Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree __ dfs+剪枝+标记数组
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝单品流量怎么看 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 10:35
A tree is an undirected connected graph without cycles.
Let's consider a rooted undirected tree with n vertices, numbered 1 through n. There are many ways to represent such a tree. One way is to create an array with n integers p1, p2, ..., pn, where pi denotes a parent of vertex i (here, for convenience a root is considered its own parent).
 For this rooted tree the array p is [2, 3, 3, 2].
For this rooted tree the array p is [2, 3, 3, 2].Given a sequence p1, p2, ..., pn, one is able to restore a tree:
- There must be exactly one index r that pr = r. A vertex r is a root of the tree.
- For all other n - 1 vertices i, there is an edge between vertex i and vertex pi.
A sequence p1, p2, ..., pn is called valid if the described procedure generates some (any) rooted tree. For example, for n = 3 sequences(1,2,2), (2,3,1) and (2,1,3) are not valid.
You are given a sequence a1, a2, ..., an, not necessarily valid. Your task is to change the minimum number of elements, in order to get a valid sequence. Print the minimum number of changes and an example of a valid sequence after that number of changes. If there are many valid sequences achievable in the minimum number of changes, print any of them.
The first line of the input contains an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ n).
In the first line print the minimum number of elements to change, in order to get a valid sequence.
In the second line, print any valid sequence possible to get from (a1, a2, ..., an) in the minimum number of changes. If there are many such sequences, any of them will be accepted.
42 3 3 4
12 3 4 4
53 2 2 5 3
03 2 2 5 3
82 3 5 4 1 6 6 7
22 3 7 8 1 6 6 7
In the first sample, it's enough to change one element. In the provided output, a sequence represents a tree rooted in a vertex 4 (because p4 = 4), which you can see on the left drawing below. One of other correct solutions would be a sequence 2 3 3 2, representing a tree rooted in vertex 3(right drawing below). On both drawings, roots are painted red.
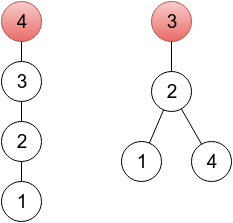
In the second sample, the given sequence is already valid.
Source
Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2)
My Solution
dfs+剪枝+标记数组
找到第一个环把其中的一个点作为 root,然后每个环切去一条边。
找root的时候优先找自环的环,如果有自环的环,则 剩余的环每个环去掉一条边把环连到root上 环的个数 - 1 个操作;
如果没有自环的环,则有 环的个数 个操作。
具体操作 用dfs+标记数组实现,且需要剪枝不然可能有大量重复或者部分重复的dfs
用 bool flag[maxn]表示本次dfs访问过的点,当出现 flag[fatehr[v]] == true 时有环,且flag数组要在dfs回溯的时候重置好,方便下一个dfs使用。
用 bool vis[maxn] 数组标记,每个点在本次运行只访问一次,如果被先前访问过了就continue;
在dfs的时候,如果 flag[father[v]] == false && vis[father[v]] == true,则该点在以前的dfs中(非本次dfs)被访问过,就不用再次访问了。
//因为接下来的部分在先前的dfs中已经处理掉了
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 2e5 + 8;int father[maxn], root, ans;bool flag[maxn], vis[maxn];void _find(int v){ if(flag[father[v]]){ if(root == -1) root = v; father[v] = root; ans++; return; } if(father[v] == v){ return; } flag[v] = true; vis[v] = true; if(!flag[father[v]] && vis[father[v]]){flag[v] = false; return;} //如果该点在以前的dfs中(非本次dfs)被访问过,就不用再次访问了。 //因为接下来的部分在先前的dfs中已经处理掉了 _find(father[v]); flag[v] = false;}int main(){ #ifdef LOCAL freopen("a.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("b.txt", "w", stdout); int T = 4; while(T--){ #endif // LOCAL int n; ans = 0, root = -1; cin >> n; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ cin >> father[i]; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ if(i == father[i]) {if(root == -1) root = i;else ans++; father[i] = root;} } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ if(vis[i]) continue; //如果该点被访问过,就不用再次访问了 if(i != root){ _find(i); } } cout << ans << "\n"; cout << father[1]; for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) cout << " " << father[i]; #ifdef LOCAL memset(vis, false, sizeof vis); cout << endl; } #endif // LOCAL return 0;}Thank you!
------from ProLights
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree __ dfs+剪枝+标记数组
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2)D. Fix a Tree
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree (并查集)
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2)D. Fix a Tree(并查集)
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) Problem D - Fix a Tree(并查集 + 构造)
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree(并查集)
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2)D. Fix a Tree并查集
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree(并查集)(判断圆环)
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree —— 并查集
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D Fix a Tree(并查集)
- Codeforces #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 1) B. Fix a Tree
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D DFS
- MySql 申明变量以及赋值
- Trie树讲解
- AlertDialog以及子类
- 运维笔记3
- C++虚函数与纯虚函数的区别
- Codeforces Round #363 (Div. 2) D. Fix a Tree __ dfs+剪枝+标记数组
- 微信公众号添加菜单
- Python中.split()和.join()方法对比
- JDBC连接数据库
- Jquery中$.get(),$.post(),$.ajax(),$.getJSON()的用法总结
- eclipse编码的设置
- JAVA——request.getParameterMap() 和 request.getInputStream() 不能共用!
- 《项霸传奇》隐私政策
- Ubuntu 14.04主机安装JetPack以及Jetson TX1安装系统教程


