PCL点云特征描述与提取(4)
来源:互联网 发布:大数据架构设计 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/06 04:07
如何从一个深度图像(range image)中提取NARF特征
代码解析narf_feature_extraction.cpp
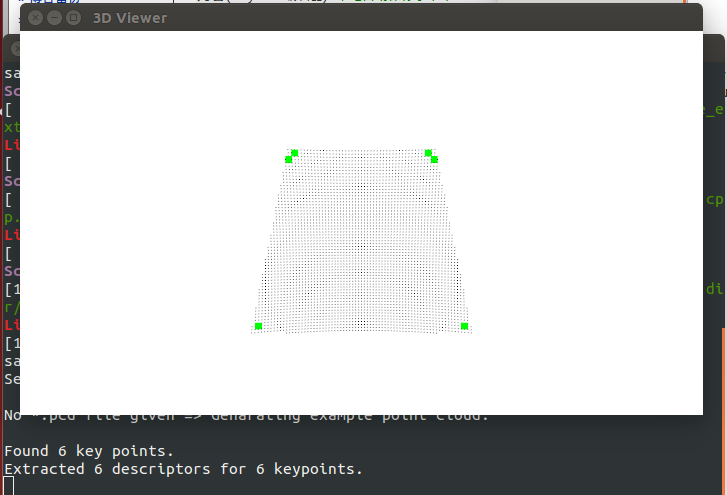
#include <iostream>#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>#include <pcl/range_image/range_image.h>#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>#include <pcl/visualization/range_image_visualizer.h>#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>#include <pcl/features/range_image_border_extractor.h>#include <pcl/keypoints/narf_keypoint.h>#include <pcl/features/narf_descriptor.h>#include <pcl/console/parse.h>typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;//参数的设置float angular_resolution = 0.5f;float support_size = 0.2f;pcl::RangeImage::CoordinateFrame coordinate_frame = pcl::RangeImage::CAMERA_FRAME;bool setUnseenToMaxRange = false;bool rotation_invariant = true;//命令帮助void printUsage (const char* progName){ std::cout << "\n\nUsage: "<<progName<<" [options] <scene.pcd>\n\n" << "Options:\n" << "-------------------------------------------\n" << "-r <float> angular resolution in degrees (default "<<angular_resolution<<")\n" << "-c <int> coordinate frame (default "<< (int)coordinate_frame<<")\n" << "-m Treat all unseen points to max range\n" << "-s <float> support size for the interest points (diameter of the used sphere - " "default "<<support_size<<")\n" << "-o <0/1> switch rotational invariant version of the feature on/off" << " (default "<< (int)rotation_invariant<<")\n" << "-h this help\n" << "\n\n";}void setViewerPose (pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer& viewer, const Eigen::Affine3f& viewer_pose)//setViewerPose{ Eigen::Vector3f pos_vector = viewer_pose * Eigen::Vector3f (0, 0, 0); Eigen::Vector3f look_at_vector = viewer_pose.rotation () * Eigen::Vector3f (0, 0, 1) + pos_vector; Eigen::Vector3f up_vector = viewer_pose.rotation () * Eigen::Vector3f (0, -1, 0); viewer.setCameraPosition (pos_vector[0], pos_vector[1], pos_vector[2], look_at_vector[0], look_at_vector[1], look_at_vector[2], up_vector[0], up_vector[1], up_vector[2]);}int main (int argc, char** argv){ // 设置参数检测 if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-h") >= 0) { printUsage (argv[0]); return 0; } if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-m") >= 0) { setUnseenToMaxRange = true; cout << "Setting unseen values in range image to maximum range readings.\n"; } if (pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-o", rotation_invariant) >= 0) cout << "Switching rotation invariant feature version "<< (rotation_invariant ? "on" : "off")<<".\n"; int tmp_coordinate_frame; if (pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-c", tmp_coordinate_frame) >= 0) { coordinate_frame = pcl::RangeImage::CoordinateFrame (tmp_coordinate_frame); cout << "Using coordinate frame "<< (int)coordinate_frame<<".\n"; } if (pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-s", support_size) >= 0) cout << "Setting support size to "<<support_size<<".\n"; if (pcl::console::parse (argc, argv, "-r", angular_resolution) >= 0) cout << "Setting angular resolution to "<<angular_resolution<<"deg.\n"; angular_resolution = pcl::deg2rad (angular_resolution); //打开一个磁盘中的.pcd文件 但是如果没有指定就会自动生成 pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr point_cloud_ptr (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>); pcl::PointCloud<PointType>& point_cloud = *point_cloud_ptr; pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithViewpoint> far_ranges; Eigen::Affine3f scene_sensor_pose (Eigen::Affine3f::Identity ()); std::vector<int> pcd_filename_indices = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, "pcd"); if (!pcd_filename_indices.empty ()) //检测是否有far_ranges.pcd { std::string filename = argv[pcd_filename_indices[0]]; if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (filename, point_cloud) == -1) { cerr << "Was not able to open file \""<<filename<<"\".\n"; printUsage (argv[0]); return 0; } scene_sensor_pose = Eigen::Affine3f (Eigen::Translation3f (point_cloud.sensor_origin_[0], point_cloud.sensor_origin_[1], point_cloud.sensor_origin_[2])) * Eigen::Affine3f (point_cloud.sensor_orientation_); std::string far_ranges_filename = pcl::getFilenameWithoutExtension (filename)+"_far_ranges.pcd"; if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (far_ranges_filename.c_str (), far_ranges) == -1) std::cout << "Far ranges file \""<<far_ranges_filename<<"\" does not exists.\n"; } else { setUnseenToMaxRange = true; cout << "\nNo *.pcd file given => Genarating example point cloud.\n\n"; for (float x=-0.5f; x<=0.5f; x+=0.01f) //如果没有打开的文件就生成一个矩形的点云 { for (float y=-0.5f; y<=0.5f; y+=0.01f) { PointType point; point.x = x; point.y = y; point.z = 2.0f - y; point_cloud.points.push_back (point); } } point_cloud.width = (int) point_cloud.points.size (); point_cloud.height = 1; } //从点云中建立生成深度图 float noise_level = 0.0; float min_range = 0.0f; int border_size = 1; boost::shared_ptr<pcl::RangeImage> range_image_ptr (new pcl::RangeImage); pcl::RangeImage& range_image = *range_image_ptr; range_image.createFromPointCloud (point_cloud, angular_resolution, pcl::deg2rad (360.0f), pcl::deg2rad (180.0f), scene_sensor_pose, coordinate_frame, noise_level, min_range, border_size); range_image.integrateFarRanges (far_ranges); if (setUnseenToMaxRange) range_image.setUnseenToMaxRange (); //打开3D viewer并加入点云 pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer ("3D Viewer"); viewer.setBackgroundColor (1, 1, 1); pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointWithRange> range_image_color_handler (range_image_ptr, 0, 0, 0); viewer.addPointCloud (range_image_ptr, range_image_color_handler, "range image"); viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "range image"); //viewer.addCoordinateSystem (1.0f, "global"); //PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointType> point_cloud_color_handler (point_cloud_ptr, 150, 150, 150); //viewer.addPointCloud (point_cloud_ptr, point_cloud_color_handler, "original point cloud"); viewer.initCameraParameters (); setViewerPose (viewer, range_image.getTransformationToWorldSystem ()); //显示 pcl::visualization::RangeImageVisualizer range_image_widget ("Range image"); range_image_widget.showRangeImage (range_image); //提取NARF特征 pcl::RangeImageBorderExtractor range_image_border_extractor; //申明深度图边缘提取器 pcl::NarfKeypoint narf_keypoint_detector; //narf_keypoint_detector为点云对象 narf_keypoint_detector.setRangeImageBorderExtractor (&range_image_border_extractor); narf_keypoint_detector.setRangeImage (&range_image); narf_keypoint_detector.getParameters ().support_size = support_size; //获得特征提取的大小 pcl::PointCloud<int> keypoint_indices; narf_keypoint_detector.compute (keypoint_indices); std::cout << "Found "<<keypoint_indices.points.size ()<<" key points.\n"; // ---------------------------------------------- // -----Show keypoints in range image widget----- // ---------------------------------------------- //for (size_t i=0; i<keypoint_indices.points.size (); ++i) //range_image_widget.markPoint (keypoint_indices.points[i]%range_image.width, //keypoint_indices.points[i]/range_image.width); //在3Dviewer显示提取的特征信息 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr keypoints_ptr (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>& keypoints = *keypoints_ptr; keypoints.points.resize (keypoint_indices.points.size ()); for (size_t i=0; i<keypoint_indices.points.size (); ++i) keypoints.points[i].getVector3fMap () = range_image.points[keypoint_indices.points[i]].getVector3fMap (); pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> keypoints_color_handler (keypoints_ptr, 0, 255, 0); viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> (keypoints_ptr, keypoints_color_handler, "keypoints"); viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 7, "keypoints"); //在关键点提取NARF描述子 std::vector<int> keypoint_indices2; keypoint_indices2.resize (keypoint_indices.points.size ()); for (unsigned int i=0; i<keypoint_indices.size (); ++i) // This step is necessary to get the right vector type keypoint_indices2[i]=keypoint_indices.points[i]; ///建立NARF关键点的索引向量,此矢量作为NARF特征计算的输入来使用 pcl::NarfDescriptor narf_descriptor (&range_image, &keypoint_indices2);//创建narf_descriptor对象。并给了此对象输入数据(特征点索引和深度像) narf_descriptor.getParameters ().support_size = support_size;//support_size确定计算描述子时考虑的区域大小 narf_descriptor.getParameters ().rotation_invariant = rotation_invariant; //设置旋转不变的NARF描述子 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Narf36> narf_descriptors; //创建Narf36的点类型输入点云对象并进行实际计算 narf_descriptor.compute (narf_descriptors); //计算描述子 cout << "Extracted "<<narf_descriptors.size ()<<" descriptors for " //打印输出特征点的数目和提取描述子的数目 <<keypoint_indices.points.size ()<< " keypoints.\n"; //主循环函数 while (!viewer.wasStopped ()) { range_image_widget.spinOnce (); // process GUI events viewer.spinOnce (); pcl_sleep(0.01); }}
编译运行./narf_feature_extraction -m
这将自动生成一个呈矩形的点云,检测的特征点处在角落处,参数-m是必要的,因为矩形周围的区域观测不到,但是属于边界部分,因此系统无法检测到这部分区域的特征点,选项-m将看不到的区域改变到最大范围读取,从而使系统能够使用这些边界区域。
(2)特征描述算子算法基准化分析
使用FeatureEvaluationFramework类对不同的特征描述子算法进行基准测试,基准测试框架可以测试不同种类的特征描述子算法,通过选择输入点云,算法参数,下采样叶子大小,搜索阀值等独立变量来进行测试。
使用FeatureCorrespondenceTest类执行一个单一的“基于特征的对应估计测试”执行以下的操作
1.FeatureCorrespondenceTest类取两个输入点云(源与目标) 它将指定算法和参数,在每个点云中计算特征描述子
2.基于n_D特征空间中的最近邻元素搜索,源点云中的每个特征将和目标点云中对应的特征相对照
3 。对于每一个点,系统将把估计的目标点的三维位置和之前已知的实际位置相比
4 。如果这两个点很接近(取决与决定的阀值)那么对应就成功,否则失败
5 计算并保存成功和失败的总数,以便进一步分析
微信公众号号可扫描二维码一起共同学习交流

0 0
- PCL点云特征描述与提取(4)
- PCL点云特征描述与提取(1)
- PCL点云特征描述与提取(2)
- PCL点云特征描述与提取(3)
- PCL点特征描述与提取
- 《PCL点云库学习&VS2010(X64)》Part 11 PCL1.72(VTK6.2.0)点特征描述与提取
- PCL:描述三维离散点的ROPS特征(Code)
- 图像特征提取与描述
- PCL特征点与配准(1)
- 特征点提取与匹配
- 《python+opencv实践》四、图像特征提取与描述——30Harris 角点检测
- SIFT特征提取与描述算法
- 图像局部不变性特征提取与描述
- OpenCV4Android 提取特征点描述符(Feature Descriptor)
- 【图像特征提取6】ORB特征点的描述----BRIEF描述子
- 【openCV】特征点提取与匹
- 特征点的提取与匹配
- ORB特征点检测与描述详解
- PCL点云特征描述与提取(1)
- Unknown system variable 'tx_read_only'
- PCL点云特征描述与提取(2)
- window7和虚拟机直接共享文件夹
- PCL点云特征描述与提取(3)
- PCL点云特征描述与提取(4)
- PCL点云曲面重建(1)
- PCL点云变换与移除NaN
- PCL点云配准(1)
- 业务与产品
- PCL点云配准(2)
- 谷歌draco
- K-means算法及OpenCV实现
- PCL的PNG文件和计算点云重心


