Codeforces 599C Day at the Beach【思维+优先队列】
来源:互联网 发布:华硕超频软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/30 16:09
One day Squidward, Spongebob and Patrick decided to go to the beach. Unfortunately, the weather was bad, so the friends were unable to ride waves. However, they decided to spent their time building sand castles.
At the end of the day there were n castles built by friends. Castles are numbered from1 to n, and the height of thei-th castle is equal to hi. When friends were about to leave, Squidward noticed, that castles are not ordered by their height, and this looks ugly. Now friends are going to reorder the castles in a way to obtain that conditionhi ≤ hi + 1 holds for alli from 1 to n - 1.
Squidward suggested the following process of sorting castles:
- Castles are split into blocks — groups ofconsecutive castles. Therefore the block fromi to j will include castlesi, i + 1, ..., j. A block may consist of a single castle.
- The partitioning is chosen in such a way that every castle is a part of exactly one block.
- Each block is sorted independently from other blocks, that is the sequence hi, hi + 1, ..., hj becomes sorted.
- The partitioning should satisfy the condition that after each block is sorted, the sequencehi becomes sorted too. This may always be achieved by saying that the whole sequence is a single block.
Even Patrick understands that increasing the number of blocks in partitioning will ease the sorting process. Now friends ask you to count the maximum possible number of blocks in a partitioning that satisfies all the above requirements.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of castles Spongebob, Patrick and Squidward made from sand during the day.
The next line contains n integers hi (1 ≤ hi ≤ 109). Thei-th of these integers corresponds to the height of thei-th castle.
Print the maximum possible number of blocks in a valid partitioning.
31 2 3
3
42 1 3 2
2
In the first sample the partitioning looks like that: [1][2][3].

In the second sample the partitioning is: [2, 1][3, 2]
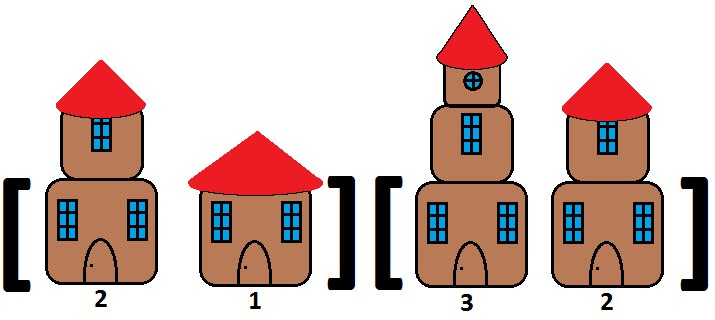
给你N个楼房的高度,我们需要对这N个楼房进行分块,我们想要分出尽可能多的块,使得各自块内的楼房按照从小到大排序之后,最终的整个序列也是非递减的。
思路:
1、分块具有线性特点,那么我们考虑O(n)枚举一个分块的终点,如果当前i作为一个可行终点出现,那么我们一定要将这个点置为一个分块的终点,因为我们想要尽可能多的分块。
2、那么考虑如何使得i算作一个可行终点。
我们考虑两个相邻分块:
【L1,R1】,【L2,R2】;
其一定是max【L1,R1】<=min【L2,R2】的。
那么我们枚举到的一点i,如果有max【上一个分块的终点+1,i】<=min【i+1,n】,那么肯定这个点i是可以作为一个分块的终点出现的。
那么对应output++.
过程维护一下即可。
这里可以维护一个后缀最小值,也可以拿优先队列动态维护一下均可。
Ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>#include<queue>using namespace std;struct node{ int val,pos; friend bool operator <(node a,node b) { if(a.val==b.val)return a.pos<b.pos; else return a.val>b.val; }}a[105000],now;int main(){ int n; while(~scanf("%d",&n)) { priority_queue<node >s; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&a[i].val); a[i].pos=i; s.push(a[i]); } int maxn=0; int output=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { maxn=max(maxn,a[i].val); node now; int flag=0; while(!s.empty()) { now=s.top(); if(now.pos<=i)s.pop(); else { flag=1; break; } } if(flag==1) { now=s.top(); if(now.val>=maxn) { output++; maxn=0; } } } printf("%d\n",output+1); }}- Codeforces 599C Day at the Beach【思维+优先队列】
- Codeforces 599C Day at the Beach 【思维】
- codeforces 599 C. Day at the Beach【思维】
- codeforces 599C Day at the Beach
- Codeforces 599 C. Day at the Beach
- CodeForces 599C Day at the Beach
- Codeforces 599 C Day at the Beach
- Codeforces 599C Day at the Beach
- CodeForces 599C Day at the Beach
- codeforces 559C Day at the Beach
- CodeForces 599C Day at the Beach(RMQ)
- CodeForces 599 C. Day at the Beach(贪心)
- codeforce 599C Day at the Beach
- Codeforces #332 C. Day at the Beach (贪心)
- Codeforces Round #332 (Div. 2) C. Day at the Beach
- Codeforces Round #332 (Div. 2) C. Day at the Beach
- Codeforces Round #332 (Div. 2) C. Day at the Beach
- Codeforces Round #332 (Div. 2) C. Day at the Beach
- 加密解密
- git改变历史
- [蓝桥杯官网测试题] 入门训练
- Q91:真实地模拟透明材质(Realistic Transparency)
- 经典排序算法
- Codeforces 599C Day at the Beach【思维+优先队列】
- js基础10-应用案例
- 替罪羊树 板子
- C++编译与链接
- linux进入一个目录以及在目录中创建文件所需要的权限
- 单例模式
- spring-data-jpa更新实体
- C3p0数据库连接池的使用
- 几种按键扫描软件处理方法


