Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
来源:互联网 发布:电视盒桌面软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/18 02:05
A. Brain’s Photos
Small, but very brave, mouse Brain was not accepted to summer school of young villains. He was upset and decided to postpone his plans of taking over the world, but to become a photographer instead.
As you may know, the coolest photos are on the film (because you can specify the hashtag #film for such).
Brain took a lot of colourful pictures on colored and black-and-white film. Then he developed and translated it into a digital form. But now, color and black-and-white photos are in one folder, and to sort them, one needs to spend more than one hour!
As soon as Brain is a photographer not programmer now, he asks you to help him determine for a single photo whether it is colored or black-and-white.
Photo can be represented as a matrix sized n × m, and each element of the matrix stores a symbol indicating corresponding pixel color. There are only 6 colors:
'C' (cyan)'M' (magenta)'Y' (yellow)'W' (white)'G' (grey)'B' (black) The photo is considered black-and-white if it has only white, black and grey pixels in it. If there are any of cyan, magenta or yellow pixels in the photo then it is considered colored.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100) — the number of photo pixel matrix rows and columns respectively.
Then n lines describing matrix rows follow. Each of them contains m space-separated characters describing colors of pixels in a row. Each character in the line is one of the ‘C’, ‘M’, ‘Y’, ‘W’, ‘G’ or ‘B’.
Output
Print the “#Black&White” (without quotes), if the photo is black-and-white and “#Color” (without quotes), if it is colored, in the only line.
Examples
Input
2 2
C M
Y Y
Output
#Color
Input
3 2
W W
W W
B B
Output
#Black&White
Input
1 1
W
Output
#Black&White
判断在输入的字符矩阵中是不是只有’W’,’B’,’G’
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;char s[2];int main(){ int n,m; bool flag = false; cin>>n>>m; for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < m; j++) { cin>>s; if(s[0]!='B' && s[0]!='W' && s[0]!='G') flag = true; } } if(flag) cout<<"#Color"<<endl; else cout<<"#Black&White"<<endl; return 0;}B. Bakery
Masha wants to open her own bakery and bake muffins in one of the n cities numbered from 1 to n. There are m bidirectional roads, each of whose connects some pair of cities.
To bake muffins in her bakery, Masha needs to establish flour supply from some storage. There are only k storages, located in different cities numbered
Unforunately the law of the country Masha lives in prohibits opening bakery in any of the cities which has storage located in it. She can open it only in one of another n - k cities, and, of course, flour delivery should be paid — for every kilometer of path between storage and bakery Masha should pay 1 ruble.
Formally, Masha will pay x roubles, if she will open the bakery in some city b (ai ≠ b for every 1 ≤ i ≤ k) and choose a storage in some city s (s = aj for some 1 ≤ j ≤ k) and b and s are connected by some path of roads of summary length x (if there are more than one path, Masha is able to choose which of them should be used).
Masha is very thrifty and rational. She is interested in a city, where she can open her bakery (and choose one of k storages and one of the paths between city with bakery and city with storage) and pay minimum possible amount of rubles for flour delivery. Please help Masha find this amount.
Input
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n, m ≤
Then m lines follow. Each of them contains three integers u, v and l (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, 1 ≤ l ≤
If k > 0, then the last line of the input contains k distinct integers a1, a2, …, ak (1 ≤ ai ≤ n) — the number of cities having flour storage located in. If k = 0 then this line is not presented in the input.
Output
Print the minimum possible amount of rubles Masha should pay for flour delivery in the only line.
If the bakery can not be opened (while satisfying conditions) in any of the n cities, print - 1 in the only line.
Examples
Input
5 4 2
1 2 5
1 2 3
2 3 4
1 4 10
1 5
Output
3
Input
3 1 1
1 2 3
3
Output
-1
Note 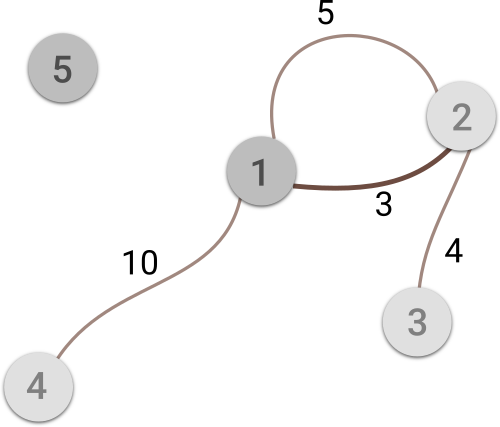
Image illustrates the first sample case. Cities with storage located in and the road representing the answer are darkened.
题意:给你一个无向图,有边权。分成两个集合,问两个集合的最短的距离。
直接的思路,枚举一个集合中的点,相邻的另外一个集合的点的最小边权就是答案。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int Max = 1e5+100;bool vis[Max];int a[Max];vector<pair<int,int> >vp[Max];int main(){ int n,m,k,u,v,w; scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&k); for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++) { scanf("%d %d %d",&u,&v,&w); vp[u].push_back(make_pair(v,w)); vp[v].push_back(make_pair(u,w)); } int ans = -1; memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis)); for(int i = 0;i<k;i++) { scanf("%d",&a[i]); vis[a[i]] = true; } for(int i = 0;i<k;i++) { for(int j = 0;j<vp[a[i]].size();j++) { if(vis[vp[a[i]][j].first]) continue; ans = ans == -1?vp[a[i]][j].second:min(ans,vp[a[i]][j].second); } } printf("%d\n",ans); return 0;}C. Pythagorean Triples
Katya studies in a fifth grade. Recently her class studied right triangles and the Pythagorean theorem. It appeared, that there are triples of positive integers such that you can construct a right triangle with segments of lengths corresponding to triple. Such triples are called Pythagorean triples.
For example, triples (3, 4, 5), (5, 12, 13) and (6, 8, 10) are Pythagorean triples.
Here Katya wondered if she can specify the length of some side of right triangle and find any Pythagorean triple corresponding to such length? Note that the side which length is specified can be a cathetus as well as hypotenuse.
Katya had no problems with completing this task. Will you do the same?
Input
The only line of the input contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 109) — the length of some side of a right triangle.
Output
Print two integers m and k (1 ≤ m, k ≤ 1018), such that n, m and k form a Pythagorean triple, in the only line.
In case if there is no any Pythagorean triple containing integer n, print - 1 in the only line. If there are many answers, print any of them.
Examples
Input
3
Output
4 5
Input
6
Output
8 10
Input
1
Output
-1
Input
17
Output
144 145
Input
67
Output
2244 2245
Note
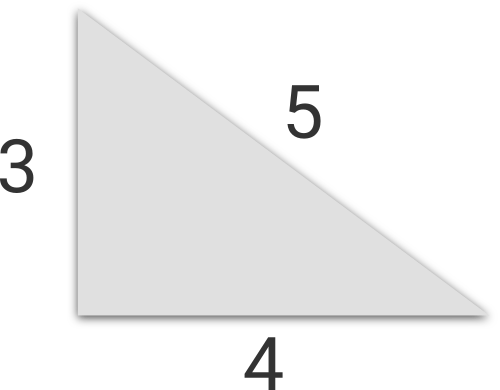
给你直角三角形的一边,求其他的边的长度
显然,当给的边的长度为1和2的时候是不可能的。
当n为奇数的时候
当n为偶数的时候
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int main(){ long long n; cin>>n; if(n == 1 || n==2) cout<<"-1"<<endl; else { if(n&1) { n>>=1; cout<<2*n*n+2*n<<" "<<2*n*n+2*n+1<<endl; } else { n>>=1; cout<<n*n-1<<" "<<n*n+1<<endl; } } return 0;}D. Persistent Bookcase
Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are data structures that always preserves the previous version of itself and access to it when it is modified.
After reaching home Alina decided to invent her own persistent data structure. Inventing didn’t take long: there is a bookcase right behind her bed. Alina thinks that the bookcase is a good choice for a persistent data structure. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf.
The bookcase consists of n shelves, and each shelf has exactly m positions for books at it. Alina enumerates shelves by integers from 1 to n and positions at shelves — from 1 to m. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf in it.
Alina wrote down q operations, which will be consecutively applied to the bookcase. Each of the operations has one of four types:
1 i j — Place a book at position j at shelf i if there is no book at it.2 i j — Remove the book from position j at shelf i if there is a book at it.3 i — Invert book placing at shelf i. This means that from every position at shelf i which has a book at it, the book should be removed, and at every position at shelf i which has not book at it, a book should be placed.4 k — Return the books in the bookcase in a state they were after applying k-th operation. In particular, k = 0 means that the bookcase should be in initial state, thus every book in the bookcase should be removed from its position.After applying each of operation Alina is interested in the number of books in the bookcase. Alina got ‘A’ in the school and had no problem finding this values. Will you do so?
Input
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 103, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the bookcase dimensions and the number of operations respectively.
The next q lines describes operations in chronological order — i-th of them describes i-th operation in one of the four formats described in the statement.
It is guaranteed that shelf indices and position indices are correct, and in each of fourth-type operation the number k corresponds to some operation before it or equals to 0.
Output
For each operation, print the number of books in the bookcase after applying it in a separate line. The answers should be printed in chronological order.
Examples
Input
2 3 3
1 1 1
3 2
4 0
Output
1
4
0
Input
4 2 6
3 2
2 2 2
3 3
3 2
2 2 2
3 2
Output
2
1
3
3
2
4
Input
2 2 2
3 2
2 2 1
Output
2
1
Note
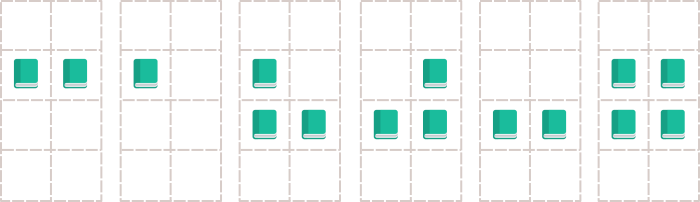
按照时间建树,每次暴力的操作就行。时间复杂度(mq)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#define rr(x) freopen(x,"r",stdin)#define ww(x) freopen(x,"w",stdout)using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const double Pi = acos(-1.0);const double e = exp(1);const int Max = 1e5+100;vector<int>vi[Max];int a[Max],b[Max];int op[Max],ans[Max];bitset<1001>bi[1100];bitset<1001>C;void dfs(int u) { if(u == 0) { for(int i = 0;i<vi[u].size();i++) { ans[vi[u][i]] = ans[u]; dfs(vi[u][i]); } return ; } if(op[u] == 1) { bool flag = false; if(!bi[a[u]][b[u]]) { ans[u]++; flag = true; bi[a[u]][b[u]] = 1; } for(int i = 0; i<vi[u].size();i++) { ans[vi[u][i]] = ans[u]; dfs(vi[u][i]); } if(flag) bi[a[u]][b[u]] = 0; } if(op[u] == 2) { bool flag = false; if(bi[a[u]][b[u]]) { ans[u]--; flag = true; bi[a[u]][b[u]] = 0; } for(int i = 0;i<vi[u].size();i++) { ans[vi[u][i]] = ans[u]; dfs(vi[u][i]); } if(flag) bi[a[u]][b[u]] = 1; } if(op[u] == 3) { ans[u]-=bi[a[u]].count(); bi[a[u]] ^=C; ans[u]+=bi[a[u]].count(); for(int i = 0;i<vi[u].size();i++) { ans[vi[u][i]] = ans[u]; dfs(vi[u][i]); } bi[a[u]] ^=C; } if(op[u] == 4) { for(int i = 0;i<vi[u].size();i++) { ans[vi[u][i]] = ans[u]; dfs(vi[u][i]); } }}int main(){ int n,m,q; scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&q); for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++) C[i] = 1; for(int i = 1;i<=q;i++) { scanf("%d",&op[i]); if(op[i] == 1 || op[i] == 2) { scanf("%d %d",&a[i],&b[i]); } else if(op[i] == 3 || op[i] == 4) { scanf("%d",&a[i]); } if(op[i] == 4) { vi[a[i]].push_back(i); } else vi[i-1].push_back(i); } dfs(0); for(int i = 1;i<= q;i++ ) printf("%d\n",ans[i]); return 0;}- Codeforces Round #368 (DIV 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div.2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- 【codeforces】Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) C
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) Bakery
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) A~D
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) Pythagorean Triples
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) A C
- 关于storybord加视图控制器的代码实现方式
- mysql 数据库通过命令导出数据库文件
- Python读取和写入Excel文件[整]
- 常用的http方法和http响应码详解
- OpenCV使用霍夫变换检测图像中的形状
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
- Linux Socket CAN驱动 <4.接收数据流程>
- 解压包含文件夹的压缩包
- Linux内存管理之页面回收
- Python 下的 return 关键字
- Adidas F50 No matter she has how
- oracle怎样修改表名、列名、字段类型、添加表列、删除表列
- 为什么你有10年经验,但成不了专家?
- The All-purpose Zero


