HDU1208-Pascal's Travels(DP)
来源:互联网 发布:淘宝灯笼是什么意思 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/04 23:20
Pascal's Travels
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2406 Accepted Submission(s): 1134
Problem Description
An n x n game board is populated with integers, one nonnegative integer per square. The goal is to travel along any legitimate path from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the board. The integer in any one square dictates how large a step away from that location must be. If the step size would advance travel off the game board, then a step in that particular direction is forbidden. All steps must be either to the right or toward the bottom. Note that a 0 is a dead end which prevents any further progress.
Consider the 4 x 4 board shown in Figure 1, where the solid circle identifies the start position and the dashed circle identifies the target. Figure 2 shows the three paths from the start to the target, with the irrelevant numbers in each removed.
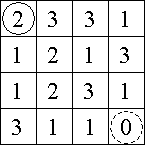
Figure 1
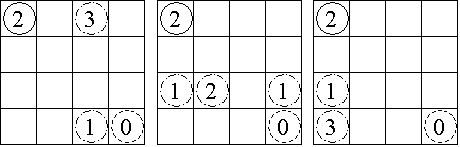
Figure 2
Consider the 4 x 4 board shown in Figure 1, where the solid circle identifies the start position and the dashed circle identifies the target. Figure 2 shows the three paths from the start to the target, with the irrelevant numbers in each removed.


Input
The input contains data for one to thirty boards, followed by a final line containing only the integer -1. The data for a board starts with a line containing a single positive integer n, 4 <= n <= 34, which is the number of rows in this board. This is followed by n rows of data. Each row contains n single digits, 0-9, with no spaces between them.
Output
The output consists of one line for each board, containing a single integer, which is the number of paths from the upper left corner to the lower right corner. There will be fewer than 2^63 paths for any board.
Sample Input
423311213123131104333212131232212051110101111111111110111101-1
Sample Output
307Brute force methods examining every path will likely exceed the allotted time limit. 64-bit integer values are available as "__int64" values using the Visual C/C++ or "long long" values using GNU C/C++ or "int64" values using Free Pascal compilers.HintHint
由[1][1]出发,dp[1][1]设为1,由前一点加上步数到达后一点,那么后一点直接加上前一点的状态即可,由于题中说了,都是直来直去地走,那么,就只有横着走竖着走两种情况,直接遍历一下即可,无法到达的点dp值始终为1,不用考虑,另把数组开大点可以不用判断边界,因为边界外的遍历不到,不影响结果,或者判断一下边界也行,数组开小不判断边界访问非法内存会wa
#include <iostream>#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>#include<algorithm>#include<cmath>#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))#define N 100using namespace std;int e[N][N];long long dp[N][N];int main(){ int n; while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n!=-1) { mem(dp,0); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) for(int j=1; j<=n; j++) scanf("%1d",&e[i][j]); dp[1][1]=1; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) { if(!e[i][j])continue; dp[i+e[i][j]][j]+=dp[i][j]; dp[i][j+e[i][j]]+=dp[i][j]; } } printf("%lld\n",dp[n][n]); }}阅读全文
0 0
- HDU1208:Pascal's Travels(DP)
- HDU1208 Pascal's Travels(DP)
- HDU1208-Pascal's Travels(DP)
- HDU1208:Pascal's Travels(dp)
- hdu1208 Pascal's Travels
- hdu1208-Pascal's Travels
- HDU1208 Pascal's Travels
- POJ2704 Pascal's Travels (记忆化DP)
- hdu 1208 Pascal's Travels--DP
- POJ 2704(Pascal's Travels-裸dp)
- HDOJ 1208 Pascal's Travels(水DP)
- HDU 1208 Pascal's Travels(dp)
- hdu Pascal's Travels(DP)
- 1274. Pascal's Travels
- BIT1021 Pascal's Travels
- Pascal's Travels
- Pascal's Travels HDU
- Pascal's Travels HDU
- 进阶9_多线程3_线程池的基本
- Android之内置和外置sdcard路径显示并且写入数据
- css reset 解释****
- 对于Spring AOP的理解
- leaflet可视化平台搭建
- HDU1208-Pascal's Travels(DP)
- C# 网络编程(TCP、UDP)
- Spring Web MVC
- [leetcode]581. Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray
- 【JavaSE系列-基础篇3】——面向对象编程概念之继承
- Struts2中StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter源码浅析
- jdbc hibernate(session) jpa (entityManager ) spring-data-jpa mybatis完全混用
- *最小生成树
- 测试人员使用idea+git查看代码逻辑


