插入符显示为方括号中的第一个字符,它为相反模式。这可以匹配除了a或b或c外的任何字符7[a-d1-7]范围:从1到7、a和d之间的字符
8X|Z查找X或Z
9XZ查找X直接跟着Z
10$检查一行是否结束
一些非空白字符
18\b匹配一个单词边界,在一个字字符 [a-zA-Z0-9_].出现 x 次,{}描述了前自由的顺序
23{X,Y}X和Y之间出现的次数
24*?? 后一个量词使其成为一个勉强的限定符。它试图找到最小匹配。3- Java中正则表达式中的特殊字符
在Java中的正则表达式中的特殊字符:
\.[{(*+?^$| 例如点字符。如果想让它解释为正常所需的标志,那在点字符java的正则表达式前加"\"被解释为任意字符。
// Regex pattern describe any character.String regex = ".";// Regex pattern describe a dot character.String regex = "\\.";
4- 使用String.matches(String)
- Class String
...// Check the entire String object matches the regex or not.public boolean matches(String regex)..
使用String.matches (String regex) 方法,可以检查整个字符串是否匹配正则表达式。这是最常见的方式。考虑以下例子:
- StringMatches.java
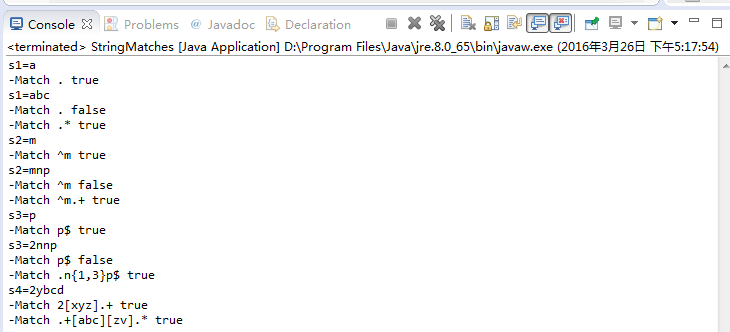
package com.yiibai.tutorial.regex.stringmatches;public class StringMatches { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "a"; System.out.println("s1=" + s1); // Check the entire s1 // Match any character // Rule . // ==> true boolean match = s1.matches("."); System.out.println("-Match . " + match); s1 = "abc"; System.out.println("s1=" + s1); // Check the entire s1 // Match any character // Rule . // ==> false (Because s1 has three characters) match = s1.matches("."); System.out.println("-Match . " + match); // Check the entire s1 // Match with any character 0 or more times // Combine the rules . and * // ==> true match = s1.matches(".*"); System.out.println("-Match .* " + match); String s2 = "m"; System.out.println("s2=" + s2); // Check the entire s2 // Start by m // Rule ^ // ==> true match = s2.matches("^m"); System.out.println("-Match ^m " + match); s2 = "mnp"; System.out.println("s2=" + s2); // Check the entire s2 // Start by m // Rule ^ // ==> false (Because s2 has three characters) match = s2.matches("^m"); System.out.println("-Match ^m " + match); // Start by m // Next any character, appearing one or more times. // Rule ^ and. and + // ==> true match = s2.matches("^m.+"); System.out.println("-Match ^m.+ " + match); String s3 = "p"; System.out.println("s3=" + s3); // Check s3 ending with p // Rule $ // ==> true match = s3.matches("p$"); System.out.println("-Match p$ " + match); s3 = "2nnp"; System.out.println("s3=" + s3); // Check the entire s3 // End of p // ==> false (Because s3 has 4 characters) match = s3.matches("p$"); System.out.println("-Match p$ " + match); // Check out the entire s3 // Any character appearing once. // Followed by n, appear one or up to three times. // End by p: p $ // Combine the rules: . , {X, y}, $ // ==> true match = s3.matches(".n{1,3}p$"); System.out.println("-Match .n{1,3}p$ " + match); String s4 = "2ybcd"; System.out.println("s4=" + s4); // Start by 2 // Next x or y or z // Followed by any one or more times. // Combine the rules: [abc]. , + // ==> true match = s4.matches("2[xyz].+"); System.out.println("-Match 2[xyz].+ " + match); String s5 = "2bkbv"; // Start any one or more times // Followed by a or b, or c: [abc] // Next z or v: [zv] // Followed by any // ==> true match = s5.matches(".+[abc][zv].*"); System.out.println("-Match .+[abc][zv].* " + match); }}运行示例的结果如下:


- SplitWithRegex.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.regex.stringmatches;public class SplitWithRegex { public static final String TEXT = "This is my text"; public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("TEXT=" + TEXT); // White space appears one or more times. // The whitespace characters: \t \n \x0b \r \f // Combining rules: \ s and + String regex = "\\s+"; String[] splitString = TEXT.split(regex); // 4 System.out.println(splitString.length); for (String string : splitString) { System.out.println(string); } // Replace all whitespace with tabs String newText = TEXT.replaceAll("\\s+", "\t"); System.out.println("New text=" + newText); }}运行示例的结果如下:



EitherOrCheck.java
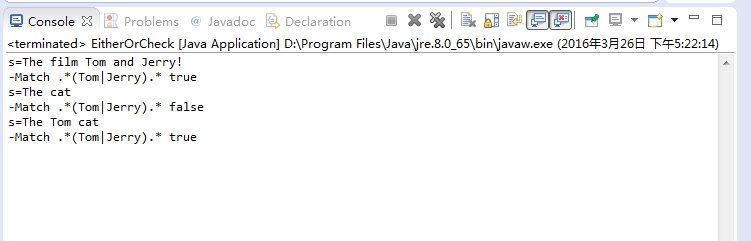
package com.yiibai.tutorial.regex.stringmatches;public class EitherOrCheck { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "The film Tom and Jerry!"; // Check the whole s // Begin by any characters appear 0 or more times // Next Tom or Jerry // End with any characters appear 0 or more times // Combine the rules:., *, X | Z // ==> true boolean match = s.matches(".*(Tom|Jerry).*"); System.out.println("s=" + s); System.out.println("-Match .*(Tom|Jerry).* " + match); s = "The cat"; // ==> false match = s.matches(".*(Tom|Jerry).*"); System.out.println("s=" + s); System.out.println("-Match .*(Tom|Jerry).* " + match); s = "The Tom cat"; // ==> true match = s.matches(".*(Tom|Jerry).*"); System.out.println("s=" + s); System.out.println("-Match .*(Tom|Jerry).* " + match); }}运行示例的结果如下:


5- 使用Pattern和Matcher
1. Pattern对象是正则表达式的编译版本。它没有任何公开的构造函数,我们使用它的公共静态方法编译(字符串)通过传递正则表达式参数来创建模式(pattern)对象。
2. Matcher是正则表达式引擎对象与创建模式对象的输入字符串模式相匹配。这个类没有任何公共构造函数,我们使用模式匹配对象的方法,将它输入字符串作为参数来获得一个Matcher对象。 然后,我们使用方法来返回基于输入的字符串正则表达式模式匹配或不匹配的布尔结果值。
3. 如果正则表达式的语法不正确则会抛出PatternSyntaxException异常。
2. Matcher是正则表达式引擎对象与创建模式对象的输入字符串模式相匹配。这个类没有任何公共构造函数,我们使用模式匹配对象的方法,将它输入字符串作为参数来获得一个Matcher对象。 然后,我们使用方法来返回基于输入的字符串正则表达式模式匹配或不匹配的布尔结果值。
3. 如果正则表达式的语法不正确则会抛出PatternSyntaxException异常。
String regex= ".xx.";// Create a Pattern object through a static method.Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);// Get a Matcher objectMatcher matcher = pattern.matcher("MxxY");boolean match = matcher.matches();System.out.println("Match "+ match);- Class Pattern:
public static Pattern compile(String regex, int flags) ;public static Pattern compile(String regex);public Matcher matcher(CharSequence input);public static boolean matches(String regex, CharSequence input);
- Class Matcher:
public int start()public int start(int group)public int end()public int end(int group)public String group()public String group(int group)public String group(String name)public int groupCount()public boolean matches()public boolean lookingAt()public boolean find()
下面是使用匹配器(Matcher)和find()方法来搜索子串匹配正则表达式的例子。


- MatcherFind.java
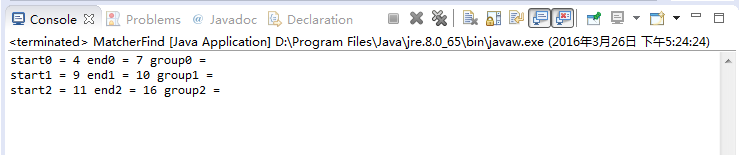
package com.yiibai.tutorial.regex;import java.util.regex.Matcher;import java.util.regex.Pattern;public class MatcherFind { public static void main(String[] args) { final String TEXT = "This \t is a \t\t\t String"; // Spaces appears one or more time. String regex = "\\s+"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(TEXT); int i = 0; while (matcher.find()) { System.out.print("start" + i + " = " + matcher.start()); System.out.print(" end" + i + " = " + matcher.end()); System.out.println(" group" + i + " = " + matcher.group()); i++; } }}运行示例的结果如下:


方法Matcher.lookingAt()
- MatcherLookingAt.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.regex;import java.util.regex.Matcher;import java.util.regex.Pattern;public class MatcherLookingAt { public static void main(String[] args) { String country1 = "iran"; String country2 = "Iraq"; // Start by I followed by any character. // Following is the letter a or e. String regex = "^I.[ae]"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(country1); // lookingAt () searches that match the first part. System.out.println("lookingAt = " + matcher.lookingAt()); // matches() must be matching the entire System.out.println("matches = " + matcher.matches()); // Reset matcher with new text: country2 matcher.reset(country2); System.out.println("lookingAt = " + matcher.lookingAt()); System.out.println("matches = " + matcher.matches()); }}6- Group/分组
正则表达式可以分组:
// A regular expressionString regex = "\\s+=\\d+";// Writing as three group, by marking ()String regex2 = "(\\s+)(=)(\\d+)";// Two groupString regex3 = "(\\s+)(=\\d+)";
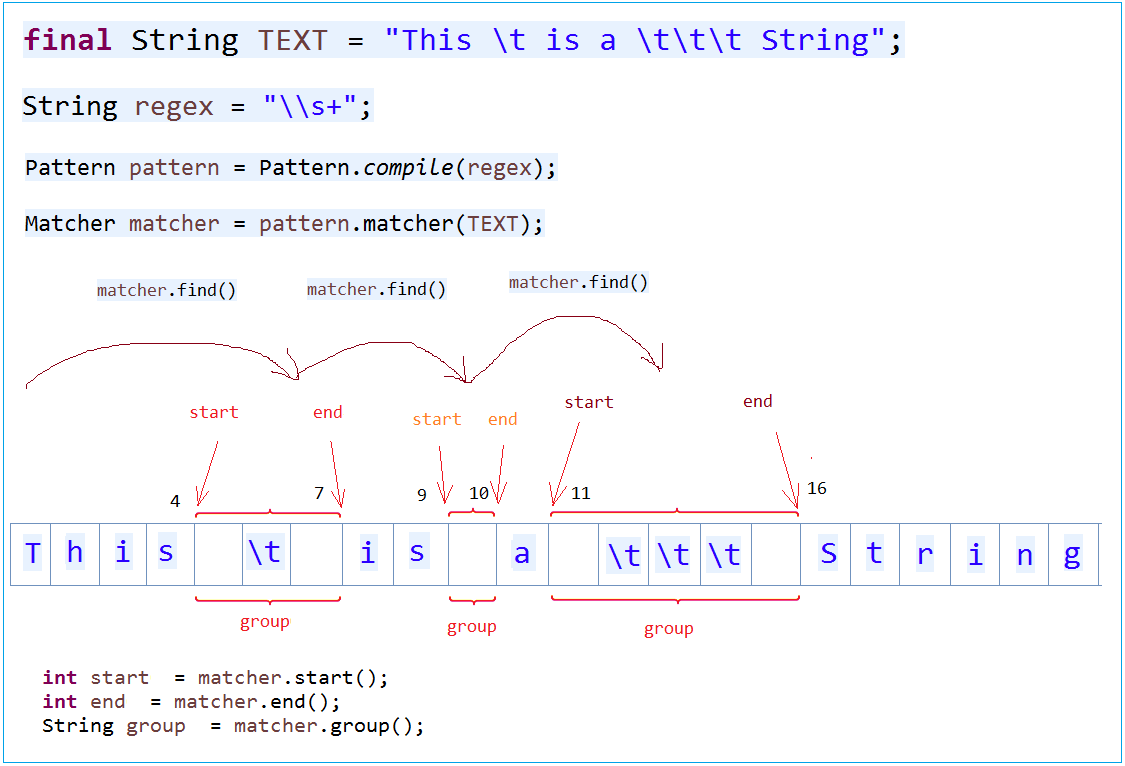
分组可以嵌套,因此需要一个规则索引组。 整个模式被定义为组0,其余组介绍如下类似图:
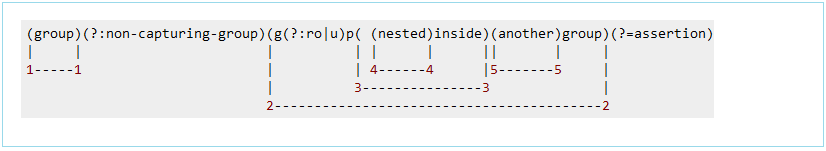


从Java7,您可以定义一个名为捕获组(?<名称>模式),并且您可以访问Matcher.group(字符串名称)匹配的内容。正则表达式较长,但代码更有意义,因为它表明您要匹配,或者使用正则表达式提取。注意:使用(?:模式),告知Java不要认为这是一个组(非捕获组)
命名捕获组也可以通过Matcher.group(int group) ,使用相同的编号模式访问。
在内部,Java实现只是从名字到组编号映射。所以不能对2个不同的捕获组使用相同的名称。-让我们为组命名来看一个例子(Java>=7)
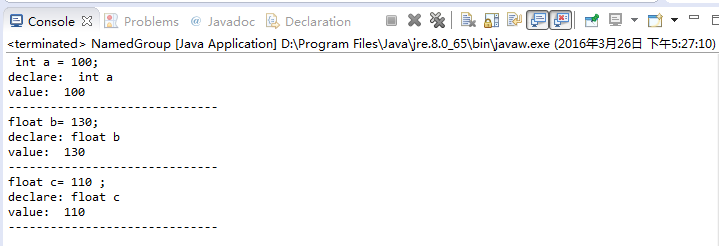
- NamedGroup.java
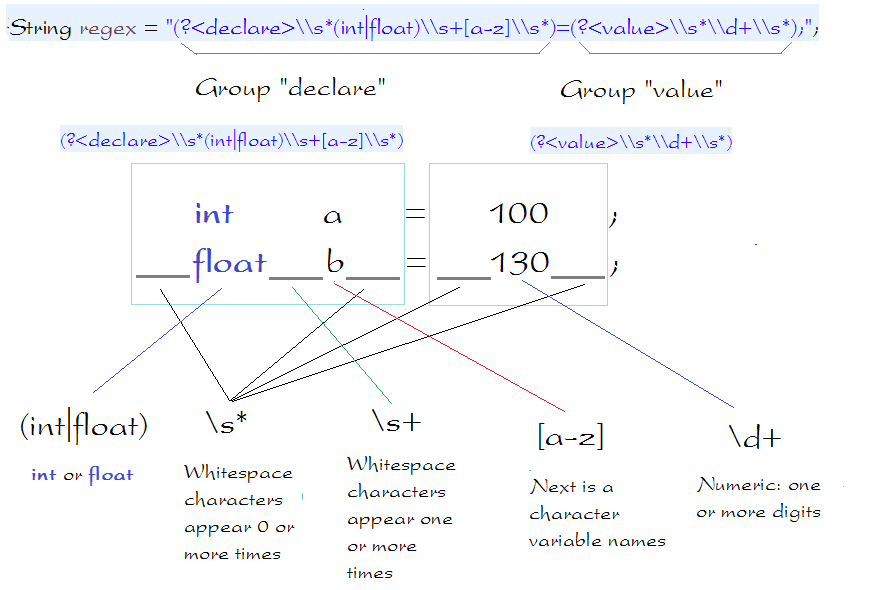
package com.yiibai.tutorial.regex;import java.util.regex.Matcher;import java.util.regex.Pattern;public class NamedGroup { public static void main(String[] args) { final String TEXT = " int a = 100;float b= 130;float c= 110 ; "; // Use (?<groupName>pattern) to define a group named: groupName // Defined group named declare: using (?<declare>...) // And a group named value: use: (?<value>..) String regex = "(?<declare>\\s*(int|float)\\s+[a-z]\\s*)=(?<value>\\s*\\d+\\s*);"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(TEXT); while (matcher.find()) { String group = matcher.group(); System.out.println(group); System.out.println("declare: " + matcher.group("declare")); System.out.println("value: " + matcher.group("value")); System.out.println("------------------------------"); } }}运行示例的结果如下:


如果想弄清楚,你可以看看下图所示:


7- 使用Pattern, Matcher, Group 和 *?
在某些情况下 *? 很重要,看看下面的例子:
// This is a regex// any characters appear 0 or more times,// followed by ' and >String regex = ".*'>";// TEXT1 match the regex.String TEXT1 = "FILE1'>";// And TEXT2 match the regexString TEXT2 = "FILE1'> <a href='http://HOST/file/FILE2'>";


*? 将找到的最小的匹配。考虑下面的例子:
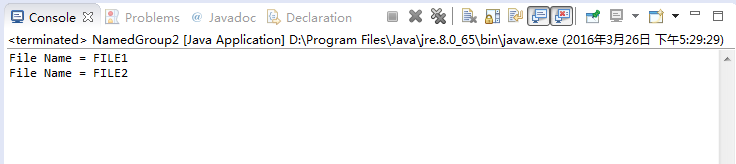
- NamedGroup2.java
package com.yiibai.tutorial.regex;import java.util.regex.Matcher;import java.util.regex.Pattern;public class NamedGroup2 { public static void main(String[] args) { String TEXT = "<a href='http://HOST/file/FILE1'>File 1</a>" + "<a href='http://HOST/file/FILE2'>File 2</a>"; // Java >= 7. // Define group named fileName. // *? ==> ? after a quantifier makes it a reluctant quantifier. // It tries to find the smallest match. String regex = "/file/(?<fileName>.*?)'>"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(TEXT); while (matcher.find()) { System.out.println("File Name = " + matcher.group("fileName")); } }}运行示例的结果如下:


0 0
- JAVA正则表达式实例教程
- Java正则表达式实例教程
- 正则表达式--实例教程
- JAVA正则表达式实例教程(转帖收藏)
- Java 正则表达式正则
- 【正则表达式】Java正则表达式
- 正则表达式 JAVA正则表达式
- 【Java】【正则表达式】正则表达式
- java 实例教程
- Java 正则表达式详解_正则表达式
- java正则表达式!正则表达式踩坑!!!
- 正则表达式工具类,正则表达式封装,Java正则表达式
- Java正则表达式详解
- Java正则表达式详解
- Java正则表达式详解
- Java正则表达式详解
- Java正则表达式详解
- java和正则表达式
- 自己动手做一个adb的wifi连接及adb命令的apk
- Java8语法和新功能
- mv遇到空格和小括号文件引发的问题
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)C.Pythagorean Triples 本原勾股数组
- JDK---API文档
- Java正则表达式实例教程
- Java多线程编程教程
- linuxshell --sed 常用指南
- Java JDBC连接各种数据库实例
- linux系统编程笔记1
- #191 Maximum Product Subarray
- NodeJS 学习笔记
- python 调用win32pai 操作cmd
- 欢迎使用CSDN-markdown编辑器


