第36篇 Asp.Net源码解析(一)
来源:互联网 发布:阿里云cdn隐藏ip 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/29 16:39
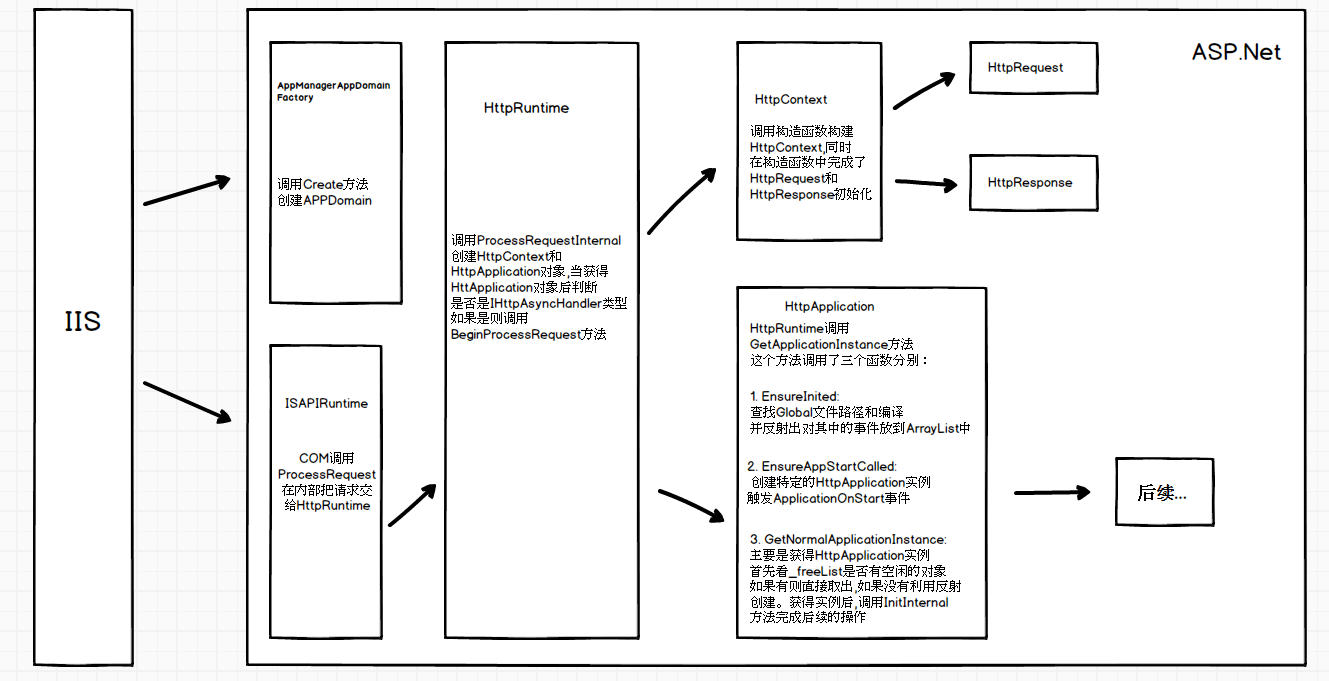
上面两篇文章说了http协议和IIS处理,这次说下当IIS把请求交给Asp.net后的过程。
AppManagerAppDomainFactory
当IIS把请求交给asp.net时候,如果AppDomain还不存在则创建APPDomain,将AppDomain指派给与请求对应的应用程序,这通过AppManagerAppDomainFactory类中的Create方法实现,代码如下:
public Object Create(String appId, String appPath) { try { if (appPath[0] == '.') { System.IO.FileInfo file = new System.IO.FileInfo(appPath); appPath = file.FullName; } if (!StringUtil.StringEndsWith(appPath, '\\')) { appPath = appPath + "\\"; } ... ISAPIApplicationHost appHost = new ISAPIApplicationHost(appId, appPath,false); //创建环境,包括编译环境 ISAPIRuntime isapiRuntime = (ISAPIRuntime)_appManager.CreateObjectInternal(appId, typeof(ISAPIRuntime), appHost, false, null); isapiRuntime.StartProcessing(); return new ObjectHandle(isapiRuntime); } catch (Exception e) { ... } }创建完成后,非托管代码开始调用 ISAPIRuntime 中ProcessRequest方法(通过COM调用 )
ISAPIRuntime--asp.net入口
首先看下ISAPIRuntime中的ProcessRequest方法签名
public int ProcessRequest(IntPtr ecb, int iWRType);ProcessRequest有两个参数,一个是请求报文的ecb句柄,一个请求的类型,在运行的过程中,ecb首先被再次封装成托管资源的请求报文wr。 把封装好的代码传递给HttpRuntime类中的ProcessRequestNoDemand. 核心代码如下:
bool useOOP = (iWRType == WORKER_REQUEST_TYPE_OOP); wr = ISAPIWorkerRequest.CreateWorkerRequest(ecb, useOOP); wr.Initialize(); // check if app path matches (need to restart app domain?) String wrPath = wr.GetAppPathTranslated(); String adPath = HttpRuntime.AppDomainAppPathInternal; if (adPath == null || StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(wrPath, adPath)) { HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestNoDemand(wr); return 0; } else { // need to restart app domain HttpRuntime.ShutdownAppDomain(ApplicationShutdownReason.PhysicalApplicationPathChanged, SR.GetString(SR.Hosting_Phys_Path_Changed, adPath, wrPath)); return 1; }
HttpRuntime
HttpRuntime收到传递过来的HttpWorkerRequest类的实例对象wr,通过调用当前类中的ProcessRequestNow方法,把参数传递给ProcessRequestInternal(ProcessRequestNow的调用了ProcessRequestInternal)。
internal static void ProcessRequestNoDemand(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { RequestQueue rq = _theRuntime._requestQueue; wr.UpdateInitialCounters(); if (rq != null) // could be null before first request wr = rq.GetRequestToExecute(wr); if (wr != null) { CalculateWaitTimeAndUpdatePerfCounter(wr); wr.ResetStartTime(); ProcessRequestNow(wr); } } internal static void ProcessRequestNow(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { _theRuntime.ProcessRequestInternal(wr); }在ProcessRequestInternal中,创建了HttpContext和HttpApplication对象实例,核心代码如下
private void ProcessRequestInternal(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { ... // Construct the Context on HttpWorkerRequest, hook everything together HttpContext context; try { context = new HttpContext(wr, false /* initResponseWriter */); } catch { ... } ... try { ... // Get application instance IHttpHandler app = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(context); if (app == null) throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Unable_create_app_object)); ... if (app is IHttpAsyncHandler) { // asynchronous handler IHttpAsyncHandler asyncHandler = (IHttpAsyncHandler)app; context.AsyncAppHandler = asyncHandler; asyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest(context, _handlerCompletionCallback, context); } else { // synchronous handler app.ProcessRequest(context); FinishRequest(context.WorkerRequest, context, null); } } catch (Exception e) { ... } }在ProcessRequestInternal方法的内部,实现对HttpContext类和HttpApplicationFactory的对象实例的创建,核心代码: 根据上面代码,当获得HttApplication对象后,判断是否是IHttpAsyncHandler类型,如果是则调用BeginProcessRequest方法,此处的if条件是一直成立的,因为HttpApplication实现了IHttpAsyncHandler接口,而ProcessRequest方法的实现也仅仅是抛出了一个异常,笔者觉得此处应该是微软留了一个扩展的地方。
public class HttpApplication:IComponent,IHttpAsyncHandler, IRequestCompletedNotifier, ISyncContext { ... }void IHttpHandler.ProcessRequest(HttpContext context) { throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Sync_not_supported)); }
HttpContext对象
这个对象是一个请求响应的结合体,里面包含了HttpRequest和HttpResponse对象,在构造HttpContext对象时,同时也对HttpRequest和HttpResponse也进行了初始化,代码如下:
internal HttpContext(HttpWorkerRequest wr, bool initResponseWriter) { _wr = wr; Init(new HttpRequest(wr, this), new HttpResponse(wr, this)); if (initResponseWriter) _response.InitResponseWriter(); PerfCounters.IncrementCounter(AppPerfCounter.REQUESTS_EXECUTING); }创建HttpApplication
通过HttpApplicationFactory中的静态方法GetApplicationInstance来获得实例对象(常用的工厂模式),在创建对象的时候调用了 _theApplicationFactory.GetNormalApplicationInstance(context);方法(其中context形参是上文创建的HttpContext)来执行实例化操作,核心代码如下:
internal static IHttpHandler GetApplicationInstance(HttpContext context) { if (_customApplication != null) return _customApplication; // Check to see if it's a debug auto-attach request if (context.Request.IsDebuggingRequest) return new HttpDebugHandler(); _theApplicationFactory.EnsureInited(); _theApplicationFactory.EnsureAppStartCalled(context); return _theApplicationFactory.GetNormalApplicationInstance(context); } 这个方法里有三个方法的调用,分别是:
i. _theApplicationFactory.EnsureInited()
主要功能是对Global.asxc文件进行编译和处理,并反射出对其中的事件,放到ArrayList中,核心代码如下:
找到global.asax路径进行编译
private void Init() { if (_customApplication != null) return; try { try { _appFilename = GetApplicationFile(); CompileApplication(); } finally { SetupChangesMonitor(); } } catch { throw; } }调用ReflectOnApplicationType方法把事件装入ArrayList
private void CompileApplication() { _theApplicationType = BuildManager.GetGlobalAsaxType(); BuildResultCompiledGlobalAsaxType result = BuildManager.GetGlobalAsaxBuildResult(); if (result != null) { if (result.HasAppOrSessionObjects) { GetAppStateByParsingGlobalAsax(); } _fileDependencies = result.VirtualPathDependencies; } if (_state == null) { _state = new HttpApplicationState(); } ReflectOnApplicationType(); } private void ReflectOnApplicationType() { ArrayList handlers = new ArrayList(); MethodInfo[] methods; // get this class methods methods = _theApplicationType.GetMethods(BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Static); foreach (MethodInfo m in methods) { if (ReflectOnMethodInfoIfItLooksLikeEventHandler(m)) handlers.Add(m); } Type baseType = _theApplicationType.BaseType; if (baseType != null && baseType != typeof(HttpApplication)) { methods = baseType.GetMethods(BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Static); foreach (MethodInfo m in methods) { if (m.IsPrivate && ReflectOnMethodInfoIfItLooksLikeEventHandler(m)) handlers.Add(m); } } _eventHandlerMethods = new MethodInfo[handlers.Count]; for (int i = 0; i < _eventHandlerMethods.Length; i++) _eventHandlerMethods[i] = (MethodInfo)handlers[i]; }ii. _theApplicationFactory.EnsureAppStartCalled(context)
创建特定的HttpApplication实例,触发ApplicationOnStart事件,执行ASP.global_asax中的Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)方法。这里创建的HttpApplication实例在处理完事件后,就被回收。 具体实现:
private void EnsureAppStartCalled(HttpContext context) { if (!_appOnStartCalled) { lock (this) { if (!_appOnStartCalled) { using (new DisposableHttpContextWrapper(context)) { // impersonation could be required (UNC share or app credentials) WebBaseEvent.RaiseSystemEvent(this, WebEventCodes.ApplicationStart); // fire outside of impersonation as HttpApplication logic takes // care of impersonation by itself FireApplicationOnStart(context); } _appOnStartCalled = true; } } } } iii. _theApplicationFactory.GetNormalApplicationInstance(context);
主要是获得HttpApplication实例,首先从队列中去取,如果取出为空,则利用反射创建,调用InitInternal方法
private HttpApplication GetNormalApplicationInstance(HttpContext context) { HttpApplication app = null; lock (_freeList) { if (_numFreeAppInstances > 0) { app = (HttpApplication)_freeList.Pop(); _numFreeAppInstances--; if (_numFreeAppInstances < _minFreeAppInstances) { _minFreeAppInstances = _numFreeAppInstances; } } } if (app == null) { // If ran out of instances, create a new one app = (HttpApplication)HttpRuntime.CreateNonPublicInstance(_theApplicationType); using (new ApplicationImpersonationContext()) { // 调用BuildSteps和获得所有的HttpModule app.InitInternal(context, _state, _eventHandlerMethods); } } if (AppSettings.UseTaskFriendlySynchronizationContext) { // When this HttpApplication instance is no longer in use, recycle it. app.ApplicationInstanceConsumersCounter = new CountdownTask(1); // representing required call to HttpApplication.ReleaseAppInstance app.ApplicationInstanceConsumersCounter.Task.ContinueWith((_, o) => RecycleApplicationInstance((HttpApplication)o), app, TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously); } return app; }从代码中可以分析到,在HttpApplication创建的过程中,是有一个_freeList的一个堆栈来控制的。当对象创建成功后,执行app.InitInternal(context, _state, _eventHandlerMethods)来进行后续的操作。整个的代码流程,可以理解成以下过程:
源码git地址:https://github.com/fuwei199006/Source/tree/master/dotnet46/Source
写于 2017.03.07
- 第36篇 Asp.Net源码解析(一)
- 第36篇 Asp.Net源码解析(一)
- 第36篇 Asp.Net源码解析(一)
- 第36篇 Asp.Net源码解析(一)
- 第36篇 Asp.Net源码解析(二)--详解HttpApplication
- ASP.NET MVC 音乐商店源码解析
- ASP.Net常见技术疑难解析(一)
- Asp.net生成二维码和解析二维码源码
- Android源码解析Handler系列第(一)篇 --- Message全局池
- Android源码解析Handler系列第(一)篇 --- Message全局池
- Asp.net简单ORM示例源码详细讲解一
- 一印度学生Asp.net源码分享讨论
- ASP.NET MVC 6源码分析(一)
- ASP.NET Google Maps Javascript API V3 实战基础篇一地址解析
- ASP.NET Google Maps Javascript API V3 实战基础篇一反向地址解析
- asp.net 源码网站
- ASP.NET源码网站
- asp.net门户源码
- Oracle DB内存分配: 使用HugePage、tmpfs
- 有效的数据传输zero copy
- [php入门]使用wampserver配置php开发环境
- C++ const与指针之间组合的辨析
- JavaWeb学习(七)
- 第36篇 Asp.Net源码解析(一)
- 用Java命令执行jar包
- 深入理解android service的基本知识
- 坐公交车学习(一) Java设计模式之一:工厂类模式
- 日期倒计时
- 子网掩码
- Android Studio 2.3正式版发布;Android8.0或命名为奥利奥
- 一道HOJ上的题--Mixing milk
- 洛谷1419 寻找段落(单调队列+二分)


