Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) C. Hongcow Builds A Nation 并查集+贪心+组合学、图论、dfs
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝怎么秒杀抢东西 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/21 02:54
Hongcow is ruler of the world. As ruler of the world, he wants to make it easier for people to travel by road within their own countries.
The world can be modeled as an undirected graph with n nodes and m edges. k of the nodes are home to the governments of the kcountries that make up the world.
There is at most one edge connecting any two nodes and no edge connects a node to itself. Furthermore, for any two nodes corresponding to governments, there is no path between those two nodes. Any graph that satisfies all of these conditions is stable.
Hongcow wants to add as many edges as possible to the graph while keeping it stable. Determine the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add.
The first line of input will contain three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 1 000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) — the number of vertices and edges in the graph, and the number of vertices that are homes of the government.
The next line of input will contain k integers c1, c2, ..., ck (1 ≤ ci ≤ n). These integers will be pairwise distinct and denote the nodes that are home to the governments in this world.
The following m lines of input will contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n). This denotes an undirected edge between nodes ui andvi.
It is guaranteed that the graph described by the input is stable.
Output a single integer, the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add to the graph while keeping it stable.
4 1 21 31 2
2
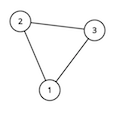
3 3 121 21 32 3
0
For the first sample test, the graph looks like this:
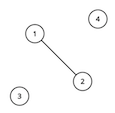
For the second sample test, the graph looks like this:
Source
Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2)
My Solution
题意:有n个点(其中有k个关键点),m条边,要求添加尽可能多的边使得k个关键点之间没有路径,问最多可以添加多少条边。
并查集+贪心+组合学、图论、dfs
用并查集处理这个图,相关联的点构成一颗树,然后把每棵树的结点数储存在该树的根节点上,
然后开始贪心,找出k个关键点里,关键点所在树的结点个数最多的结点 maxci,
然后把这个ci 以及它所关联的点 与 所有没有关键点出现的树相结合(free),形成一个连通块,这个连通块的总边数是 (free + maxcnt) * (free + maxcnt - 1) / 2;
然后剩下的是除了这个maxci之外的有关键点的树,这些树储存的点构成完全图的边数是 if(i != maxci) ans += cnt[_find(c[i])] * (cnt[_find(c[i])] - 1) / 2;
所有得到的ans 是满足条件时的图的总边数,减点输入的m条边, ans - m 即为在合理的情况下可以添加的最大边数
复杂度 O(n^2)
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 1e3 + 8;//有时可能需要 并查集+离散化int father[maxn], _rank[maxn];inline void DisjointSet(int n){ for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){ father[i] = i; }}inline int _find(int v){ return father[v] = father[v] == v ? v : _find(father[v]); //同时压缩路径,有时不能压缩路径,有时必须压缩路径,看具体情况}inline void _merge(int x, int y){ int a = _find(x), b = _find(y); // if(_rank[a] < _rank[b]){ father[a] = b; } else{ father[b] = a; if(_rank[a] == _rank[b]){ _rank[a]++; } }}LL c[maxn], cnt[maxn], maxci;bool flag[maxn];int main(){ #ifdef LOCAL freopen("d.txt", "r", stdin); //freopen("d.out", "w", stdout); int T = 4; while(T--){ #endif // LOCAL ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); int n, m, k, u, v; cin >> n >> m >> k; for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){ cin >> c[i]; } DisjointSet(n); for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ cin >> u >> v; if(_find(u) != _find(v)) _merge(u, v); } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ cnt[_find(i)]++; } LL maxcnt = 0; for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){ if(maxcnt < cnt[_find(c[i])]){ maxcnt = cnt[_find(c[i])]; maxci = i; } flag[_find(c[i])] = true; } LL free = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ if(!flag[i]){ free += cnt[i]; } } LL ans = (free + maxcnt) * (free + maxcnt - 1) / 2; for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){ if(i != maxci){ ans += cnt[_find(c[i])] * (cnt[_find(c[i])] - 1) / 2; } } cout << ans - m << endl; #ifdef LOCAL memset(flag, false, sizeof flag); memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt); cout << endl; } #endif // LOCAL return 0;}Thank you!
------from ProLights
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) C. Hongcow Builds A Nation 并查集+贪心+组合学、图论、dfs
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2)C. Hongcow Builds A Nation【并查集+贪心】好题~
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) -- C. Hongcow Builds A Nation(并查集)
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 1)A. Hongcow Builds A Nation
- 745 C. Hongcow Builds A Nation codeforces (并查集)
- Codeforces 745C - Hongcow Builds A Nation 并查集乱搞,注意路径压缩
- CodeForces 744A Hongcow Builds A Nation (并查集)
- CodeForces - 744A Hongcow Builds A Nation (并查集+容斥)
- 并查集——Codeforces744A Hongcow Builds A Nation
- Codeforces 745C Hongcow Builds A Nation
- Hongcow Builds A Nation CodeForces
- 【26.42%】【codeforces 745C】Hongcow Builds A Nation
- Codefocres 744A Hongcow Builds A Nation(并查集记录树上结点数)
- CodeForces - 744A Hongcow Builds A Nation
- CF745C_Hongcow Builds A Nation(并查集+贪心)
- CodeForces745C C - Hongcow Builds A Nation 图论+容斥
- Codeforces Round #376 (Div. 2) C dfs+并查集
- Codeforces Round #369 (Div. 2) D. Directed Roads 图论、组合学、二重dfs、并查集形式的图、Interesting、好题
- Linux Shell编程入门
- MySQL command Line 中命令无效解决
- 练习
- java多线程基础知识(一)
- Altium Designer初试-贴片51系统板
- Codeforces Round #385 (Div. 2) C. Hongcow Builds A Nation 并查集+贪心+组合学、图论、dfs
- App Shortcuts 快捷方式 Android7.1 的"3D Touch"
- 优化MYSchool数据库设计第三章
- JS中全局变量和局部变量
- GD库基础
- 乐观锁和悲观锁
- 自动驾驶全球布局(3)传统汽车厂商
- ListView真的过时了吗?
- 理解镜像和容器,并运行whalesay镜像


