Codeforces 811D Vladik and Favorite Game【思维+Bfs】
来源:互联网 发布:离线背单词软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 17:03
This is an interactive problem.
Vladik has favorite game, in which he plays all his free time.
Game field could be represented as n × m matrix which consists of cells of three types:
- «.» — normal cell, player can visit it.
- «F» — finish cell, player has to finish his way there to win. There is exactly one cell of this type.
- «*» — dangerous cell, if player comes to this cell, he loses.
Initially player is located in the left top cell with coordinates (1, 1).
Player has access to 4 buttons "U", "D", "L", "R", each of them move player up, down, left and right directions respectively.
But it’s not that easy! Sometimes friends play game and change functions of buttons. Function of buttons "L" and "R" could have been swapped, also functions of buttons "U" and "D" could have been swapped. Note that functions of buttons can be changed only at the beginning of the game.
Help Vladik win the game!
First line contains two space-separated integers n andm (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100) — number of rows and columns respectively.
Each of next n lines contains m characters describing corresponding row of field. Set of characters in field is described above.
Guaranteed that cell with coordinates (1, 1) is normal and there is at least one way from initial cell to finish cell without dangerous cells.
You can press buttons no more than 2·n·m times.
To press a button you should print "U", "D", "L", "R" in new line. It’s necessary to print newline character and flush output. After flushing buffer you should read answer from input data. Answer is the pair of space-separated integersx, y — new position of player. In case, if there is no cell in direction of moving, position will not change. If after any move player lost, in other words player move to dangerous cell, then x and y will be equal to - 1.
If after any move player is in finish or dangerous cell, then you should terminate your program.
To finish output buffer (i. e. for operation flush) right after printing direction and newline you should do next:
- fflush(stdout) in C++
- System.out.flush() in Java
- stdout.flush() in Python
- flush(output) in Pascal
- read documentation for other languages.
Hacks
To perform a hack you should use this format:
n m swapLR swapUD a_1 a_2 ... a_n
Where n, m — number of rows and columns in game field.swapLR is equal to 1 in case, when directions "L’’ and "R’’ is swapped, and equal to0 otherwise. swapUD is equal to1, when directions "U’’ and "D’’ is swapped, and equal to0 otherwise. a1, a2, ..., an — description of corresponding rows of game field.
4 3...**.F*....1 11 21 31 32 33 34 34 24 13 1
RLLDUUURRD
In first test case all four directions swapped with their opposite directions. Protocol of interaction In more convenient form:
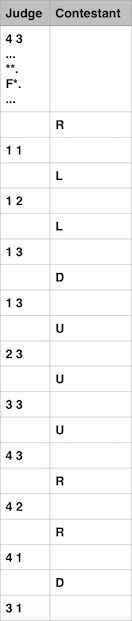
This test could be presenter for hack in following way:
4 3 1 1...**.F*....
题目大意:
现在给你一个n*m大小的图,你输出一个方向之后,系统反馈给你一个坐标,表示走完这步之后到的位子,我们需要在2*n*m步之内走到终点,问怎样走才行(多解输出任意一个即可)。
我们一开始的位子是(1,1),终点位子是“F”,‘*’表示不能走的位子,游戏开始的时候,有一些小伙伴比较调皮,会将U和D互换,就是说假设我们操作了U,但是实际是走到了D.或者也可能将L和R互换,当然也可能都没有互换过,当然也可能都互换过。
然你模拟整个过程。
思路:
预处理Bfs随便跑出来一个可行解,然后我们按照这个过程模拟的去走,如果发现下一步走到的位子和预期走到的位子不同,那么肯定这个键子就被小伙伴们调皮的换过了,
那么此时我们反过去走就行。
Ac代码:
#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>#include<queue>using namespace std;struct node{ int x,y;}now,nex;char a[105][105];int path[105*105*3][2];int pre[105][105][2];int vis[105][105];int fx[4]={0,0,1,-1};int fy[4]={1,-1,0,0};char ans[4]{'R','L','D','U'};int n,m;int cnt;void Bfs(){ memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); queue<node >s; now.x=1; now.y=1; s.push(now); pre[now.x][now.y][0]=1; pre[now.y][now.y][1]=1; vis[now.x][now.y]=1; while(!s.empty()) { now=s.front(); if(a[now.x][now.y]=='F')break; s.pop(); for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { nex.x=now.x+fx[i]; nex.y=now.y+fy[i]; if(nex.x>=1&&nex.x<=n&&nex.y>=1&&nex.y<=m&&a[nex.x][nex.y]!='*') { if(vis[nex.x][nex.y]==0) { vis[nex.x][nex.y]=1; s.push(nex); pre[nex.x][nex.y][0]=now.x; pre[nex.x][nex.y][1]=now.y; } } } }}void Slove(){ /* for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { printf("(%d,%d) ",pre[i][j][0],pre[i][j][1]); } printf("\n"); }*/ int ex,ey; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { if(a[i][j]=='F') { ex=i,ey=j; } } } cnt=0; while(1) { path[cnt][0]=ex; path[cnt][1]=ey; int tmpx=ex,tmpy=ey; ex=pre[tmpx][tmpy][0]; ey=pre[tmpx][tmpy][1]; cnt++; if(ex==1&&ey==1) { path[cnt][0]=ex; path[cnt][1]=ey; cnt++; break; } }}int main(){ while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)) { for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%s",a[i]+1); Bfs(); Slove(); int now=cnt-1; /* for(int i=cnt-1;i>=0;i--) { printf("%d %d\n",path[i][0],path[i][1]); } */ while(now>0) { int flag=-1; for(int j=0;j<4;j++) { int xx=path[now][0]+fx[j]; int yy=path[now][1]+fy[j]; if(xx==path[now-1][0]&&yy==path[now-1][1])flag=j; } printf("%c\n",ans[flag]); fflush(stdout); int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); if(x==path[now-1][0]&&y==path[now-1][1])now--; else { if(ans[flag]=='L'||ans[flag]=='R')swap(ans[0],ans[1]); else swap(ans[2],ans[3]); } } }}- Codeforces 811D Vladik and Favorite Game【思维+Bfs】
- codeforces 811D——Vladik and Favorite Game(bfs)
- Codeforces 811D Vladik and Favorite Game[模拟][bfs]
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) D. Vladik and Favorite Game【交互题+BFS】
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) D. Vladik and Favorite Game 交互, BFS
- Vladik and Favorite Game CodeForces
- Codeforces 586D Phillip and Trains【思维+Bfs】好题~!
- Codeforces 877D Olya and Energy Drinks【思维优化Bfs】
- CodeForces 811B——Vladik and Complicated Book ——思维,模拟
- codeforces 811C Vladik and Memorable Trip
- Codeforces 811A Vladik and Courtesy
- Codeforces 811B Vladik and Complicated Book
- codeforces 811A Vladik and Courtesy
- Codeforces 811 A Vladik and Courtesy
- Codeforces 811 B Vladik and Complicated Book
- Vladik and flights CodeForces
- Codeforces 327D Block Tower【思维+Bfs】
- Codeforces 330D Biridian Forest【思维+Bfs】
- U-Boot的配置、编译、连接过程
- 指针及指针变量
- 树与树算法
- wxPython制作桌面软件的一些简单示例-来自官方文档
- 2017 计蒜之道 第四场 商汤科技的行人检测(简单)
- Codeforces 811D Vladik and Favorite Game【思维+Bfs】
- Ubuntu下vim打开文件时,提示请按ENTER或其它命令继续
- 数据表中主键、外键和索引的区别?
- USACO-Section 1.3 Ski Course Design Lock[...]
- display:flex 意思是弹性布局
- UDPSender 一个基于NIO的UDP发送器/接收器
- 随笔(mybatis)——Error getting nested result map values for ''.
- TCP为什么是三次握手?
- OpenGL蓝宝书源码学习(八)第四章——SphereWorld.cpp


