C语言:哲学家就餐问题
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝上的代理可靠吗 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 05:01
场景:
原版的故事里有五个哲学家(不过我们写的程序可以有N个哲学家),这些哲学家们只做两件事--思考和吃饭,他们思考的时候不需要任何共享资源,但是吃饭的时候就必须使用餐具,而餐桌上的餐具是有限的,原版的故事里,餐具是叉子,吃饭的时候要用两把叉子把面条从碗里捞出来。很显然把叉子换成筷子会更合理,所以:一个哲学家需要两根筷子才能吃饭。
现在引入问题的关键:这些哲学家很穷,只买得起五根筷子。他们坐成一圈,两个人的中间放一根筷子。哲学家吃饭的时候必须同时得到左手边和右手边的筷子。如果他身边的任何一位正在使用筷子,那他只有等着。
假设哲学家的编号是A、B、C、D、E,筷子编号是1、2、3、4、5,哲学家和筷子围成一圈如下图所示:
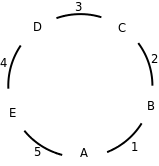
实现代码如下:
#include <pthread.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <errno.h>pthread_mutex_t chopstick[6];void *eat_think(void *arg){char phi = *(char*)arg;int left, right;int i = 0;switch(phi){case 'A':left = 5;right = 1;break;case 'B':left = 1;right = 2;break;case 'C':left = 2;right = 3;break;case 'D':left = 3;right = 4;break;case 'E':left = 4;right = 5;break;default:break;}while(1){sleep(2); //思考pthread_mutex_lock(&chopstick[left]); //拿起左边的筷子printf("Phi %c fetches chopstick %d\n", phi, left);if(pthread_mutex_trylock(&chopstick[right]) == EBUSY) //拿起右边的筷子{pthread_mutex_unlock(&chopstick[left]); //如果右边的筷子被拿走则放下左边的筷子continue;}//pthread_mutex_lock(&chopstick[right]); //如果要观察死锁,则将上一句if注释,再将该行注释取消printf("Phi %c fetch chopstick %d\n", phi, right);printf("Phi %c is eating...\n", phi);sleep(2); //吃饭pthread_mutex_unlock(&chopstick[left]); //放下左边的筷子printf("Phi %c release the chopstick %d\n", phi, left);pthread_mutex_unlock(&chopstick[right]); //放下右边的筷子printf("Phi %c release the chopstick %d\n", phi, right);}}int main(){pthread_t A, B, C, D, E; //五位哲学家int i = 0;for(i = 0; i < 5; ++i){pthread_mutex_init(&chopstick[i], NULL);}pthread_create(&A, NULL, eat_think, "A");pthread_create(&B, NULL, eat_think, "B");pthread_create(&C, NULL, eat_think, "C");pthread_create(&D, NULL, eat_think, "D");pthread_create(&E, NULL, eat_think, "E");pthread_join(A, NULL);pthread_join(B, NULL);pthread_join(C, NULL);pthread_join(D, NULL);pthread_join(E, NULL);return 0;}注意:编译时要加上-lpthread选项,如:gcc eating -o main -lpthread
0 0
- C语言:哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题(C语言实现)
- 哲学家就餐问题 Java语言实现
- linux c学习之哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题 锁
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 关于哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 哲学家就餐问题
- 一维王国问题,最少需要几颗炸弹
- 通过Excel生成批量SQL语句,处理大量数据的好办法
- iOS ScrollView的 contentSize contentInset contentOffset 三个属性直接的区别
- USACO2014Open Gold Cow Optics
- 1min了解ANR
- C语言:哲学家就餐问题
- NOIP提高组【JZOJ4786】小a的强迫症
- Java GDAL开发环境搭建
- RN中RCTScrollView中属性重名
- Android修改系统语言
- 9.最佳实践
- ora-4031原因和解决方法
- HandlerThread
- mysql 联合主键的作用


