Python 绘制函数图形
来源:互联网 发布:手机网络共享怎么设置 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/21 15:16
1安装依赖库
2.实验一个例子
import pylab as pl
x=list(range(0,6))
y=[]
for index in x:
y.append(x[index]*x[index])
pl.plot(x,y)
pl.title("y=x*x")
pl.xlabel('x')
pl.ylabel('y')
pl.xlim(0.0,7.0)
pl.ylim(0.0,40.0)
pl.show()
转载一个网友
>>> import pylab as pl
1 安装numpy和matplotlib
>>> import numpy
>>> numpy.__version__
>>> import matplotlib
>>> matplotlib.__version__
2 两种常用图类型:Line and scatter plots(使用plot()命令), histogram(使用hist()命令)
2.1 折线图&散点图 Line and scatter plots
2.1.1 折线图 Line plots(关联一组x和y值的直线)
import numpy as npimport pylab as plx = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]# Make an array of x valuesy = [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]# Make an array of y values for each x valuepl.plot(x, y)# use pylab to plot x and ypl.show()# show the plot on the screen

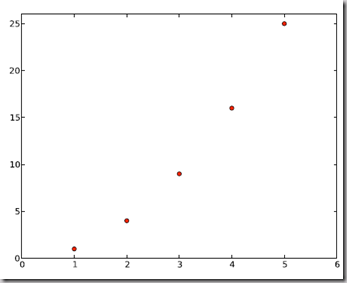
2.1.2 散点图 Scatter plots
把pl.plot(x, y)改成pl.plot(x, y, 'o')即可,下图的蓝色版本
2.2 美化 Making things look pretty
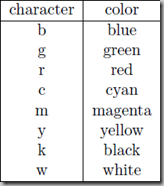
2.2.1 线条颜色 Changing the line color
红色:把pl.plot(x, y, 'o')改成pl.plot(x, y, ’or’)
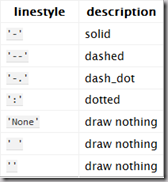
2.2.2 线条样式 Changing the line style
虚线:plot(x,y, '--')
2.2.3 marker样式 Changing the marker style
蓝色星型markers:plot(x,y, ’b*’)

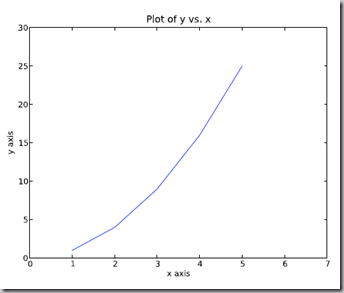
2.2.4 图和轴标题以及轴坐标限度 Plot and axis titles and limits
import numpy as npimport pylab as plx = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]# Make an array of x valuesy = [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]# Make an array of y values for each x valuepl.plot(x, y)# use pylab to plot x and ypl.title(’Plot of y vs. x’)# give plot a titlepl.xlabel(’x axis’)# make axis labelspl.ylabel(’y axis’)pl.xlim(0.0, 7.0)# set axis limitspl.ylim(0.0, 30.)pl.show()# show the plot on the screen
2.2.5 在一个坐标系上绘制多个图 Plotting more than one plot on the same set of axes
做法是很直接的,依次作图即可:
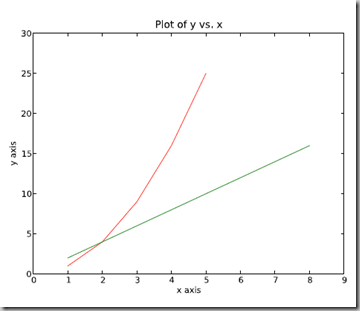
import numpy as npimport pylab as plx1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]# Make x, y arrays for each graphy1 = [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]x2 = [1, 2, 4, 6, 8]y2 = [2, 4, 8, 12, 16]pl.plot(x1, y1, ’r’)# use pylab to plot x and ypl.plot(x2, y2, ’g’)pl.title(’Plot of y vs. x’)# give plot a titlepl.xlabel(’x axis’)# make axis labelspl.ylabel(’y axis’)pl.xlim(0.0, 9.0)# set axis limitspl.ylim(0.0, 30.)pl.show()# show the plot on the screen
2.2.6 图例 Figure legends
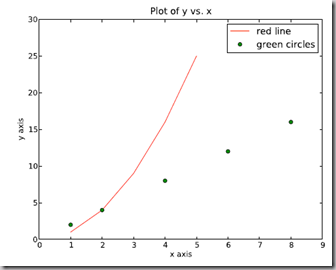
pl.legend((plot1, plot2), (’label1, label2’), 'best’, numpoints=1)
其中第三个参数表示图例放置的位置:'best’‘upper right’, ‘upper left’, ‘center’, ‘lower left’, ‘lower right’.
如果在当前figure里plot的时候已经指定了label,如plt.plot(x,z,label="$cos(x^2)$"),直接调用plt.legend()就可以了哦。
import numpy as npimport pylab as plx1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]# Make x, y arrays for each graphy1 = [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]x2 = [1, 2, 4, 6, 8]y2 = [2, 4, 8, 12, 16]plot1 = pl.plot(x1, y1, ’r’)# use pylab to plot x and y : Give your plots namesplot2 = pl.plot(x2, y2, ’go’)pl.title(’Plot of y vs. x’)# give plot a titlepl.xlabel(’x axis’)# make axis labelspl.ylabel(’y axis’)pl.xlim(0.0, 9.0)# set axis limitspl.ylim(0.0, 30.)pl.legend([plot1, plot2], (’red line’, ’green circles’), ’best’, numpoints=1)# make legendpl.show()# show the plot on the screen
2.3 直方图 Histograms
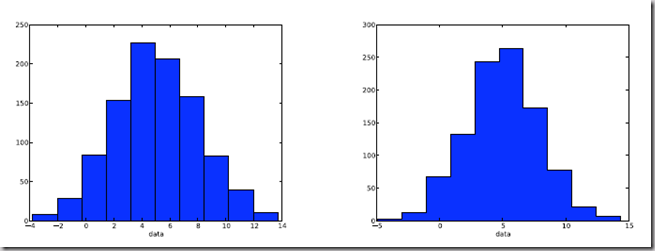
import numpy as npimport pylab as pl# make an array of random numbers with a gaussian distribution with# mean = 5.0# rms = 3.0# number of points = 1000data = np.random.normal(5.0, 3.0, 1000)# make a histogram of the data arraypl.hist(data)# make plot labelspl.xlabel(’data’)pl.show()
如果不想要黑色轮廓可以改为pl.hist(data, histtype=’stepfilled’)
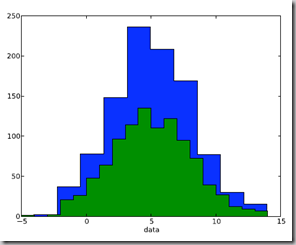
2.3.1 自定义直方图bin宽度 Setting the width of the histogram bins manually
增加这两行
bins = np.arange(-5., 16., 1.) #浮点数版本的range
pl.hist(data, bins, histtype=’stepfilled’)
3 同一画板上绘制多幅子图 Plotting more than one axis per canvas
如果需要同时绘制多幅图表的话,可以是给figure传递一个整数参数指定图标的序号,如果所指定
序号的绘图对象已经存在的话,将不创建新的对象,而只是让它成为当前绘图对象。
fig1 = pl.figure(1)
pl.subplot(211)
subplot(211)把绘图区域等分为2行*1列共两个区域, 然后在区域1(上区域)中创建一个轴对象. pl.subplot(212)在区域2(下区域)创建一个轴对象。
You can play around with plotting a variety of layouts. For example, Fig. 11 is created using the following commands:
f1 = pl.figure(1)
pl.subplot(221)
pl.subplot(222)
pl.subplot(212)
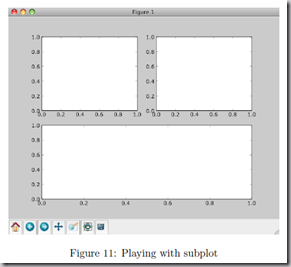
当绘图对象中有多个轴的时候,可以通过工具栏中的Configure Subplots按钮,交互式地调节轴之间的间距和轴与边框之间的距离。如果希望在程序中调节的话,可以调用subplots_adjust函数,它有left, right, bottom, top, wspace, hspace等几个关键字参数,这些参数的值都是0到1之间的小数,它们是以绘图区域的宽高为1进行正规化之后的坐标或者长度。
pl.subplots_adjust(left=0.08, right=0.95, wspace=0.25, hspace=0.45)
4 绘制文件中的数据Plotting data contained in files
4.1 从Ascii文件中读取数据 Reading data from ascii files
读取文件的方法很多,这里只介绍一种简单的方法,更多的可以参考官方文档和NumPy快速处理数据(文件存取)。
numpy的loadtxt方法可以直接读取如下文本数据到numpy二维数组
**********************************************
# fakedata.txt
0 0
1 1
2 4
3 9
4 16
5 25
6 36
7 49
8 64
9 81
0 0
1 1
2 4
3 9
4 16
5 25
6 36
7 49
8 64
9 81
**********************************************
import numpy as npimport pylab as pl# Use numpy to load the data contained in the file# ’fakedata.txt’ into a 2-D array called datadata = np.loadtxt(’fakedata.txt’)# plot the first column as x, and second column as ypl.plot(data[:,0], data[:,1], ’ro’)pl.xlabel(’x’)pl.ylabel(’y’)pl.xlim(0.0, 10.)pl.show()
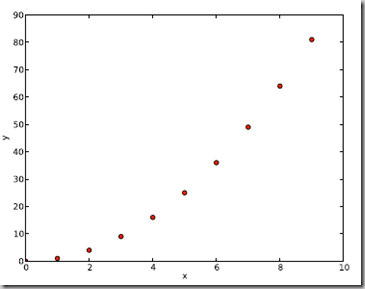
4.2 写入数据到文件 Writing data to a text file
写文件的方法也很多,这里只介绍一种可用的写入文本文件的方法,更多的可以参考官方文档。
import numpy as np# Let’s make 2 arrays (x, y) which we will write to a file# x is an array containing numbers 0 to 10, with intervals of 1x = np.arange(0.0, 10., 1.)# y is an array containing the values in x, squaredy = x*xprint ’x = ’, xprint ’y = ’, y# Now open a file to write the data to# ’w’ means open for ’writing’file = open(’testdata.txt’, ’w’)# loop over each line you want to write to filefor i in range(len(x)):# make a string for each line you want to write# ’\t’ means ’tab’# ’\n’ means ’newline’# ’str()’ means you are converting the quantity in brackets to a string typetxt = str(x[i]) + ’\t’ + str(y[i]) + ’ \n’# write the txt to the filefile.write(txt)# Close your filefile.close()
这部分是翻译自:Python Plotting Beginners Guide
对LaTeX数学公式的支持
Matlplotlib对LaTeX有一定的支持,如果记得使用raw字符串语法会很自然:
xlabel(r"$\frac{x^2}{y^4}$")
在matplotlib里面,可以使用LaTex的命令来编辑公式,只需要在字符串前面加一个“r”即可
Here is a simple example:
# plain text
plt.title('alpha > beta')
produces “alpha > beta”.
Whereas this:
# math text
plt.title(r'$\alpha > \beta$')
produces " ".
".
这里给大家看一个简单的例子。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = arange(1,1000,1)
r = -2
c = 5
y = [5*(a**r) for a in x]
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.loglog(x,y,label = r"$y = \frac{1}{2\sigma_1^2}, c=5,\sigma_1=-2$")
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel(r"x")
ax.set_ylabel(r"y")
程序执行结果如图3所示,这实际上是一个power-law的例子,有兴趣的朋友可以继续google之。
再看一个《用Python做科学计算》中的简单例子,下面的两行程序通过调用plot函数在当前的绘图对象中进行绘图:
plt.plot(x,y,label="$sin(x)$",color="red",linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x,z,"b--",label="$cos(x^2)$")
plot函数的调用方式很灵活,第一句将x,y数组传递给plot之后,用关键字参数指定各种属性:
- label : 给所绘制的曲线一个名字,此名字在图示(legend)中显示。只要在字符串前后添加"$"符号,matplotlib就会使用其内嵌的latex引擎绘制的数学公式。
- color : 指定曲线的颜色
- linewidth : 指定曲线的宽度
详细的可以参考matplotlib官方教程:
Writing mathematical expressions
- Subscripts and superscripts
- Fractions, binomials and stacked numbers
- Radicals
- Fonts
- Custom fonts
- Accents
- Symbols
- Example
Text rendering With LaTeX
- usetex with unicode
- Postscript options
- Possible hangups
- Troubleshooting
有几个问题:
- matplotlib.rcParams属性字典
- 想要它正常工作,在matplotlibrc配置文件中需要设置text.markup = "tex"。
- 如果你希望图表中所有的文字(包括坐标轴刻度标记)都是LaTeX'd,需要在matplotlibrc中设置text.usetex = True。如果你使用LaTeX撰写论文,那么这一点对于使图表和论文中其余部分保持一致是很有用的。
- 在matplotlib中使用中文字符串时记住要用unicode格式,例如:u''测试中文显示''
matplotlib使用小结
- Python 绘制函数图形
- Python GUI 图形绘制
- opencv-python绘制图形
- python中matplotlib绘制图形
- python中matplotlib绘制图形
- python opencv 绘制简单图形
- 【Python】绘制各种图形08
- 使用python绘制二维图形
- python绘制规则网络图形
- python绘制随机网络图形
- Win32App绘制封闭图形函数
- 用python绘制漂亮的图形
- python结合G2绘制精美图形
- python matlibplot绘制3D图形
- Python图形工具turtle绘制国际象棋棋盘
- 利用python中的turtle库绘制图形
- python绘制ws小世界网络图形
- 使用python matplotlib绘制简单图形
- ARM 指令的条件码
- Golang 优化之路——空结构
- ruby基础记录
- 第四次上机实验
- SQLSERVER聚合函数
- Python 绘制函数图形
- C语言综合实践-----C程序操作
- Run loop简析
- php+memcached实现定时静态页面生成
- hdu-5880 AC自动机 + 差分优化
- No.7 week9 optimal division
- 阅读effective stl 有感(一)
- thinkphp实现上传图文消息中的图片的接口
- 四区例


