python 线性回归示例
来源:互联网 发布:java开发安卓app 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/18 02:09
说明:此文的第一部分参考了这里
用python进行线性回归分析非常方便,有现成的库可以使用比如:numpy.linalog.lstsq例子、scipy.stats.linregress例子、pandas.ols例子等。
不过本文使用sklearn库的linear_model.LinearRegression,支持任意维度,非常好用。
一、二维直线的例子
预备知识:线性方程
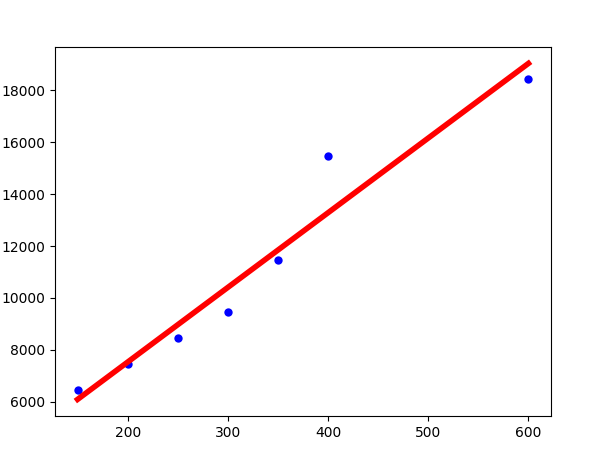
下面的例子中,我们根据房屋面积、房屋价格的历史数据,建立线性回归模型。
然后,根据给出的房屋面积,来预测房屋价格。这里是数据来源
import pandas as pdfrom io import StringIOfrom sklearn import linear_modelimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 房屋面积与价格历史数据(csv文件)csv_data = 'square_feet,price\n150,6450\n200,7450\n250,8450\n300,9450\n350,11450\n400,15450\n600,18450\n'# 读入dataframedf = pd.read_csv(StringIO(csv_data))print(df)# 建立线性回归模型regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()# 拟合regr.fit(df['square_feet'].reshape(-1, 1), df['price']) # 注意此处.reshape(-1, 1),因为X是一维的!# 不难得到直线的斜率、截距a, b = regr.coef_, regr.intercept_# 给出待预测面积area = 238.5# 方式1:根据直线方程计算的价格print(a * area + b)# 方式2:根据predict方法预测的价格print(regr.predict(area))# 画图# 1.真实的点plt.scatter(df['square_feet'], df['price'], color='blue')# 2.拟合的直线plt.plot(df['square_feet'], regr.predict(df['square_feet'].reshape(-1,1)), color='red', linewidth=4)plt.show()
二、三维平面的例子
预备知识:线性方程
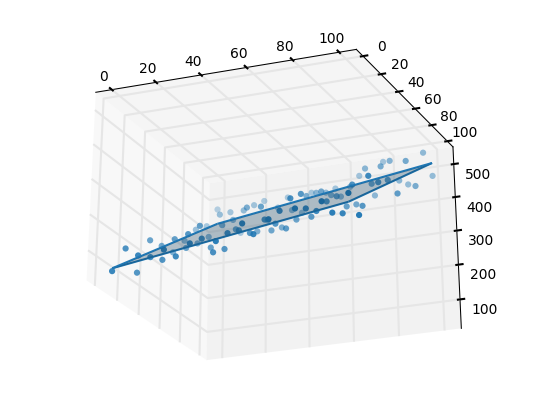
由于找不到真实数据,只好自己虚拟一组数据。
import numpy as npfrom sklearn import linear_modelfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltxx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(0,10,10), np.linspace(0,100,10))zz = 1.0 * xx + 3.5 * yy + np.random.randint(0,100,(10,10))# 构建成特征、值的形式X, Z = np.column_stack((xx.flatten(),yy.flatten())), zz.flatten()# 建立线性回归模型regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()# 拟合regr.fit(X, Z)# 不难得到平面的系数、截距a, b = regr.coef_, regr.intercept_# 给出待预测的一个特征x = np.array([[5.8, 78.3]])# 方式1:根据线性方程计算待预测的特征x对应的值z(注意:np.sum)print(np.sum(a * x) + b)# 方式2:根据predict方法预测的值zprint(regr.predict(x))# 画图fig = plt.figure()ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')# 1.画出真实的点ax.scatter(xx, yy, zz)# 2.画出拟合的平面ax.plot_wireframe(xx, yy, regr.predict(X).reshape(10,10))ax.plot_surface(xx, yy, regr.predict(X).reshape(10,10), alpha=0.3)plt.show()
效果图
0 0
- python 线性回归示例
- python线性回归示例
- 多元线性回归示例
- spark python 线性回归
- python 求线性回归
- 线性回归python实现
- 线性回归---Python实现
- python 自定义线性回归
- Python 线性回归
- 线性回归的python实现
- Python线性回归学习笔记
- 用python实现线性回归
- python 线性回归 预测数据
- python实现简单线性回归
- 使用python、numpy线性回归
- Python线性回归实例--Python,sklearn,LinearRegression
- 通俗易懂地介绍梯度下降法(以线性回归为例,配以Python示例代码)
- python 梯度下降应用于线性回归
- PCIe学习笔记(8)--- 配置地址空间
- @RestController
- Vue学习之路---No.2(分享心得,欢迎批评指正)
- CoreSeek(Sphinx)配置文件详细解释
- 人工智能与人类世界的迷思
- python 线性回归示例
- xutils 数据库
- java提高篇-----HashMap
- Android UI开发----国际化
- ThinkPHP5的权限控制Auth
- Linux系统MySQL开启远程连接
- Android的Activity的四种启动模式
- Linux操作系统哪个版本最好用?
- Fragment详解之一——概述


