Mummer文档翻译
来源:互联网 发布:六级分数算法 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/06 06:40
http://mummer.sourceforge.net/manual/#program
Table of Contents (目录)
- Introduction
- Description
- Comparative genomics
-1. Available sequence
-2. Human vs. Human
-3. OSI open source
- Comparative genomics
- Introduction
- Installation
- System requirements
- Obtaining MUMmer
- Compilation and installation
- Installation
- Running MUMmer
- Use cases and walk-throughs
- Aligning two finished sequences
- Highly similar sequences without rearrangements
- Highly similar sequences with rearrangements
- Fairly similar sequences
- Fairly dissimilar sequences
- Aligning two draft sequences
- Mapping a draft sequence to a finished sequence
- SNP detection
- Identifying repeats
- Use cases and walk-throughs
- Program descriptions
- Maximal exact matching
- mummer
- repeat-match
- exact-tandems
- Clustering
- gaps
- mgaps
- Alignment generators
- NUCmer
- PROmer
- run-mummer1
- run-mummer3
- Utilities
- delta-filter
- mapview
- mummerplot
- show-aligns
- show-coords
- show-snps
- show-tiling
- Program descriptions
- Known problems
- Acknowledgements
- Contact information
1. Introduction (引言)
MUMmer is an open source software package for the rapid alignment of very large DNA and amino acid sequences. The latest version, release 3.0, includes a new suffix tree algorithm that has further improved the efficiency of the package and has been integral to making MUMmer an open source product. If you are familiar with the previous versions of MUMmer, you will find the new version is very similar because most of the changes have been to the implementation and not the interface, however this document assumes no previous experience with MUMmer, so past users may find it desirable to skip or skim through some of the sections.
Mummer是一个快速比对非常大的DNA和氨基酸序列的开源软件包。最新的版本(V3.0)包含了一个新的后缀树算法,这进一步提高了封装的效率,并且使MUMmer成为了一个开源产品。如果你是MUMmer的老用户,你会发现新版本是非常相似的,因为大多数的更改已经被实现而不是增加新的接口,本文档假定以前没有使用MUMmer的经验,因此过去的用户可能会发现跳过或略过某些部分。
1.1. Description (描述)
MUMmer is a modular and versatile package that relies on a suffix tree data structure for efficient pattern matching. Suffix trees are suited for large data sets because they can be constructed and searched in linear time and space. This allows mummer to find all 20 base pair maximal exact matches between two ~5 million base pair bacterial genomes in 20 seconds, using 90 MB of RAM, on a typical 1.7 GHz Linux desktop computer. Using a seed and extend strategy, other parts of the MUMmer pipeline use these exact matches as alignment anchors to generate pair-wise alignments similar to BLAST output. Also included are some utilities to handle the alignment output and a primitive plotting tool (mummerplot) that allows the user to convert MUMmer output to gnuplot files for dot and percent identity plots. Another graphical utility called MapView is included with the MUMmer distribution and displays sequence alignments to a annotated reference sequence for exon refinement and investigation.
MUMmer是一种模块化和多功能的软件包,依赖于后缀树数据结构来实现有效的模式匹配。后缀树适用于大型数据集,因为它们可以在线性时间和空间中构建和搜索。这使得MUMmer能够在1.7 GHz的桌面版Linux电脑上花费90MB RAM,在20秒内找到2〜5百万碱基对细菌基因组之间的所有20个碱基对的最大精确匹配。使用种子和扩展策略,MUMmer pipeline的其他部分使用这些精确匹配作为对齐锚点,生成类似于BLAST成对比对的输出。还包括一些处理比对输出的实用程序和一个原始绘图工具(mummerplot),允许用户将MUMmer输出转换为gnuplot文件,用于点和百分比的身份图(PIP,专业词汇)。名为MapView的另一个图形化实用程序包含在MUMmer中,显示序列对齐到注释参考序列情况以进行外显子细化和调查。
This modular design has an important side effect, it allows for the easy reuse of MUMmer modules in other software. For instance, one can imagine primer design, repeat masking and even comparative annotation tools based on the efficient matching algorithm MUMmer provides. Another advantage of MUMmer is its speed. Its low runtime and memory requirements allow it to be used on most any computer. MUMmer’s efficiency also makes it ideal for aligning huge sequences such as completed and draft eukarotic genomes. MUMmer has been successfully used to align the mouse and human genomes, showing it can handle most any input available. In addition, its ability to handle multiple sequences facilitate many vs. many searches, and make the comparison of unfinished draft sequence quite simple. However, because of it’s many abilities, inexperienced users may find it difficult to determine the best methods for their application, so please refer to the Running MUMmer and Use cases sections for brief descriptions, use case examples, and tips on making the most of the MUMmer package, or if you want to understand more about a specific utility, refer to Program descriptions section for more detailed information and output formats.
这种模块化设计具有重要的副作用,它允许在其他软件中轻松重复使用MUMmer模块。例如,可以想象基于MUMmer提供的有效匹配算法的引物设计,重复掩蔽甚至是比较注释工具。MUMmer的另一个优点是它的速度。 它的较低的运行时间和内存要求允许它在大多数计算机上使用。MUMmer的效率也使得它非常适合于比对巨大的序列,如完成和初步绘制真核生物的基因组。MUMmer已经成功地用于比对小鼠和人类基因组,显示它可以处理大多数任何可用的输入。此外,它可以轻松的处理多对多的多序列搜索,并使得比较未完成的草稿序列非常简单。然而,由于具有很多能力,没有经验的用户可能会发现难以确定实现其目的的最佳方法,因此请参阅Running MUMmer和Use cases部分,了解简要说明,用例示例以及有关充分利用MUMmer包的技巧,如果您想了解有关特定实用程序的更多信息,请参阅Program descriptions部分了解更多详细信息和输出格式。
1.2. Comparative genomics (比较基因组学)
1.2.1. Available sequence (可用序列)
The MUMmer package provides efficient means for comparing an entire genome against another. However, until 1999 there were no two genomes of sufficient similarity to compare. With the publication of the second strain of Helicobacter pylori in 1999, following the publication of the first strain in 1997, the scientific world had its first chance to look at two complete bacterial genomes whose DNA sequences were highly similar. The number of pairs of closely-related genomes has exploded in recent years, facilitating many comparative studies. For instance, the published databases include the following genomes for which multiple strains and/or multiple species have been sequenced:
MUMmer包提供了将整个基因组与另一个基因组进行比较的有效手段。 然而,直到1999年,才有两个具有足够相似性的可以进行比较的的基因组。随着1999年幽门螺杆菌第二次公布,1997年首次公布,科学界首次看到DNA序列高度相似的两个完整的细菌基因组。近几年年,成对的密切相关的基因组数量激增,促进了许多比较研究。例如,已发表的数据库包括以下基因组,多个菌株和/或多个物种已被测序:
Most of these genomes can be obtained from the NCBI ftp site: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes
大多数这些基因组可以从NCBI ftp站点获得:ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes
1.2.2. Human vs. Human
With the capability to align the entire human genome to itself, there is no genome too large for MUMmer. The following table gives run times and space requirements for a cross comparison of all human chromosomes. The 1st column indicates the chromosome number, with “Un” referring to unmapped contigs. Column 2 shows chromosome length and column 4 shows the length of the total genomic DNA searched against the chromosome in column 1. Column 3 shows the time to construct the suffix tree, and column 5 the time to stream the query sequence through it. Column 6 shows the maximum amount of computer memory occupied by the program and data, and column 7 shows memory usage for the suffix tree in bytes per base pair. Each human chromosome was used as a reference, and the rest of the genome was used as a query and streamed against it. To avoid duplication, we only included chromosomes in the query if they had not already been compared; thus we first used chromosome 1 as a reference, and streamed the other 23 chromosomes against it. Then we used chromosome 2 as a reference, and streamed chromosomes 3–22, X, and Y against that, and so on.
具有将整个人类基因组自身和自身比较的能力,没有更大的基因组是MUMmer驾驭不了的。下表给出了对所有人类染色体进行交叉比较的运行时间和空间要求。第一列表示染色体数目,“Un”表示未映射的重叠群。 第2列显示染色体长度,第4列显示在第1列中针对染色体搜索的总基因组DNA的长度。第3列显示构建后缀树的时间,第5列显示通过其查询序列的时间。 第6列显示程序和数据占用的计算机内存的最大数量,第7列显示后缀树的每个碱基对的字节数的内存使用量。将每个人染色体用作参照,并将其余的染色体用作查询并进行流水式比较。为了避免重复,如果尚未比较,我们只将染色体包含在查询中;因此,我们首先使用染色体1作为参照,并将其他23条染色体与其对应。 然后我们使用染色体2作为参考,并且将染色体3-22,X和Y反过来,其余类似。
The Human Chromosomes can be obtained from the NCBI ftp site: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/genomes/H_sapiens
1.3. OSI open source
The key difference between version 3.0 and previous versions of MUMmer, is its qualification as an open source project. Previous versions of MUMmer were always free for non-profit, but now MUMmer is free for all organizations, both for- and non-profit. Please refer to the LICENSE file included in the package for a description of the Artistic License, the same OSI certified open source license used by Perl and countless other packages. We encourage you to contact us (though you are not required to) if you wish to contribute to our ongoing improvement and development of the software, and simple suggestions on how to improve MUMmer are always welcome. Enjoy the freedom of open source!
To receive software update notices, please join the MUMmer mailing list. This list will only be used to announce major version releases and help us keep track of MUMmer users.
2. Installation
MUMmer comes as a source distribution only, and needs to be compiled before use. This sections describes the steps and requirements necessary to compile the package. Installation problems are usually caused by incompatible versions of one or more OS utilities, so if installation fails please check that you have the needed system requirements before alerting us of your problem. The INSTALL file included in the source distribution also contains much of the same information provided in this section.
2.1. System Requirements
MUMmer is mostly written in C and C++. With some technical expertise it could be ported to any system with a C++ compiler, but our distribution was specifically designed to be compiled with the GNU GCC compiler and has been successfully tested on the following three platforms:
- Redhat Linux 6.2 and 7.3 (Pentium 4)
- Compaq Tru64 UNIX 5.1 (alpha)
- SunOS UNIX 5.8 (sparc)
- Mac OS X 10.2.8 (PowerPC G4)
MUMmer also requires some third party software to run successfully. In the absence of one or more of the below utilities, certain MUMmer programs may fail to run correctly. Listed in parenthesis are the versions used to test the MUMmer package. These versions, or subsequent versions should assure the proper execution of the various MUMmer programs. These utilities must be accessible via the system path:
- make (GNU make 3.79.1)
- perl (PERL 5.6.0)
- sh (GNU sh 1.14.7)
- csh (tcsh 6.10.00)
- g++ (GNU gcc 2.95.3)
- sed (GNU sed 3.02)
- awk (GNU awk 3.0.4)
- ar (GNU ar 2.9.5)
For running the MUMmer display programs, these additional system utilities are required:
- fig2dev (fig2dev 3.2.3)
- gnuplot (gnuplot 4.0)
- xfig (xfig 3.2)
Sufficient memory and disk space are also necessary, but required sizes vary considerably with input size, so please be aware of your disk and memory usage, as insufficient capacities will result in incorrect or missing output. In general, 512 MB of RAM and 1 GB of disk space is sufficient for most mid-sized comparisons. For Mac OSX, the Mac development kit must be downloaded and installed. This kit will include gcc, ar, and make which are necessary for building MUMmer. MUMmer is not supported for any Mac operating system other than OSX.
2.2. Obtaining MUMmer
The current MUMmer release can be downloaded from our SourceForge.net project page.
2.3. Compilation and installation
For explanation purposes, let’s suppose you just downloaded the MUMmer3.0.tar.gz distribution from the SourceForge site. The first step would be to move this file to the desired installation directory and type:
tar -xvzf MUMmer3.0.tar.gzto extract the MUMmer source into a MUMmer3.0 subdirectory. Switch to this newly created subdirectory and execute:
make checkto assure the makefile can identify the necessary utilities. If no error messages appear, the diagnostics were successful and you may continue. However, if error messages are displayed, the listed programs are not accessible via your system path. Install the utilities if necessary, add them to your system PATH variable, and continue with the MUMmer installation by typing:
make installThis will attempt to compile the MUMmer scripts and executables. If the make command issues no errors, the compilation was successful and you are ready to begin using MUMmer. If the command fails, it is likely that make was confused by the existence of more than one copy of the same utility, such as two versions of gcc. When this happens, it is important to arrange you system PATH variable so that the more recent versions are listed first, or to hard code the location of your utility location in the makefile. The same advice goes for your LD_LIBRARY_PATH variable if your system is having a difficult time locating the appropriate C or C++ libraries at runtime.
It is important to note that the make command dynamically builds the MUMmer scripts to reference the install directory, therefore if the install directory is moved after the make command is issued the MUMmer scripts will fail. If you need certain MUMmer executables in a directory other than the install directory, it is recommend to leave the install directory untouched and link the needed executables to the desired destination. An alternative would be to move the install directory and reissue the make command at the new location.
3. Running MUMmer
The five most commonly used programs in the MUMmer package are mummer, nucmer, promer, run-mummer1 and run-mummer3, so this section covers the basics of executing these tools and what each of them specializes in. To better understand how to view the outputs of these programs, please refer to the use cases section or the MUMmer examples webpage for a brief walk-through of each major module with full input data and expected outputs. For further information, please refer to the Program descriptions section for a detailed explanation of each program and its output.
MUMmer软件包中最常用的五个程序是mummer,nucmer,promer,run-mummer1和run-mummer3,因此本节将介绍执行这些工具的基础知识,以及他们每个的专长。为了更好地了解如何查看这些程序的输出,请参考use cases部分或MUMmer examples页面,了解具有完整输入数据和预期输出的每个主要模块的简要步骤。 有关详细信息,请参阅Program descriptions部分,了解每个程序及其输出的详细说明。
mummer
mummer efficiently locates maximal unique matches between two sequences using a suffix tree data structure. This makes mummer most suited for generating lists of exact matches that can be displayed as a dot plot, or used as anchors in generating pair-wise alignments.
mummer使用后缀树数据结构有效地定位两个序列之间的最大唯一匹配。 这使得mummer最适合生成可以显示为dot plot的精确匹配列表,或者用作生成成对比对中的锚点。
mummer [options] <reference file> <query file1> . . . [query file32]There must be exactly one reference file and at least one query file. Both the reference and query files should be in multi-FastA format and may contain any set of upper and lowercase characters, thus DNA and protein sequences are both allowed and matching is case insensitive. The maximum number of query files is 32, but there is no limit on how many sequences each reference or query file may contain. Output is to stdout. Refer to the mummer section for a list of options and output descriptions.
必须有一个参考文件和至少一个查询文件。 引用和查询文件都应该是Multi-FastA格式,并且可以包含任何一组大小写字符,因此,DNA和蛋白质序列都被允许,匹配是不区分大小写的。 查询文件的最大数量为32,但每个引用或查询文件可能包含多少个序列没有限制。 输出是stdout。 有关选项和输出说明的列表,请参阅“mummer”部分。
NUCmer
NUCmer is a Perl script pipeline for the alignment of multiple closely related nucleotide sequences. It begins by finding maximal exact matches of a given length, it then clusters these matches to form larger inexact alignment regions, and finally, it extends alignments outward from each of the matches to join the clusters into a single high scoring pair-wise alignment. This makes NUCmer most suited for locating and displaying highly conserved regions of DNA sequence. To increase NUCmer’s accuracy, it may be desirable to mask the input sequences to avoid the alignment of uninteresting sequence, or to change the uniqueness constraints (see the NUCmer section) to reduce the number of repeat induced alignments.
NUCmer是一个Perl脚本管道,用于比对多个closely related的核苷酸序列。它首先找到给定长度的最大精确匹配,然后将这些匹配集群形成更大的非精确比对区域,最后,它从每个匹配向外扩展对齐,以将聚类结合成单个高得分的成对比对。这使得NUCmer最适合于定位和显示高度保守的DNA序列区域。为了增加NUCmer的准确性,可能需要掩盖输入序列以避免不感兴趣的序列的对齐,或者改变唯一性约束(参见NUCMER部分)以减少重复导致的比对的数目。
nucmer [options] <reference file> <query file>Both the reference and query files should be in multi-FastA format and may contain any set of upper and lowercase characters, however only the DNA characters a, c, t and g will be aligned (case insensitive). There is no limit on how many sequences the reference or query files may contain. Output is written to the file out.delta This is an ASCII file, but not formatted for human consumption, so it is necessary to run a utility program to parse the output. The two primary utility programs for viewing the contents of a .delta file are show-aligns, and show-coords. show-aligns displays all of the pair-wise alignments between two sequences, while show-coords displays a summary of the coordinates, percent identity, etc. of the alignment regions. Refer to the NUCmer section for a list of options and output descriptions.
参考文件和查询文件都应该是多重FastA格式,并且可以包含任何一组大小写字符,但只有DNA字符a,c,t和g将被比对(不区分大小写)。参考或查询文件包含多少个序列没有限制。 输出写入文件out.delta这是一个ASCII文件,但不是一个给人看的文件,因此有必要运行一个程序来解析输出。用于查看.delta文件内容的两个主要实用程序是show-aligns和show-coords。show-aligns显示两个序列之间的所有成对对齐方式,而show-coords显示对齐区域的坐标,百分比标识等的总结。 有关选项和输出说明的列表,请参阅NUCMER部分。
PROmer
PROmer is a Perl script pipeline for the alignment of multiple somewhat divergent nucleotide sequences. It works exactly like NUCmer, but with a small twist. Before any of the exact matching takes place, the input sequences are translated in all six amino acid reading frames. This allows PROmer to identify regions of conserved protein sequences that may not be conserved on the DNA level and thus gives it a higher sensitivity than NUCmer. Note however, this increase in sensitivity will result in huge amounts of output for highly similar sequences, therefore it is recommended that PROmer only be used when the input sequences are too divergent to produce a reasonable amount of NUCmer output. As with NUCmer, it is recommended to mask the input sequences to avoid the alignment of uninteresting sequence, or to change the uniqueness constraints (see the PROmer section) to reduce the number of repeat induced alignments.
PROmer是一种Perl脚本管道,用于排列多个稍微分散的核苷酸序列。它的工作原理像NUCmer,但是有一点小小的不同。在进行任何精确匹配之前,输入序列被翻译成所有六种读框的氨基酸。这使得PROmer能够鉴定在DNA水平上可能不保守的保守蛋白质序列的区域,并因此使其具有比NUCmer更高的灵敏度。然而请注意,灵敏度的增加将导致大量输出高度相似的序列,因此建议仅当输入序列太分散以产生合理数量的NUCmer输出时才使用PROmer。与NUCmer一样,建议屏蔽输入序列以避免不感兴趣的序列的对齐,或者改变唯一性约束(参见“PROmer”部分)以减少重复引发的比对数。
promer [options] <reference file> <query file>Both the reference and query files should be in multi-FastA format and may contain any set of upper and lowercase characters, however only valid DNA characters will result in correctly translated sequence, all other characters will be translated into masking characters and therefore will not be matched by the BLOSUM scoring matrix. There is no limit on how many sequences the reference or query files may contain. Output is written to the same files as NUCmer and can also be viewed with the same utility programs (see above). Refer to the PROmer section for a list of options and output descriptions.
参考和查询文件都应为多重FastA格式,并且可能包含任何大写和小写字符集,但只有有效的DNA字符才能产生正确的翻译顺序,所有其他字符将被翻译成掩蔽字符,因此不会被BLOSUM评分矩阵匹配。没有限制参考或查询文件包含多少个序列。输出文件NUCmer相同,也可以使用相同的实用程序查看(见上文)。 有关选项和输出说明的列表,请参阅PROmer部分。
run-mummer1 and run-mummer3
run-mummer1 and run-mummer3 are cshell script pipelines for the general alignment of two sequences. They follow the same three steps of NUCmer and PROmer, in that they match, cluster and extend, however they handle any input sequence, not just nucleotide. This non-discrimination can be useful, however the program interface is not very user friendly and the output can be difficult to parse. In their favor, the run-mummer* programs are good at aligning very similar DNA sequences and identifying their differences, this makes them well suited for SNP and error detection. run-mummer1 is recommended for one vs. one comparisons with no rearrangements, while run-mummer3 is recommended for one vs. many comparisons that may involved rearrangements. Sequence masking is only recommended if a different character is used to mask the reference and query sequences so that they are not aligned.
run-mummer1和run-mummer3是生成两个序列比对的cshell脚本管道。他们遵循NUCmer和PROmer相同的三个步骤,匹配,集群和扩展,但是它们可以处理任何输入序列,而不仅仅是核苷酸。这种不歧视可能是有用的,但是程序界面对用户不是非常友好,并且输出可能难以解析。在他们的支持下,run-mummer×程序很好地比对非常相似的DNA序列并识别它们的差异,这使得它们非常适合于SNP和错误检测。对于1对1的没有重排的比较,推荐使用run-mummer1;而对于1对多的可能会涉及到重排的比对,推荐使用run-mummer3。仅当使用不同的字符来屏蔽参考和查询序列以使它们不对齐时,才推荐序列屏蔽。
run-mummer1 <reference file> <query file> <prefix> [-r]or
run-mummer3 <reference file> <query file> <prefix>The reference and query files should both be in FastA format and may contain any set of upper and lowercase characters. The reference file may only contain a single sequence, and run-mummer1 only allows a single query sequence, but run-mummer3 has no limit on the number of query sequences . The -r option for run-mummer1 reverses the query sequence, while run-mummer3 automatically finds both forward and reverse matches. Output is written to the files .out, .gaps, .errorsgaps and .align. There are no utilities included to parse these files, so they must be viewed as raw text files. Refer to the run-mummer1 and run-mummer3 sections for info on changing the program parameters and output descriptions.
参考和查询文件都应该是FastA格式,并且可以包含任何一组大小写的字符。 参考文件只能包含一个序列,而run-mummer1只允许一个查询序列,但是run-mummer3对查询序列的数量没有限制。run-mummer1的-r选项反转查询序列,而run-mummer3自动查找正向和反向匹配。输出被写入文件 .out, .gaps, .errorsgaps和 .align。 没有实用程序来解析这些文件,因此它们必须作为原始文本文件被查看。 有关更改程序参数和输出说明的信息,请参阅*run-mummer1和run-mummer3部分。
4. Use cases and walk-throughs
Because of its breadth, MUMmer can be overwhelming at first, and sometimes the hardest part of using MUMmer is deciding which alignment program to run for a particular application. This section attempts to overview some of the basic MUMmer use cases and propose the best MUMmer alignment routine for each case. This section only gives a set of command line calls to generate alignments for each use case. For further information, please refer to the Program descriptions section for a detailed explanation of each program and its output, and the MUMmer examples webpage for a brief walk-through of each major module with full input data and expected outputs.
由于它的广度,首先考虑MUMMER可能是毫无置疑的,有时使用MUMmer最困难的部分是决定为特定应用程序运行哪个比对程序。本节尝试概述一些基本的MUMmer用例,并为每种情况提出最佳的MUMmer比对程序。 本节仅提供一组命令行调用以针对每种用例生成比对。 请参阅程序描述部分了解每个程序及其输出的详细说明,以及每个主要模块的简要步骤的完整输入数据和预期输出的MUMmer示例网页。
4.1. Aligning two finished sequences (比对两个已完成的序列)
The most basic use case is the alignment of two contiguous sequences. For all of the one vs. one use cases the mummer program alone, when coupled with mummerplot, may be all that is necessary to visualize a global alignment of the two sequences. This process alone can be very helpful in determining the large scale differences between the two sequences. For a single reference sequence ref.fasta and a single query sequence qry.fasta in FastA format, type:
最基本的用例是两个连续序列的对齐。 对于所有的1对1的使用情况,独立的mummer程序,当与mummerplot结合时,可能是可视化两个序列的全局比对所必需的。 这个过程本身非常有助于确定两个序列之间的大规模差异。 对于FastA格式的单个参考序列ref.fasta和单个查询序列qry.fasta,请键入:
mummer -mum -b -c ref.fasta qry.fasta > ref_qry.mumsmummerplot --postscript --prefix=ref_qry ref_qry.mumsgnuplot ref_qry.gpThen view or print the postscript plot ref_qry.ps in whatever manner you wish.
然后用你想用的方式查看或打印补充说明图ref_qry.ps
4.1.1. Highly similar sequences without rearrangements (没有重排的高度相似序列)
When comparing two near identical sequences, the object of the alignment is usually SNP and small indel identification. The original MUMmer1.0 pipeline still proves to be a handy tool for this type of analysis, although run-mummer3 with combineMUMs -D can prove to be even handier. Its LIS clustering algorithm and reliance on unique matches give it some reliability advantages over the newer pipelines. For a single reference sequence ref.fasta and a single query sequence qry.fasta in FastA format, type:
当比较两个几乎相同的序列,比对的目的通常是SNP和small InDel的鉴定。原MUMmer1.0 pipeline仍然是这类分析的一个方便的工具,尽管combineMUMs -D和run-mummer3已被证明更加方便。其LIS聚类算法和对独特匹配的依赖给予了新管道的一些可靠的优势。 对于FastA格式的单个参考序列ref.fasta和单个查询序列qry.fasta,请键入:
run-mummer1 ref.fasta qry.fasta ref_qryor for sequences that match on the reverse strand
对于在反向链上匹配的序列
run-mummer1 ref.fasta qry.fasta ref_qry -rSNP detection and one-to-one global alignment can also be performed by nucmer as described in the SNP detection walkthrough. The NUCmer pipeline provides a more user-friendly method for SNP detection while sacrificing a small degree of sensitivity.
SNP检测和一对一全局比对也可以由nucmer执行,如SNP detection演练中所述。 NUCmer pipeline牺牲了较小的灵敏度的同时为用户提供了更方便的SNP检测的方法。
4.1.2. Highly similar sequences with rearrangements (具有重排的高度相似的序列)
Often two sequences are highly similar, but large chunks of the sequence are rearranged, inverted and inserted. In order to align these and produce an output that is similar to the MUMmer1.0 pipeline, use run-mummer3. It uses a clustering method that allows for these types of large scale mutations, but retains many of the other features of run-mummer1. To hunt for SNPs more accurately, you can edit the script and add the -D option to the combineMUMs command line, thus producing a concise file of only the difference positions between the two sequences. For a single reference sequence ref.fasta and a single query sequence qry.fasta in FastA format, type:
通常两个序列是高度相似的,但是会出现大块的序列重排,颠倒的和插入。 为了比对这些并产生类似于MUMmer1.0 pipeline的输出,应该使用run-mummer3。 它使用一种聚类方法,允许这些大规模突变的类型,但保留了run-mummer1的许多其他功能。 为了更准确地寻找SNP,您可以编辑脚本,并将-D选项添加到combineMUMs命令行,从而产生一个仅两个序列之间差异位置的简明文件。 对于FastA格式的单个参考序列ref.fasta和单个查询序列qry.fasta,请键入:
run-mummer3 ref.fasta qry.fasta ref_qrySNP detection and one-to-one local alignment can also be performed by nucmer as described in the SNP detection walkthrough. The NUCmer pipeline provides a more user-friendly method for SNP detection while sacrificing a small degree of sensitivity.
SNP检测和一对一局部比对也可以由nucmer进行,如SNP detection演练中所述。 NUCmer pipeline牺牲了较小的灵敏度的同时为用户提供了更方便的SNP检测的方法。
4.1.3. Fairly similar sequences (较相似的序列)
While run-mummer1 and run-mummer3 focus more on what is different between two sequences, nucmer focuses on what is the same. It has very few restrictions on what it will align, so rearrangements, inversions and repeats will all be identified by nucmer. For a single reference sequence ref.fasta and a single query sequence qry.fasta in FastA format, type:
run-mummer1和run-mummer3更多地关注两个序列之间的区别,而nucmer关注的是什么是相同的。它对一致性对齐的限制很少,所以重新排列,反转和重复都将被nucmer识别。 对于FastA格式的单个参考序列ref.fasta和单个查询序列qry.fasta,请键入:
nucmer --maxgap=500 --mincluster=100 --prefix=ref_qry ref.fasta qry.fastashow-coords -r ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.coordsshow-aligns ref_qry.delta refname qryname > ref_qry.alignsWhere refname and qryname are the FastA IDs of the two sequences. The output of NUCmer can often be voluminous and is best visualized with mummerplot. In addition, its output can be filtered in a varity of ways with the delta-filter program. For example, to select and display a one-to-one local mapping of reference to query sequences, use:
其中refname和qryname是两个序列的FastA ID。 NUCmer的输出通常很丰富,并且可以使用mummerplot进行较好的可视化。 此外,可以使用delta-filter程序以多种方式对其输出进行过滤。 例如,要选择并显示引用查询序列的一对一本地映射,请使用:
delta-filter -q -r ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.filtermummerplot ref_qry.filter -R ref.fasta -Q qry.fastaThis will first filter the delta file, selecting only those alignments which comprise the one-to-one mapping between reference and query, and then display a dotplot of the selected alignments. Note that NUCmer allows for multiple reference and query sequences, so the above methods will also work for such and input. See the delta-filter and mummerplot sections for more details.
这将首先过滤delta file,仅选择构成引用和查询之间一对一映射的比对,然后显示所选比对的点图。 请注意,NUCmer允许多个参考和查询序列,因此上述方法也可用于此类输入。 有关详细信息,请参阅delta-filter和mummerplot部分。
4.1.4. Fairly dissimilar sequences (较不相似的序列)
Sometimes two sequences exhibit poor similarity on the DNA level, but their protein sequences are conserved. In this case, promer will be the most useful MUMmer tool, since it translates the DNA input sequences into amino acids before proceeding with the alignment. For a single DNA reference sequence ref.fasta and a single DNA query sequence qry.fasta in FastA format, type:
有时两个序列在DNA水平上表现出较差的相似性,但它们的蛋白质序列是保守的。 在这种情况下,promer将是最有用的MUMmer工具,因为它在进行比对之前将DNA输入序列翻译成氨基酸。 对于FastA格式的单个DNA参考序列ref.fasta和单个DNA查询序列qry.fasta,请键入:
promer --prefix=ref_qry ref.fasta qry.fastashow-coords -r ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.coordsshow-aligns -r ref_qry.delta refname qryname > ref_qry.alignsWhere refname and qryname are the FastA IDs of the two sequences. Note that the -k option can be added to show-coords to reduce the amount of output by only displaying the best frame in situations where the same hit is represented in multiple, overlapping frames. The output of PROmer can often be voluminous and is best visualized with mummerplot. In addition, its output can be filtered in a varity of ways with the delta-filter program. For example, to select and display a one-to-one local mapping of reference to query sequences, use:
其中refname和qryname是两个序列的FastA ID。 请注意,可以将-k选项添加到show-coords,以通过在多个重叠的frame表示相同命中的情况下仅显示最佳frame来减少输出量。 PROmer的输出通常是很丰富的,mummerplot可以较好的显示该结果。 此外,可以使用delta-filter程序以多种方式对其输出进行过滤。 例如,要选择并显示参考查询序列的一对一本地映射,请使用:
delta-filter -q -r ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.filtermummerplot ref_qry.filter -R ref.fasta -Q qry.fastaThis will first filter the delta file, selecting only those alignments which comprise the one-to-one mapping between reference and query, and then display a dotplot of the selected alignments. Note that PROmer allows for multiple reference and query sequences, so the above methods will also work for such an input. See the delta-filter and mummerplot sections for more details.
这将首先过滤delta file,仅选择构成参考和查询之间一对一映射的比对,然后显示所选比对的点图。 请注意,PROmer允许多个参考和查询序列,因此上述方法也可用于此类输入。 有关详细信息,请参阅delta-filter和mummerplot部分。
4.2. Aligning two draft sequences (比对两个draft序列)
Many times it is necessary to align two genomes that have not yet been completed, or two genomes with multiple chromosomes. This can make things a little more complicated, since a separate alignment would have to be generated for each possible pairing of the sequences. However, both NUCmer and PROmer automate this process and accept multi-FastA inputs, thus simplifying the process of aligning two sets of contigs, scaffolds or chromosomes. Since NUCmer and PROmer have an almost identical user interface, this use case will only be explained using nucmer. If the two inputs are too divergent for nucmer to align, simply use promer instead. For two sets of contigs, ref.fasta and qry.fasta, type:
很多时候有必要对齐尚未完成的两个基因组,或两个具有多个染色体的基因组。 这可以使事情更复杂一些,因为必须为每个可能的序列配对生成单独的比对。 然而,NUCmer和PROmer都可以自动化这个过程并接受多个FastA输入,从而简化了两组contig,scaffold或染色体的比对过程。 由于NUCmer和PROmer具有几乎相同的用户界面,所以这个用例只用nucmer来解释。 如果两个输入对于nucmer进行比对分歧太大,那么只需使用promer。 对于两套contigs,ref.fasta和qry.fasta,类型:
nucmer --prefix=ref_qry ref.fasta qry.fastashow-coords -rcl ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.coordsshow-aligns ref_qry.delta refname qryname > ref_qry.alignsWhere refname and qryname are the FastA IDs of two contigs. The show-aligns step will have to be repeated for every combination of contigs that the user wishes to analyze. Because the output of the all-vs-all comparison described above can be immense, it is often essential to filter the resulting alignment data with the delta-filter program. To map each reference to a position in the query, use delta-filter -r. To map each query to a position in the reference, use delta-filter -q. To determine a one-to-one mapping of each reference and query, combine the options and use delta-filter -r -q. Also, the mummerplot utility provides a very handy visualization method for viewing contig mappings, type:
其中refname和qryname是两个contigs的FastA ID。 必须对用户希望分析的contig的每个组合重复show-aligns步骤。 因为上述的全部对比全部比较的输出可能是巨大的,所以通常必须使用delta-filter程序对结果对齐数据进行过滤。 要将每个参考映射到查询中的位置,请使用delta-filter -r。 要将每个查询映射到参考中的位置,请使用delta-filter -q。 要确定每个参考和查询的一对一映射,请合并选项并使用delta-filter -r -q。 此外,mummerplot实用程序提供了一个非常方便的可视化方法来查看contig映射,键入:
mummerplot ref_qry.delta -R ref.fasta -Q qry.fasta --filter --layoutThis will generate a plot displaying the one-to-one mapping between the two contig sets. When plotted to an X11 terminal, the plot is zoom-able and browse-able via the mouse and keyboard commands provided by gnuplot 4.0. See the delta-filter and mummerplot sections for more details.
这将产生一个显示两个Contig集之间一对一映射的图。 当绘制到X11终端时,绘图可以通过gnuplot 4.0提供的鼠标和键盘命令进行缩放和浏览。 有关详细信息,请参阅delta-filter和mummerplot部分。
4.3. Mapping a draft sequence to a finished sequence (将草图序列映射到完成的序列)
There are many benefits of mapping a draft sequence to the finished sequence of a related organism. Determining the location and orientation of each query contig as it maps to the finished reference sequence can significantly speed up the closure process of the draft sequence, and by examining the areas of conservation, the annotation of the draft sequence can be improved and refined. Since NUCmer and PROmer have an almost identical user interface, this use case will only be explained using nucmer. If the two inputs are to divergent for nucmer, simply use promer instead. For a finished reference chromosome(s) ref.fasta and a set of near identical contigs qry.fasta, type:
将序列绘制到相关生物的完成序列有很多好处。 确定每个查询contig的位置和方向,因为映射到完成的参考序列可以显着加快草稿序列的关闭过程,并通过检查保守区域,可以提升和改进草图序列的注释。 由于NUCmer和PROmer具有几乎相同的用户界面,所以这个用例只能用nucmer来解释。 如果两个输入对于nucmer而言是分歧的,那么只需使用promer。 对于完整的参考染色体ref.fasta和一组近似相同的contig的qry.fasta,键入:
nucmer --prefix=ref_qry ref.fasta qry.fastashow-coords -rcl ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.coordsshow-aligns ref_qry.delta refname qryname > ref_qry.alignsshow-tiling ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.tilingWhere refname and qryname are the FastA IDs of two sequences. The show-aligns step will have to be repeated for every combination of sequences that the user wishes to analyze. If mapping the draft sequences to each of their repeat locations is not required, the delta-filter program can quickly select the optimal placement of each draft sequence to the reference using the following:
其中refname和qryname是两个序列的FastA ID。 必须对用户希望分析的每个序列组合重复show-aligns步骤。 如果不需要将草图序列映射到每个重复位置,则delta-filter程序可以使用以下内容快速选择每个草稿序列到参考的最佳位置:
delta-filter -q ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.filterThe newly created delta file ref_qry.filter can then be substituted for the original in the above procedures in order to generate slimmed down versions of the output.
新创建的delta file ref_qry.filter可以替代上述过程中的原始文件,以生成精简版本的输出。
4.4. SNP detection
Joining a couple of the MUMmer components together can form a quite reliable SNP detection pipeline. MUMmer can perform all steps of this pipeline from aligning the sequences, to selecting the one-to-one mapping, and finally calling the SNP positions. The user can then process these SNP positions to assign quality scores based on the underlying traces and surrounding context. Such methods have been successfully applied to various SNP studies for organisms including Bacillus anthracis and Yersinia pestis. Of important note, a SNP pipeline built with nucmer allows for the identification of SNPs between two genomes with many rearrangements. The Yersinia pestis strains, for example, demonstrate significant genome “shuffling”, and make SNP detection difficult with global alignment programs such as run-mummer1. However, a pipeline built with nucmer (like shown below) is capable of finding all of the SNPs between two genomes, regardless of their structural similarity.
将几个MUMmer组件连接在一起可以形成相当可靠的SNP检测pipeline。 MUMmer可以通过序列比对,选择一对一的映射,最后调用SNP位置来执行该pipeline的所有步骤。 然后,用户可以处理这些SNP位置,根据底层跟踪和周围上下文分配质量分数。 这些方法已被成功应用于各种有机体的SNP研究,包括炭疽芽孢杆菌和鼠疫耶尔森菌。 重要的是,使用nucmer构建的SNP pipeline允许识别具有许多重排的两个基因组之间的SNP。 例如,耶尔森氏菌耶尔森氏菌菌株显示出显着的基因组“洗牌”,并且使得SNP检测在全局比对程序如run-mummer1之间变得困难。 然而,用nucmer构建的pipeline(如下所示)能够找到两个基因组之间的所有SNP,不管其结构相似性如何。
To find a reliable set of SNPs between to highly similar multi-FastA sequence sets ref.fasta and qry.fasta, type:
目的是在高度相似的多FastA序列集ref.fasta和qry.fasta之间找到可靠的SNP集合,键入:
nucmer --prefix=ref_qry ref.fasta qry.fastashow-snps -Clr ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.snpsThe -C option in show-snps assures that only SNPs found in uniquely aligned sequence will be reported, thus excluding SNPs contained in repeats. An alternative method which first attempts to determine the “correct” repeat copy is:
show-snps中的-C选项保证只有在唯一对齐的序列中发现的SNP被报告,因此不包括重复序列中的SNP。 首先尝试确定“正确”重复副本的替代方法是:
nucmer --prefix=ref_qry ref.fasta qry.fastadelta-filter -r -q ref_qry.delta > ref_qry.filtershow-snps -Clr ref_qry.filter > ref_qry.snpsNow, conflicting repeat copies will first be eliminated with delta-filter and the SNPs will be re-called in hopes of finding some that were previously masked by another repeat copy.
现在,冲突的重复副本将首先用delta-filter消除,并且将重新调用SNP,希望找到先前被另一个重复副本掩盖的一些SNPs。
4.5. Identifying repeats (识别重复)
Although MUMmer was not specifically designed to identify repeats, it does has a few methods of identifying exact and exact tandem repeats. In addition to these methods, the nucmer alignment script can be used to align a sequence (or set of sequences) to itself. By ignoring all of the hits that have the same coordinates in both inputs, one can generate a list of inexact repeats. When using this method of repeat detection, be sure to set the –maxmatch and –nosimplify options to ensure the correct results.
尽管MUMmer没有专门设计来识别重复序列,但它确实具有几种确定精确和精确的串联重复的方法。 除了这些方法之外,可以使用nucmer对齐脚本来将序列(或一组序列)与其自身对齐。 通过忽略在两个输入中具有相同坐标的所有命中,可以生成不精确重复的列表。 当使用这种重复检测方法时,请务必设置–maxmatch和–nosimplify选项以确保正确的结果。
To find large inexact repeats in a set of sequences seq.fasta, type the following and ignore all hits with the same start coordinate in each copy of the sequence:
要在一系列序列seq.fasta中查找大的不精确重复,请键入以下内容,并忽略序列的每个副本中具有相同起始坐标的所有匹配:
nucmer --maxmatch --nosimplify --prefix=seq_seq seq.fasta seq.fastashow-coords -r seq_seq.delta > seq_seq.coordsTo find exact repeats of length 50 or greater in a single sequence seq.fasta, type:
要在单个序列seq.fasta中找到长度为50或更大的精确重复序列,请键入:
repeat-match -n 50 seq.fasta > seq.repeatsTo find exact tandem repeats of length 50 or greater in a single sequence seq.fasta, type:
要在单个序列seq.fasta中找到长度为50或更大的精确串联重复序列,请键入:
exact-tandems seq.fasta 50 > seq.tandems5. Program descriptions
The most commonly used MUMmer pipelines (nucmer, promer, run-mummer1 and run-mummer3) are comprised of three main sections. The first section identifies a certain subset of maximal exact matches between the two inputs, the second section clusters these matches into groups that will likely make good alignment anchors, and the third and final section extends alignments between these clustered matches to produce the final gapped alignment. These three sections also outline the primary types of programs included in the MUMmer package - the Maximal exact matching section describes the programs that compute different types maximal exact matches, the Clustering section describes the two different types of clustering algorithms, and Alignment generators describes the scripts that combine matching, clustering and extending in order to produce high scoring pair-wise alignments. Finally, the Utilities section reviews a few of the tools that have been developed for interpreting and displaying the output of the MUMmer alignment routines.
最常用的MUMmer管道(nucmer,promer,run-mummer1和run-mummer3)由三个主要部分组成。第一部分标识两个输入之间的最大精确匹配的某个子集,第二部分将这些匹配集合成可能产生良好对齐锚点的组,第三部分和最后一部分扩展这些聚类匹配之间的比对,以产生最终含间隙的比对。这三个部分还概述了MUMmer包中包含的程序的主要类型 - 最大精确匹配部分描述了计算不同类型最大精确匹配的程序,“聚类”部分描述了两种不同类型的聚类算法,“对齐生成器”描述了脚本结合匹配,聚类和扩展,以产生高得分的成对比对。最后,“实用程序”部分回顾了为解释和显示MUMmer对齐例程的输出而开发的一些工具。
It is noteworthy to point out the simplicity of improving the current MUMmer pipeline. For instance, if a different and/or better clustering algorithm was needed for a certain application, a program could be written in any language and inserted into the pipeline. So long as the program was able to read the appropriate input and produce output that mimics the existing module, it could be swapped for the existing module with a single edit to the calling script. NUCmer for example is a Perl script that invokes various MUMmer routines. If you were to develop a new clustering algorithm called mygaps you could edit the line in NUCmer that defines the location of mgaps to instead define the location of mygaps. It’s that easy, as long as mygaps had the same input and output mgaps the transition would be seamless.
值得注意的是,目前MUMmer管道的易用性的得到了提升。 例如,如果某个应用程序需要不同的和/或更好的聚类算法,则程序可以用任何语言编写并插入到管道中。 只要程序能够读取适当的输入并产生模拟现有模块的输出,就可以通过对调用脚本的单一编辑将现有模块进行交换。 例如,NUCmer是一个调用各种MUMmer例程的Perl脚本。 如果要开发一种称为mygaps的新的聚类算法,您可以编辑NUCmer中的行,该行定义了mgaps的位置,从而定义了mygaps的位置。 只要mygaps有相同的输入和输出,mgaps过渡是很容易的。
5.1. Maximal exact matching (最大精确匹配)
The heart of the MUMmer package is its suffix tree based maximal matching routines. These can be used for repeat detection within a single sequence as is done by repeat-match and exact-tandems, or can be used for the alignment of two or more sequences as is done by mummer. Most every other program in the MUMmer packages builds off of the output of the mummer maximal exact matcher, so it is of great importance to first understand the workings of this program.
MUMmer包的核心是其基于后缀树的最大匹配例程。 这些可以用于在单个序列中重复检测,如通过repeat-match和exact-tandems进行的,或者可以用于两个或更多个序列的比对,如同mummer完成的工作。 MUMmer软件包中的大多数其他程序都是建立在mummer最大精度匹配器的输出之上的,因此首先了解此程序的工作非常重要。
5.1.1. mummer
mummer is a suffix tree algorithm designed to find maximal exact matches of some minimum length between two input sequences. MUMmer’s namesake program originally stood for Maximal Unique Matcher, however in subsequent versions the meaning of unique has been skewed. The original version (1.0) required all maximal matches to be unique in both the reference and the query sequence (MUMs); the second version (2.0) required uniqueness only in the reference sequence (MUM-candidates); and the current version (3.0) can ignore uniqueness completely, however it defaults to finding MUM-candidates and can be switched on the command line. To restate, by default mummer will only find maximal matches that are unique in the entire set of reference sequences. The match lists produced by mummer can be used alone to generate alignment dot plots, or can be passed on to the clustering algorithms for the identification of longer non-exact regions of conservation. These match lists have great versatility because they contain huge amounts of information and can be passed forward to other interpretation programs for clustering, analysis, searching, etc.
mummer使用一种后缀树算法,旨在找到两个输入序列之间的一些最小长度的最大精确匹配。 MUMmer的同名程序最初代表最大唯一匹配器(Maximal Unique Matcher,MUM),但是在随后的版本中,唯一的含义已被扭曲。原始版本(1.0)要求所有最大匹配在参考和查询序列(MUMs)中都是唯一的;第二版(2.0)仅在参考序列(MUM-candidates)中要求唯一性;并且当前版本(3.0)可以完全忽略唯一性,但是默认情况下会发现MUM-candidates,并且可以在命令行上打开。要重申,默认情况下,mummer将只找到在整个参考序列集中唯一的最大匹配。由mummer生成的匹配列表可以单独使用来生成比对点图,或者可以传递给聚类算法,用于识别更长的非精确保守区域。这些匹配列表具有很大的通用性,因为它们包含大量的信息,并且可以转发到其他用于聚类,分析,搜索等的解释程序。
mummer achieves its high performance by using a very efficient data structure known as a suffix tree. This data structure can be both constructed and searched in linear time, making it ideal for large scale pattern matching. To save memory, only the reference sequence(s) is used to construct the suffix tree and the query sequences are then streamed through the data structure while all of the maximal exact matches are extracted and displayed to the user. Because only the reference sequence is loaded into memory, the space requirement for any particular mummer run is only dependent on the size of the reference sequence. Therefore, if you have a reasonably sized sequence set that you want to match against an enormous set of sequences, it is wise to make the smaller file the reference to assure the process will not exhaust your computer’s memory resources. The query files are loaded into memory one at a time, so for an enormous query that will require a significant amount of memory just to load the character string, it is helpful to partition the query into multiple smaller files using the syntax described below.
通过使用称为后缀树的非常有效的数据结构,mummer实现了其高性能。该数据结构可以在线性时间内构建和搜索,使其成为大规模模式匹配的理想选择。为了节省内存,仅使用参考序列构建后缀树,然后通过数据结构流式传输查询序列,同时提取所有最大精确匹配并将其显示给用户。因为只有参考序列被加载到存储器中,任何特定的mummer运行的空间要求只取决于参考序列的大小。因此,如果您有一个合理的大小的序列集,您想要匹配一大堆序列,明智的做法是使较小的文件参考,以确保该过程不会耗尽您的计算机的内存资源。查询文件一次一个地加载到内存中,所以对于需要大量内存的巨大查询只是为了加载字符串,使用下面描述的语法将查询分成多个较小的文件是有帮助的。
Command line syntax
mummer [options] <reference file> <query file1> . . . [query file32]There must be exactly one reference file and at least one query file. Both the reference and query files should be in multi-FastA format and may contain any set of upper and lowercase characters, thus DNA and protein sequences are both allowed and matching is case insensitive. The maximum number of query files is 32, but there is no limit on how many sequences each reference or query file may contain.
必须有一个参考文件和至少一个查询文件。 引用和查询文件都应该是Multi-FastA格式,并且可以包含任何一组大小写字符,因此,DNA和蛋白质序列都被允许,匹配是不区分大小写的。 查询文件的最大数量为32,但每个参考或查询文件可能包含多少个序列没有限制。
Program options
-mum Compute MUMs, i.e. matches that are unique in both the reference and query计算MUMs,即在参考和查询中都是唯一的匹配-mumreference Compute MUM-candidates, i.e. matches that are unique in the reference but not necessarily in the query计算MUM-candidates,即参考中唯一的匹配,但不一定在查询中-maxmatch Compute all maximal matches regardless of their uniqueness计算所有最大匹配,而不管它们的唯一性-n Only match the characters a, c, g, or t (case insensitive)只匹配字符a,c,g或t(不区分大小写)-l int Minimum match length (default 20)最小匹配长度(默认为20)-b Compute both forward and reverse complement matches计算正向和反向互补匹配-r Only compute reverse complement matches仅计算反向互补匹配-s Show the matching substring in the output在输出中显示匹配的子串-c Report the query position of a reverse complement match relative to the forward strand of the query sequence报告相对于查询序列的正向链的反向互补匹配的查询位置-F Force 4 column output format that prepends every match line with the reference sequence identifier强制4列输出格式,每个匹配行与参考序列标识符相加-L Show the length of the query sequence on the header line在标题行上显示查询序列的长度-help Show the possible options and exit显示可能的选项并退出Option grouping is not allowed, therefore each option should be separated by a space. The options -mum, -mumreference, and -maxmatch cannot be combined, and if neither is used, then the program will default to -mumreference. For a string to be unique in the reference, it must occur only once in the concatenation of all the reference superstrings, but for string to be unique in the query it need only be unique in its own superstring. Setting either the -mum or -mumreference option can significantly cut down on the number of repeat induced matches as opposed to -maxmatch, and is recommended for most all applications. Also, setting the -l option any lower than around 15 can significantly increase the number of spurious matches and therefore balloon the runtime. When dealing with masked DNA sequence, use the -n option to avoid matching the masking characters. Options -b and -r exclude each other, and if neither is used then only forward matches will be reported. All reverse complementing will affect only the query sequences. Option -c can only be used in combination with -b or -r, as it would have no relevance without these options. The -F option is useful for forcing mummer to output a consistent format regardless of the number of input sequences.
选项分组是不允许的,因此每个选项应该由一个空格分开。选项-mum,-mumreference和-maxmatch不能组合,如果不使用,那么程序将默认为-mumreference。对于refernece中唯一的字符串,它必须在所有reference superstrings的连接中只发生一次,但是对于在query中唯一的字符串,它只需在其自己的superstrings中是唯一的。设置-mum或-mumreference选项可以显着减少重复引用匹配的数量,而不是使用-maxmatch,并且对于大多数应用程序是推荐的。此外,将-l选项设置为低于约15可以显着增加虚拟匹配数量,从而激增运行时间。当处理掩蔽的DNA序列时,使用-n选项来避免匹配掩蔽字符。选项-b和-r不兼容,如果两者都不使用,则仅报告正向匹配。所有反向互补将仅影响查询序列。选项-c只能与-b或-r组合使用,因为在没有这些选项的情况下它们将无关。 -F选项对于强制mummer输出一致的格式非常有用,无论输入序列的数量如何。
For those familiar with the previous versions of MUMmer, the -mum option mimics the functionality of MUMmer1.0; the -mumreference option mimics the functionality of MUMmer2.0; and the -maxmatch option mimics the functionality of the max-match program included with MUMmer2.0. The default behavior of the current version is -mumreference because it is a good balance between finding all matches and only unique matches.
熟悉MUMmer以前版本的人,-mum选项模仿MUMmer1.0的功能; -mumreference选项模仿MUMmer2.0的功能; 而-maxmatch选项模仿MUMmer2.0附带的最大匹配程序的功能。 当前版本的默认行为是-mumreference,因为它是查找所有匹配和唯一匹配之间的良好平衡。
Output format
Output formatting varies depending on the command line parameters used. Program diagnostic information is always output to stderr while the match lists are output to stdout. This allows for the match output to be redirected into a file, which is quite useful since the output is generally quite large. The standard output format that results from running mummer on a single reference sequence with the -b option is as follows:
输出格式取决于所使用的命令行参数。 当匹配列表输出到stdout时,程序诊断信息总是输出到stderr。 这允许将匹配输出重定向到文件中,这是非常有用的,因为输出通常相当大。 使用-b选项在单个参考序列上运行的mummer产生的标准输出格式如下所示:
> ID1 4655667 1 31 4655699 33 319 4656019 353 520 4656540 874 20> ID1 Reverse 741743 22 872> ID2 4655520 1 498 4656019 500 274 4656317 798 39 4656376 855 29> ID2 Reverse> ID3> ID3 Reverse 4655178 27 840 4656019 868 171(output continues ...)For each query sequence, the corresponding ID tag is reported on each line beginning with a ‘>’ symbol, even if there are no matches corresponding to this sequence. Reverse complemented matches follow a query header that has the keyword Reverse following the sequence tag, thus creating two headers for each query sequence and alternating forward and reverse match lists. For each match, the three columns list the position in the reference sequence, the position in the query sequence, and the length of the match respectively. Reverse complemented query positions are reported relative to the reverse of the query sequence unless the -c option was used. As was stated above the -L option adds the sequence lengths to the header line and the -s option adds the match strings to the output, if these options were used the format would be as follows:
对于每个查询序列,对应的ID标签在以“>”符号开始的每一行上报告,即使没有与此序列相对应的匹配。 反向互补匹配遵循按照序列标签具有关键字Reverse的查询头,从而为每个查询序列创建两个标题,并且交替的正向和反向匹配列表。 对于每个匹配,三列分别列出参考序列中的位置,查询序列中的位置和匹配的长度。 反向互补的查询位置相对于相反的查询序列被报告,除非使用-c选项。 如上所述,-L选项将序列长度添加到标题行,并且-s选项将匹配字符串添加到输出,如果使用这些选项,格式将如下所示:
> ID1 Len = 893 4655667 1 31ctgacgacaaccatgcaccacctgtcactct 4655699 33 319ctcccgaaggagaagccctatctctagggttgtcagaggatgtcaagacctgg . . . 4656019 353 520gttcctccatatctctacgcatttcaccgctacacatggaattccactttcct . . . 4656540 874 20tttcgaaccatgcggttcaa> ID1 Reverse Len = 893 741743 22 872tgaaaggcggcttcggctgtcacttatggatggacccgcgtcgcattagctag . . .> ID2 Len = 884 4655520 1 498tcataaggggcatgatgatttgacgtcatccccaccttcctccggtttgtcac . . . 4656019 500 274gttcctccatatctctacgcatttcaccgctacacatggaattccactttcct . . . 4656317 798 39aagccttcatcactcacgcggcgttgctccgtcagactt 4656376 855 29cctactgctgcctcccgtaggagtctggg> ID2 Reverse Len = 884> ID3 Len = 1039> ID3 Reverse Len = 1039 4655178 27 840atcaattctccatagaaaggaggtgatccagccgcaccttccgatacggctac . . . 4656019 868 171gttcctccatatctctacgcatttcaccgctacacatggaattccactttcct . . .(output continues ...)Where the length of each query is noted after the Len keyword and the match string is listed on the line after its match coordinates. Note that the ellipsis marks are not part of the actual output, but added to fit the output into the webpage. Finally, when dealing with multiple reference sequences (or the -F option), it is necessary to output the ID of the reference sequence. This is placed at the beginning of each match line, creating an four column output format as follows:
在Len关键字之后注明每个查询的长度,并且匹配字符串在其匹配坐标之后的行上列出。 请注意,省略号不是实际输出的一部分,而是添加到输入到网页中。 最后,当处理多个参考序列(或-F选项)时,需要输出参考序列的ID。 这将放置在每个匹配行的开头,创建一个四列输出格式,如下所示:
> ID1 220594 479 1 728> ID1 Reverse 220716 3527 1 20 220716 3548 22 840> ID2> ID2 Reverse 219093 13 401 484 220716 3682 2 29 220716 3731 49 39 220716 3794 112 693> ID3 219093 13 188 721 220716 3897 2 590 220716 4488 593 423> ID3 Reverse 220594 1 38 509(output continues ...)5.1.2. repeat-match
repeat-match is a suffix tree algorithm designed to find maximal exact repeats within a single input sequence. It uses a similar algorithm to mummer, but altered slightly to find maximal exact matches within a single sequence.
repeat-match是一种后缀树算法,设计用于在单个输入序列内找到最大精确重复。 它使用类似mummer的算法,但稍微改变以在单个序列中找到最大精确匹配。
Command line syntax
repeat-match [options] <sequence file>The sequence file should contain only one sequence in FastA format, however if multiple sequences exist the first one will be used. The sequence may contain any set of upper and lowercase characters, thus DNA and protein sequences are both allowed and matching is case insensitive.
序列文件应该只包含FastA格式的一个序列,但是如果存在多个序列,则使用第一个序列。 该序列可以包含任何一组大小写字母,因此DNA和蛋白质序列都被允许,并且匹配是不区分大小写的。
Program options
-f Use the forward strand only仅使用正向链-n int Minimum match length (default 20)最小匹配长度(默认为20)-t Only output tandem repeats仅输出串联重复The program will report both forward and reverse complement repeats by default unless the -f option is used. While the -t option identifies tandem repeats, the exact-tandems script is a wrapper for repeat-match and does a more graceful job of reporting the tandem repeats.
除非使用-f选项,否则程序将默认报告正向和反向互补重复。 虽然-t选项标识串联重复,但是exact-tandems脚本是repeat-match的包装器,并且更加优雅地报告串联重复。
Output format
Output formatting varies depending on the command line parameters. Program diagnostic information is always output to stderr while the match lists are output to stdout. This allows for the match output to be redirected into a file, which is quite useful since the output can be quite large. The standard output format that results from running repeat-match with default parameters is as follows:
输出格式取决于命令行参数。 当匹配列表输出到stdout时,程序诊断信息总是输出到stderr。 这允许将匹配输出重定向到一个文件,这是非常有用的,因为输出可能相当大。 运行与默认参数重复匹配的标准输出格式如下:
Long Exact Matches: Start1 Start2 Length 4919485 4919506r 22 4997298 4997319r 22 4919485 4997298 22 3461866 3751066 53 537897 4650529r 76(output continues ...)The three columns are the first position of the repeat, the second position of the repeat, and the length of the repeat respectively. Reverse complement repeat positions are denoted by an ‘r’ following the Start2 position, and are relative to the forward strand of the sequence.
三列分别是是重复的第一个位置,重复的第二个位置和重复的长度。 反向互补重复位置由Start2位置之后的’r’表示,并且是相对于序列的正向链。
5.1.3. exact-tandems
exact-tandems is a wrapper cshell script for the repeat-match program. It provides a list of exact tandem repeats within a single input sequence.
exact-tandems是重复匹配程序的一个包装cshell脚本。 它提供单个输入序列中精确串联重复的列表。
Command line syntax
exact-tandems <sequence file> <min length>As with repeat-match the sequence file should contain only one sequence in FastA format, however if multiple sequences exist the first one will be used. The sequence may contain any set of upper and lowercase characters, thus DNA and protein sequence are both allowed and matching is case insensitive. The minimum match length parameter should be a positive integer, this value will be passed to the repeat-match program via the -n option.
与repeat-match一样,序列文件应仅包含FastA格式的一个序列,但是如果存在多个序列,则将使用第一个序列。 该序列可以包含任何一组大小写字母,因此DNA和蛋白质序列都被允许并且匹配是不区分大小写的。 最小匹配长度参数应为正整数,该值将通过-n选项传递给repeat-match程序。
Output format
Program diagnostic information is always output to stderr while the match lists are output to stdout. This allows for the match output to be redirected into a file, which is quite useful since the output can be quite large. The output format of exact-tandems is as follows:
当匹配列表输出到stdout时,程序诊断信息总是输出到stderr。 这允许将匹配输出重定向到一个文件,这是非常有用的,因为输出可能相当大。 精确串联的输出格式如下:
Finding matchesTandem repeats Start Extent UnitLen Copies 416173 150 45 3.3 554810 102 42 2.4 554943 109 42 2.6 880346 191 63 3.0 880370 62 21 3.0(output continues ...)The four columns are the first position of the tandem, the extent of the repeat region, the length of each tandem repeat unit, and the number of repeat units respectively.
四列分别是串联的第一个位置,重复区域的范围,每个串联重复单元的长度以及重复单元的数量。
5.2. Clustering
MUMmer’s clustering algorithms attempt to order small individual matches into larger match clusters in order to make the output of mummer more intelligible. A dot plot makes it easy to spot alignment regions from a match list, however when examining the data without graphic aids, it is very difficult to draw any reasonable conclusions from the simple flat file list of matches. Clustering the matches together into larger groups of neighboring matches makes this process much easier by ordering the data and removing spurious matches.
MUMmer的聚类算法尝试将较小的个体匹配排序成较大的匹配簇,以使得mummer的输出更易理解。 点阵图可以很容易地从匹配列表中找出对齐区域,但是在没有图形辅助功能的情况下检查数据时,很难从简单的平面文件列表中获得合理的结论。 将匹配集合到较大的相邻匹配组中,可以通过排序数据和消除虚假匹配来简化此过程。
5.2.1. gaps
gaps is the primary clustering algorithm for run-mummer1, and although classified as a “clustering” step, gaps is more of a sorting routine. It implements the LIS (longest increasing subset) algorithm to extract the longest consistent set of matches between two sequences, and generates a single cluster that represents the best “straight-line” arrangement of matches between the sequences. By straight-line, we mean no rearrangements or inversions, just a simple path of agreeing matches between the two sequences. This limits the usability of this program to the alignment of genomes that are very similar and with no large scale mutations. To further illustrate the purpose of this program, consider the following set of MUMs (illustrated as line connecting two rectangles) between two sequences:
gaps是run-mummer1的主要聚类算法,虽然被分类为“聚类”步骤,但gaps更多的是排序例程。 它实现LIS(最长增加子集)算法来提取两个序列之间最长一致的匹配集合,并生成代表序列之间匹配的最佳“直线”排列的单个群集。 通过直线,我们的意思是没有重新排列或反转,只是两个序列之间的匹配的简单路径。 这限制了该程序对于非常相似且没有大规模突变的基因组的排列的可用性。 为了进一步说明此程序的目的,请考虑以下两个序列之间的一组MUM(以线连接两个矩形):

The rectangles connected by lines are maximal exact matches between two sequences, however only the red rectangles would be included in the LIS because they form the longest increasing subset of matches, i.e. the longest subset of matches that are consistently ordered in both genomes. Note that the empty rectangles will be discarded, even though they probably represent a major rearrangement between the two sequences. Because of this limitation gaps is best suited for the comparison of near identical sequences with the goal of finding minor mutations like SNPs and small indels.
通过线连接的矩形是两个序列之间的最大精确匹配,但是只有红色矩形将包含在LIS中,因为它们形成了最长的增加的匹配子集,即在两个基因组中始终排列的最长的匹配子集。 请注意,空矩形将被丢弃,尽管它们可能代表两个序列之间的主要重排。 由于这种限制,gaps最适合于近似相同序列的比较,目的是发现像SNP和小插入物这样的小突变。
Command line syntax
mummer [params] | tail +2 | gaps <reference file> [-r]or
gaps <reference file> [-r] < <match list>Because gaps receives its input from stdin, the input can either be piped directly from filtered mummer output, or redirected as input from a file. The strange syntax is a result of a legacy issue described in the Known problems section, and requires the header be stripped from the mummer output. In addition, gaps is only designed to handle a single reference and a single query sequence, thus the preceding mummer run must also follow this constraint. The -r is optional and designates the incoming matches as reverse complement matches which must reference the reverse complement of the sequence, therefore forcing mummer to be run without the -c option. Please refer to the run-mummer1 script for an example of how to use this program in an alignment pipeline. A rewrite of this algorithm to handle multiple reference and/or query sequences may eventually appear, but is not currently in development.
因为gaps从stdin接收到它的输入,所以输入可以直接从过滤的mummer输出中输入,或者从文件重定向为输入。 奇怪的语法是“Known problems”部分中描述的遗留问题的结果,并且要求将标题从“mummer”输出中删除。 此外,gaps仅用于处理单个参考和单个查询序列,因此,上述的mummer运行也必须遵循该约束。 -r是可选的,并将输入的匹配指定为反向互补匹配,必须引用序列的反向互补,因此强制mummer在没有-c选项的情况下运行。 请参阅run-mummer1脚本,了解如何在对齐管道中使用此程序的示例。 可以最终出现对该算法的重写以处理多个引用和/或查询序列,但是目前尚未开发。
Output format
The stdout output of gaps shares much in common with the standard three column match output, with the addition of three extra columns:
gaps的stdout与标准三列匹配输出共享,增加了三列:
> /home/aphillip/data/GHP.1con Consistent matches 183 17 22 none - - 238 72 108 none 33 33 347 181 92 none 1 1 458 292 50 none 19 19 705 539 44 none 1 1 750 584 38 none 1 1 807 641 23 -16 0 4(output continues ...)> Wrap around 334398 329917 47 none - 225 334446 329965 62 none 1 1 334539 330058 20 none 31 31 334560 330079 92 none 1 1 334653 330172 77 none 1 1 334740 330259 41 none 10 10(output continues ...)> /home/aphillip/data/GHP.1con Other matches 1317231 4891 21 none - - 1317275 4927 21 none - - 1317804 5399 25 none 508 451 947580 5436 36 none - - 23406 5518 34 none - - 333079 6592 32 none - -(output continues ...)Where the first line is the location of the reference file, and the first three columns are the same as the three column match format described in the mummer section. The final three columns are the overlap between this match and the previous match, the gap between the start of this match and the end of the previous match in the reference, and the gap between the start of this match and the end of the previous match in the query respectively. A couple suggestions on how to visually scan through this output: a gap size == 1 means a single mismatch between the two sequences, e.g. a SNP, an overlap like seen in the last line of the Consistent matches indicates the existence of a tandem repeat, and a ‘-’ character means that the gap size could not be calculated. The Wrap around list is for circular genomes where the consistent set of matches wraps around the origin of the reference, and the Other matches list shows the matches that were not included in the LIS (like the white boxes in the above image). Finally, if the -r was passed on the command line the Consistent matches and Other matches headers would contain the reverse keyword after the reference file.
第一行是参考文件的位置,前三列与mummer部分中描述的三列匹配格式相同。最后三列是该匹配与前一个匹配之间的重叠,该匹配的开始与参考中前一个匹配的结束之间的差距,以及该匹配的开始与前一个查询的结束分别之间的间隙。关于如何可视地扫描此输出的几个建议:间隙大小== 1表示两个序列之间的单一错配,例如, SNP,如同Consistent matches的最后一行所示的重叠表示串联重复的存在,“ - ”字符意味着无法计算间隙大小。 “Wrap around”列表适用于循环基因组,其中一致的一组匹配包围参考的原点,而“Other matches”列表显示未包含在LIS中的匹配项(如上图中的白框)。最后,如果-r在命令行上传递,则Consistent matches和Other Match头将在引用文件后面包含反向关键字。
5.2.2. mgaps
mgaps was introduced into the MUMmer pipeline in an effort to better handle large-scale rearrangements and duplications. Unlike gaps, mgaps is a full clustering algorithm that is capable of generating multiple groups of consistently ordered matches. Clustering is controlled by a set of command-line parameters that adjust the minimum cluster size, maximum gap between matches, etc. Only matches that were included in clusters will appear in the output, so by adjusting the command-line parameters it is possible to filter out many of the spurious matches, thus leaving only the larger areas of conservation between the input sequences. The major advantage of mgaps is its ability to identify these “islands” of conservation. This frees the user from the single LIS restraints of the gaps program and allows for the identification of large-scale rearrangements, duplications, gene families and so on. To further illustrate the purpose of this program, consider once again the following set of MUMs (illustrated as line connecting two rectangles) between two sequences:
为了更好地处理大规模的重新排列和重复,将mgaps引入了MUMmmer管道。与gaps不同,mgaps是一个完整的聚类算法,能够生成多组一致的有序匹配。集群由一组调整最小集群大小,匹配之间的最大间隙等的命令行参数控制。只有在集群中包含的匹配才会出现在输出中,因此通过调整命令行参数,可以滤除许多杂散匹配,从而在输入序列之间只留下更大的保守区域。mgaps的主要优点是其识别这些保守“islands”的能力。这样可以让用户从gaps程序的单一LIS限制中释放出来,并允许用户识别大规模的重排,重复,基因家族等。为了进一步说明此程序的目的,请再次考虑以下两个序列之间的MUMs(以线连接两个矩形的方式):

Just like before the rectangles connected by lines are maximal exact matches between two sequences, with each distinct cluster having its own unique color. In the previous demonstration using this MUM set, gaps failed to identify the blue cluster because it was not consistent with the LIS. However, by using mgaps, all regions of conservation have now been identified. The only fallback being the increased complexity of the output, where you once had only one cluster for the whole comparison, you now have four. Because of this, it can sometimes be difficult separating the repetitive clusters from “correct” clusters, making mgaps more suited for global alignments instead of localized error detection.
就像之前,由线条连接的矩形是两个序列之间的最大精确匹配,每个不同的集群都有自己独特的颜色。 在以前使用此MUM集的演示中,由于与LIS不一致,因此gaps无法识别蓝色集群。 然而,通过使用mgaps,现在已经识别了所有的保守区域。 唯一的回退是输出的复杂性增加,您曾经只有一个集群用于整个比较,现在有四个。 因此,有时难以将重复的群集与“正确的”群集分开,使得mgaps更适合于全局比对而不是局部错误检测。
Command line syntax
mummer [params] | mgaps [options]or
mgaps < <match list>Because gaps receives its input from stdin, the input can either be piped directly from raw mummer output, or redirected as input from a mummer output file. mgaps is only designed to handle a single reference and one or more query sequences, thus the preceding mummer run must also follow this constraint. Please refer to the run-mummer3 script for an example of how to use this program in an alignment pipeline. Note that in order to cluster reverse complement matches, the reverse complement matches must reference the reverse complement strand of the query sequence, therefore forcing mummer to be run without the -c option. A rewrite of this algorithm to handle multiple reference sequences and a better coordinate system (forward coordinates for reverse complement matches) is doubtful but may eventually appear.
因为gaps从stdin接收到它的输入,所以输入可以直接从原始的mummer输出管道,或者从mummer输出文件重定向为输入。 mgaps分布仅用于处理单个参考和一个或多个查询序列,因此前一个mummer运行也必须遵循该约束。 有关如何在对齐管道中使用此程序的示例,请参阅run-mummer3脚本。 请注意,为了对反向互补进行聚类匹配,反向互补匹配必须引用查询序列的反向互补链,因此强制mummer在没有-c选项的情况下运行。 重写该算法以处理多个参考序列和更好的坐标系统(反向补码匹配的正向坐标)是可疑的,但可能最终出现。
Program options
-C Check that input header labels alternately have the "Reverse" keyword检查输入标题标签交替显示“反向”关键字-d int Maximum fixed diagonal difference (default 5)最大固定对角线差值(默认值5)-e Use extent of cluster (end - start) rather than the sum of the match lengths to determine cluster length使用簇的范围(end-start),而不是匹配长度的总和来确定簇长度-f float Maximum fraction of separation for diagonal difference (default 0.05)对角差异的最大分离度(默认为0.05)-l int Minimum cluster length (default 200)最小群集长度(默认为200)-s int Maximum separation between adjacent matches in a cluster (default 1000)集群中相邻匹配之间的最大间隔(默认为1000)The -d option can be interpreted as the number of insertions allowed between two matches in the same cluster, while the -f option is a fraction equal to (diagonal difference / match separation) where a higher value will increase the indel tolerance. Minimum cluster length is the sum of the contained matches unless the -e option is used. The best way to get a feel for what each parameter controls is to cluster the same data set numerous times with different values and observe the resulting differences. It can also be helpful to set these parameters to the size of the element you wish to capture, i.e. set the minimum cluster size to say the smallest exon you expect and set the max gap to the smallest intron you expect to obtain clusters that could represent single exons (depending of course of the similarity of the two sequences).
-d选项可以解释为在同一个集群中的两个匹配之间允许的插入次数,而-f选项是等于(对角差分/匹配分隔)的分数,其中较高的值将增加indel度量。 最小簇长度是包含的匹配之和,除非使用-e选项。 了解每个参数控制的最佳方法是用不同的值对同一数据集进行多次聚类,并观察产生的差异。 将这些参数设置为要捕获的元素的大小也是有帮助的,即将最小集群大小设置为所期望的最小外部程序,并将最大间隙设置为希望获取可能代表的集群的最小内含子 单个外显子(取决于两个序列相似性的过程)。
Output format
The stdout output of mgaps shares much in common with the output of mummer and gaps, with a slightly different header formatting than gaps to allow for multiple query sequences and multiple clusters. The output of mgaps run on both forward and reverse complement matches is as follows:
mgaps的标准输出与mummer和gaps的输出大致相同,标题格式与间隙稍微不同,以允许多个查询序列和多个集群。 正向和反向补码匹配运行的mgaps输出如下:
> ID41> ID41 Reverse 5177399 1 232 none - - 5177632 234 6794 none 1 1 5184433 7035 24 none 7 7 5184468 7069 23 none 11 10> ID42 10181 43 1521 none - -> ID42 Reverse 4654536 17 36 none - - 4654578 57 298 none 6 4 4654877 356 226 none 1 1# 4655139 845 28 none - - 4655178 884 694 none 11 11 4655873 1579 20 none 1 1# 4850044 17 1492 none - - 4851537 1510 711 none 1 1 4852249 2222 42 none 1 1(output continues ...)Headers containing the ID for each query sequence are listed after the ‘>’ characters, and a following Reverse keyword identifies the reverse matches for that query sequence. Individual clusters for each sequence are separated by a ‘#’ character, and the six columns are exactly the same as the gaps output (see the gaps section for more details).
包含每个查询序列的ID的标题在“>”字符后面列出,并且以下“反向”关键字标识该查询序列的反向匹配。 每个序列的单个簇由“#”字符分隔,六列与gaps输出完全相同(有关详细信息,请参阅gaps部分)。
5.3. Alignment generators (比对生成器)
The alignment scripts described in this section build upon the data generated by the previous two sections, maximal exact matching and clustering. Each of these scripts independently runs the matching and clustering steps, and then generates pair-wise alignments for each of the clusters. This translates to a basic seed and extend method of alignment. The individual matches within each cluster are used as alignment anchors and only the mismatching sequence between the matches is processed by the Smith-Waterman dynamic programming routine. This reduces both the time and memory necessary to align large sequences, while still producing accurate alignments.
本节中描述的对齐脚本基于前两部分生成的数据,最大精确匹配和聚类。 这些脚本中的每一个独立地运行匹配和聚类步骤,然后为每个集群生成成对的对齐。 这转化为基本种子和扩展对齐方法。 每个簇内的个体匹配用作对齐锚点,只有匹配之间的不匹配序列由Smith-Waterman动态规划程序处理。 这减少了排列大序列所需的时间和内存,同时仍然产生准确的对准。
5.3.1. NUCmer
NUCmer (NUCleotide MUMmer) is the most user-friendly alignment script for standard DNA sequence alignment. It is a robust pipeline that allows for multiple reference and multiple query sequences to be aligned in a many vs. many fashion. For instance, a very common use for nucmer is to determine the position and orientation of a set of sequence contigs in relation to a finished sequence, however it can be just as effective in comparing two finished sequences to one another. Like all of the other alignment scripts, it is a three step process - maximal exact matching, match clustering, and alignment extension. It begins by using mummer to find all of the maximal unique matches of a given length between the two input sequences. Following the matching phase, individual matches are clustered into closely grouped sets with mgaps. Finally, the non-exact sequence between matches is aligned via a modified Smith-Waterman algorithm, and the clusters themselves are extended outwards in order to increase the overall coverage of the alignments. nucmer uses the mgaps clustering routine which allows for rearrangements, duplications and inversions; as a consequence, nucmer is best suited for large-scale global alignments, as is shown in the following plot:
NUCmer(NUCleotide MUMmer)是用于标准DNA序列比对的最友好的对齐脚本。它是一个强大的pipeline,允许多个参考和多个查询序列以多种方式对齐。例如,非常普遍的用途是确定一组序列contigs相对于完成的序列的位置和取向,然而它可以在将两个完成的序列彼此进行比较时同样有效。像所有其他对齐脚本一样,它是一个三步过程 - 最大精确匹配,匹配聚类和对齐扩展。它通过使用mummer来查找两个输入序列之间给定长度的所有最大唯一匹配开始。在匹配阶段之后,单个匹配被聚集成具有mgaps的紧密分组的集合。最后,通过经修改的Smith-Waterman算法对齐匹配之间的非精确序列,并且将簇本身向外扩展,以增加比对的总体覆盖。 nucmer采用mgaps聚类程序,允许重排、重复和倒置;因此,nucmer最适合于大规模的全局对齐,如下图所示:

This dot plot represents a nucmer alignment of two different strains of Helicobacter pylori (26695 on the x-axis and J99 on the y-axis). Forward matches are shown in red, while reverse matches are shown in green. This alignment, which took only 12 seconds to compute, clearly shows a major inversion event centered around the origin of replication, and demonstrates NUCmer’s ability to handle large scale rearrangements between sequences of high nucleotide similarity.
该点图表示幽门螺杆菌的两个不同菌株(x轴上为26695,y轴为J99)的nucmer比对。 正向匹配显示为红色,反向匹配以绿色显示。 这种排列只需要12秒计算,就清楚地显示了以复制起点为中心的主要反转事件,并且证明了NUCmer在核苷酸高度相似的序列之间处理大规模重排的能力。
Command line syntax
nucmer [options] <reference file> <query file>The reference and query files should both be in multi-FastA format and have no limit on the number of sequences they man contain. However, because nucmer uses mummer for its maximal exact matching, the memory usage will be dependent on the size of the reference file, so it may be advisable to make the smaller of the input files the reference to assure the program does not exhaust your computer’s memory resources. In addition, masking the uninteresting regions of the input with any character other than a, c, g, or t will both speed up nucmer by reducing the number of possible matches and also cut down on the number of alignments induced by repetitive sequence.
引用和查询文件都应该是Multi-FastA格式,并且对它们包含的序列数没有限制。 然而,因为nucmer使用mummer进行最大的精确匹配,所以内存使用将取决于引用文件的大小,因此建议使较小的输入文件为参考,以确保程序不会耗尽计算机的内存资源。 另外,用除了a,c,g或t之外的任何字符掩蔽输入的不感兴趣的区域都将通过减少可能匹配的数量并且还减少由重复序列引起的比对数量来加速nucmer。
Program options
--mum Use anchor matches that are unique in both the reference and query使用参考和查询中唯一的锚匹配--mumreference Use anchor matches that are unique in the reference but not necessarily unique in the query (default behavior)使用引用中唯一的锚匹配,但在查询中不一定唯一(默认行为)--maxmatch Use all anchor matches regardless of their uniqueness使用所有锚匹配,而不管其唯一性-b int--breaklen Distance an alignment extension will attempt to extend poor scoring regions before giving up (default 200)距离对齐扩展将尝试在放弃之前扩展差评分区域(默认为200)-c int--mincluster Minimum cluster length (default 65)最小群集长度(默认为65)--[no]delta Toggle the creation of the delta file. Setting --nodelta prevents the alignment extension step and only outputs the match clusters (default --delta)切换增量文件的创建。设置--nodelta可防止对齐扩展步骤,仅输出匹配群集(默认--delta)--depend Print the dependency information and exit打印依赖关系信息并退出-d float--diagfactor Maximum diagonal difference factor for clustering, i.e. diagonal difference / match separation (default 0.12)用于聚类的最大对角差分因子,即对角差分/匹配分离(默认0.12)--[no]extend Toggle the outward extension of alignments from their anchoring clusters. Setting --noextend will prevent alignment extensions but still align the DNA between clustered matches and create the .delta file (default --extend)从其锚定簇切换对齐的向外延伸。设置--noextend将阻止对齐扩展,但仍然在聚类匹配之间对齐DNA并创建.delta文件(默认--extend)-f--forward Align only the forward strands of each sequence仅对齐每个序列的正向链-g int--maxgap Maximum gap between two adjacent matches in a cluster (default 90)集群中两个相邻匹配之间的最大间隙(默认为90)-h--help Print the help information and exit打印帮助信息并退出-l int--minmatch Minimum length of an maximal exact match (default 20)最大完全匹配的最小长度(默认为20)-o--coords Automatically generate the <prefix>.coords file using the 'show-coords' program with the -r option使用-r选项使用'show-coords'程序自动生成<前缀> .coords文件--[no]optimize Toggle alignment score optimization. Setting --nooptimize will prevent alignment score optimization and result in sometimes longer, but lower scoring alignments (default --optimize)切换对齐分数优化。设置 - --nooptimize将阻止对齐分数优化并导致有时更长,但较低的评分对齐(默认 --optimize)-p string--prefix Set the output file prefix (default out)设置输出文件前缀(默认值)-r--reverse Align only the reverse strand of the query sequence to the forward strand of the reference将查询序列的反向对齐到引用的正向链--[no]simplify Simplify alignments by removing shadowed clusters. Turn this option off if aligning a sequence to itself to look for repeats (default --simplify)通过删除阴影集群简化对齐。如果将序列与其自身对齐以查找重复,则关闭此选项(默认--simplify)-V--version Print the version information and exit打印版本信息并退出All values are measured in DNA bases unless otherwise noted. Using either the -mum or -mumreference options (along with masking the input sequences) can help reduce the number of repeat induced alignments, and is suggested for most applications. If no uniqueness options are set, the program will default to -mumreference. Decreasing the values of the -mincluster and –minmatch options will increase the sensitivity of the alignment but may produce less reliable alignments. In addition, significantly raising the value of the –maxgap value (say to 1000) can be crucial in producing alignments for more divergent genomes. Setting –noextend speeds up the process by preventing alignment extensions outward from each cluster, while –nodelta takes this a step further and doesn’t even align the sequence between the matches in a cluster, however both of these reduce the amount of information contained in the output. See mgaps description for hints on setting the clustering parameters –mincluster, –diagdiff and –maxgap. The –coords option exists only for NUCmer1.0 compatibility; instead, it is recommended to run show-coords afterwards with more specific options. The –nooptimize option will force alignments within –breaklen bases of the sequence end to extend all the way to the sequence end, regardless of the resulting alignment score. The –prefix string should be unique in the output directory to prevent overwriting pre-existing data. Finally, by default nucmer matches the forward and reverse strands of the query sequences to the forward strand of the reference sequence unless the –forward or –reverse options were used, and all output coordinates always reference the forward strand of their respective sequence. Only use the –nosimplify option when aligning a sequence to itself in order to find inexact repeats.
所有值均以DNA碱基测量,除非另有说明。使用-mum或-mumreference选项(以及屏蔽输入序列)可以帮助减少重复导致对齐的次数,并为大多数应用程序提出建议。如果没有设置唯一性选项,程序将默认为-mumreference。降低-mincluster和-minmatch选项的值将增加对齐的灵敏度,但可能产生较不可靠的对齐。此外,显着提高-maxgap值(例如1000)的值可能对于产生更多不同基因组的比对是至关重要的。设置–noextend通过阻止每个集群向外的对齐扩展来加速进程,而–nodelta进一步提高了一步,甚至不排除集群中的匹配之间的顺序,但是这两个都减少了包含在输出中的信息量。有关设置聚类参数–mincluster,–diagdiff和–maxgap的提示,请参阅mgaps描述。 –coords选项仅适用于NUCmer1.0兼容性;相反,建议以更具体的选项运行show-coords。 –noptimize选项将强制序列末尾的–breaklen基数内的对齐方式一直延伸到序列结束,而不管得到的对齐分数如何。输出目录中的–prefix字符串应该是唯一的,以防止覆盖预先存在的数据。最后,默认情况下,nucmer将查询序列的正向和反向链与参考序列的正向链匹配,除非使用–forward或–reverse选项,并且所有输出坐标始终引用其各自序列的正向链。只有在将序列与自身对齐时才能使用–nosimplify选项,以便找到不正确的重复。
Output format
Because nucmer and promer produce the same output files, this section will serve to explain the .delta format for both programs. The delta file contains an encoded representation of all the alignments generated in the “extend” phase of the pipeline, and is a unique format for concise, machine representation of the pair-wise alignments. Several tools described in the Utilities section were designed to interpret these files and extract useful, human-readable information from them, however the full format description the delta file is described below to aid developers.
因为nucmer和promer产生相同的输出文件,本节将用于解释这两个程序的 .delta格式。 delta file包含在pipeline的“扩展”阶段中生成的所有对齐的编码表示,并且是用于简洁的成对对齐的机器表示的唯一格式。 实用程序部分中描述的几个工具旨在解释这些文件,并从中提取有用的,可读取的信息,但是delta file的完整格式描述如下所述,以帮助开发人员。
The “delta” file format
The “delta” file is an encoded representation of the all-vs-all alignment between the input sequences to either the NUCmer or PROmer pipeline. It is the primary output of these alignment scripts and there are various utilities described in section 5.4. that are designed to take the delta file as input, and output some human-readable information to the user. Also, the delta-filter utility is designed to manipulate these files and select desired alignments. The primary function of the delta file is to catalog the coordinates of each alignment and note the distance between insertions and deletions contained in these alignments. By only storing the location of each indel as an offset, disk space is efficiently utilized, and a potentially enormous alignment can be stored in a relatively small space. The first line lists the two original input files separated by a space, while the second line specifies the alignment data type, either “NUCMER” or “PROMER”. Every grouping of alignments have a unique header specifying the two aligning sequences. Only sequences with shared alignments will have a header; therefore, there can be no empty headers (i.e. those that have no alignments following them). An example header might look like
“delta”文件表示的是NUCmer或PROmer管道的输入序列之间的all vs all比对。它是这些对齐脚本的主要输出,并且有第5.4节中描述的各种实用程序。它被设计为将delta文件作为输入,并向用户输出一些可读的信息。此外,delta-filter实用程序旨在操纵这些文件并选择所需的对齐方式。 delta文件的主要功能是对每个对齐的坐标进行编目,并注意这些对齐所包含的插入和删除之间的距离。通过仅存储每个indel的位置作为偏移,可以有效地利用磁盘空间,并且潜在的巨大对准可以存储在相对较小的空间中。第一行列出以空格分隔的两个原始输入文件,而第二行则指定对齐数据类型,即“NUCMER”或“PROMER”。每组对齐具有指定两个对准序列的唯一标题。只有具有共享对齐的序列才具有标题;因此,不能有空的标题(即那些在它们之后没有对齐的标题)。示例头可能看起来像
>tagA1 tagB1 500 20000000Following this sequence header is the alignment data. Each alignment following also has a header that describes the coordinates of the alignment and some error information. These coordinates are inclusive and reference the forward strand of the DNA sequence, regardless of the alignment type (DNA or amino acid). Thus, if the start coordinate is greater than the end coordinate, the alignment is on the reverse strand. The four coordinates are the start and end in the reference and the start and end in the query respectively. The three digits following the location coordinates are the number of errors (non-identities + indels), similarity errors (non-positive match scores), and stop codons (does not apply to DNA alignments, will be “0”). An example header might look like:
序列头后面的是比对数据。 每个对齐跟随的还有一个标题描述对齐的坐标和一些错误信息。 这些坐标是包含性的,并且参考DNA序列的正向链,不管对准类型(DNA或氨基酸)如何。 因此,如果起始坐标大于终点坐标,则对齐在反向链上。 四个坐标分别是参考中的开始和结束以及查询中的开始和结束。 位置坐标后面的三位数字是错误数(non-identities+ indels),相似性错误(非正匹配得分)和终止密码子(不适用于DNA比对,将为“0”)。 示例标题可能如下所示:
2631 3401 2464 3234 15 15 2Notice that the start coordinate points to the first base in the first codon, and the end coordinate points to the last base in the last codon. Therefore making (end - start + 1) % 3 = 0. This makes determining the frame of the amino acid alignment a simple matter of determining the reading frame of the start coordinate for the reference and query. Obviously, these calculations are not necessary when dealing with vanilla DNA alignments.
请注意,起始坐标指向第一个密码子的第一个碱基,最后一个坐标指向最后一个密码子的最后一个碱基。 因此,(end-start + 1)%3 = 0。这使得确定氨基酸对齐的框架是确定参考和查询的开始坐标的阅读框的简单事项。 显然,在处理普通的DNA比对时,这些计算是不必要的。
Each of these alignment headers is followed by a string of signed digits, one per line, with the final line before the next header equaling 0 (zero). Each digit represents the distance to the next insertion in the reference (positive int) or deletion in the reference (negative int), as measured in DNA bases OR amino acids depending on the alignment data type. For example, with the PROMER data type, the delta sequence (1, -3, 4, 0) would represent an insertion at positions 1 and 7 in the translated reference sequence and an insertion at position 3 in the translated query sequence. Or with letters:
每个这些对齐标题后跟一个有符号数字的字符串,每行一个,下一个标题之前的最后一行等于0(zero)。 每个数字表示在引用(正整数)中的下一个插入的距离或引用中的删除(负整数),如在DNA碱基或氨基酸中测定,取决于对齐数据类型。 例如,使用PROMER数据类型,delta序列(1,-3,4,0)将表示翻译的参考序列中位置1和7处的插入以及翻译的查询序列中的位置3处的插入。 Or with letters:
A = ABCDACBDCAC$B = BCCDACDCAC$Delta = (1, -3, 4, 0)A = ABC.DACBDCAC$B = .BCCDAC.DCAC$Using this delta information, it is possible to re-generate the alignments calculated by nucmer or promer as is done in the show-coords program. This allows various utilities to be crafted to process and analyze the alignment data using a universal format. This also means the delta only needs to be created once, yet it can be analyzed numerous times without ever having to rerun the costly alignment algorithm. Below is an example of what a delta file might look like:
使用该delta信息,可以像在show-coords程序中一样重新生成由nucmer或promer计算的对齐。 这使得可以使用通用格式来制作各种实用程序来处理和分析对齐数据。 这也意味着delta只需要创建一次,但可以多次分析,而无需重新运行耗时的对齐算法。 以下是delta file的示例:
/home/username/reference.fasta /home/username/query.fastaPROMER>tagA1 tagB1 3000000 20000001667803 1667078 1641506 1640769 14 7 2-145-3-1-4001667804 1667079 1641507 1640770 10 5 3-146-1-1-340>tagA2 tagB4 4000 30002631 3401 2464 3234 4 0 002608 3402 2456 3235 10 5 0711110(output continues ...)5.3.2. PROmer
PROmer (PROtein MUMmer) is a close relative to the NUCmer script. It follows the exact same steps as NUCmer and even uses most of the same programs in its pipeline, with one exception - all matching and alignment routines are performed on the six frame amino acid translation of the DNA input sequence. This provides promer with a much higher sensitivity than nucmer because protein sequences tends to diverge much slower than their underlying DNA sequence. Therefore, on the same input sequences, promer may find many conserved regions that nucmer will not, simply because the DNA sequence is not as highly conserved as the amino acid translation.
PROmer(PROtein MUMmer)是与NUCmer相关的脚本。 它遵循与NUCmer完全相同的步骤,甚至使用其pipeline中的大部分相同的程序,但有一个例外 - 所有匹配和对齐程序都在DNA输入序列的六个帧氨基酸翻译上进行。 这为promer提供比nucmer高得多的灵敏度,因为蛋白质序列倾向于比其潜在的DNA序列慢得多。 因此,在相同的输入序列上,promer可以发现许多保守区域,而nucmer不会,因为DNA序列不如氨基酸翻译那么高度保守。
All of this is performed behind the scenes, as the input is still the raw DNA sequence and output coordinates are still reported in reference to the DNA, so the two programs (nucmer and promer) exhibit little difference in their interfaces and usability. Because of its greatly increased sensitivity, it is usually best to use promer on those sequences that cannot be adequately compared by nucmer, because if run on very similar sequences the promer output can be quite voluminous. This is because promer makes no effort to distinguish between proteins and junk amino acid translations, therefore a single highly conserved gene may have up to six alignments in promer output, one for each of the six amino acid reading frames, when only the correct reading frame would be sufficient. This makes promer ideally suited for highly divergent sequences that show little DNA sequence conservation, as is shown in the following two plots:
所有这一切都是在幕后进行的,因为输入仍然是原始DNA序列,输出坐标仍然参照DNA报告,所以两个程序(nucmer和promer)的接口和可用性几乎没有差别。 由于其灵敏度大大提高,通常最好在那些不能被nucmer充分比较的序列上使用promer,因为如果在非常相似的序列上运行,promer输出可能相当庞大。 这是因为promer不用分辨蛋白质和垃圾氨基酸的翻译,因此单个高度保守的基因可能在promer输出中可以有六个比对,用于六个氨基酸阅读框中的每一个,只有一个正确的阅读框就够了, 这使得promer非常适合显示很少的DNA序列保守的高度不同的序列,如以下两个图所示:

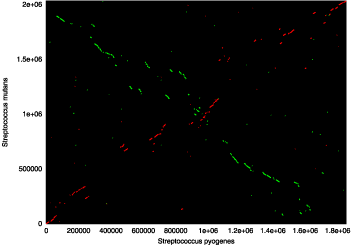
These dot plots represent two comparisons of Streptococcus pyogenes (x-axis) and Streptococcus mutans (y-axis), with forward matches colored red and reverse matches colored green. The graph generated with nucmer output is on the left, while the graph generated with promer output is on the right (both run with default parameters). It is clearly visible that promer has aligned the two genomes with a much greater sensitivity, thus demonstrating the effectiveness of comparing two divergent genomes on the amino acid level.
这些点图表示化脓链球菌(x轴)和变形链球菌(y轴)的两个比较,前向匹配为红色,反向匹配为绿色。 使用nucmer输出生成的图表在左侧,而使用promer输出生成的图表在右侧(均以默认参数运行)。 显然,promer已经使两个基因组具有更高的灵敏度,从而证明了在氨基酸水平上比较两个不同基因组的有效性。
Command line syntax
promer [options] <reference file> <query file>The reference and query files should both be in multi-FastA format and have no limit on the number of sequences they man contain. However, because promer uses mummer for its maximal exact matching, the memory usage will be dependent on the size of the reference file, so it may be advisable to make the smaller of the input files the reference to assure the program does not exhaust your computer’s memory resources. In addition, masking the uninteresting regions of the input with n or x will both speed up promer by reducing the number of possible matches and also cut down on the number of alignments induced by repetitive sequence.
参考和查询文件都应该是Multi-FastA格式,并且对它们包含的序列数没有限制。 然而,因为promer使用mummer进行最大精确匹配,所以内存使用将取决于参考文件的大小,因此建议使较小的输入文件为参考,以确保程序不会耗尽计算机的内存资源。 此外,用n或x掩蔽输入的不感兴趣的区域将通过减少可能的匹配的数量并且还减少由重复序列引起的比对数量来加快速度。
Program options
--mum Use anchor matches that are unique in both the reference and query使用参考和查询中唯一的锚匹配--mumreference Use anchor matches that are unique in the reference but not necessarily unique in the query (default behavior)使用引用中唯一的锚匹配,但在查询中不一定唯一(默认行为)--maxmatch Use all anchor matches regardless of their uniqueness使用所有锚匹配,而不管其唯一性-b int--breaklen Distance an alignment extension will attempt to extend poor scoring regions before giving up (default 60)距离对齐扩展将尝试在放弃之前扩展差评分区域(默认为60)-c int--mincluster Minimum cluster length (default 20)群集最小长度(默认为20)--[no]delta Toggle the creation of the delta file. Setting --nodelta prevents the alignment extension step and only outputs the match clusters (default --delta)切换delta file的创建。设置--nodelta可防止对齐扩展步骤,仅输出匹配群集(默认--delta)--depend Print the dependency information and exit打印依赖关系信息并退出-d float--diagfactor Maximum diagonal difference factor for clustering, i.e. diagonal difference / match separation (default 0.11)用于聚类的最大对角差分因子,即对角差分/匹配分离(默认为0.11)--[no]extend Toggle the outward extension of alignments from their anchoring clusters. Setting --noextend will prevent alignment extensions but still align the DNA between clustered matches and create the .delta file (default --extend)从其锚定簇切换对齐的向外延伸。设置--noextend将阻止对齐扩展,但仍然在聚类匹配之间对齐DNA并创建.delta文件(默认--extend)-g int--maxgap Maximum gap between two adjacent matches in a cluster (default 30)集群中两个相邻匹配之间的最大间隙(默认为30)-h--help Print the help information and exit打印帮助信息并退出-l int--minmatch Minimum length of an maximal exact match (default 6)最大完全匹配的最小长度(默认为6)-m int--masklen Maximum stop codon bookend masking length (default 8)最大终止密码子书签屏蔽长度(默认为8)-o--coords Automatically generate the <prefix>.coords file using the 'show-coords' program with the -r option使用-r选项使用'show-coords'程序自动生成<前缀> .coords文件--[no]optimize Toggle alignment score optimization. Setting --nooptimize will prevent alignment score optimization and result in sometimes longer, but lower scoring alignments (default --optimize)切换对齐分数优化。设置 - 不优化将阻止对齐分数优化并导致有时更长,但较低的评分对齐(默认 - 优化)-p string--prefix Set the output file prefix (default out)设置输出文件前缀(默认值)-V--version Print the version information and exit打印版本信息并退出-x type--matrix The alignment matrix type, 1 [BLOSUM 45], 2 [BLOSUM 62] or 3 [BLOSUM 80] (default 2)对准矩阵类型,1 [BLOSUM 45],2 [BLOSUM 62]或3 [BLOSUM 80](默认2)All values are measured in amino acids unless otherwise noted. Refer to the NUCmer Program options section for more information regarding their shared options. The –masklen value determines the number of amino acids between stop codons that will be automatically masked by promer, e.g. if an amino acid sequence were …AAA*AAAA*AAA… and the –masklen value were greater than or equal to 4, the sequence would be masked to read …AAA*XXXX*AAA… for the duration of the script. The –matrix option sets the BLOSUM matrix for scoring mismatches in the amino acid sequence, where options 1 assumes greater diversity between the two sequences and 3 assumes greater similarity between the two sequences.
所有值均以氨基酸测量,除非另有说明。 有关其共享选项的更多信息,请参阅NUCmer程序选项部分。 - masklen值决定了由promer自动掩蔽的终止密码子之间的氨基酸数量,例如 如果氨基酸序列为… AAA * AAAA * AAA …,并且–masklen值大于或等于4,则该序列将被掩码以读取… AAA * XXXX * AAA … 脚本的持续时间。 –matrix选项设置BLOSUM矩阵用于在氨基酸序列中评分错配,其中选项1假设两个序列之间具有更大的分集,并且3假设两个序列之间具有更大的相似性。
Output format
Output files follow the same format as described in the NUCmer Output format section.
输出文件遵循与NUCmer输出格式部分所述相同的格式。
5.3.3. run-mummer1
run-mummer1 is a legacy script from the original MUMmer1.0 release. It has been updated to utilize the new suffix tree code of version 3.0, however all other programs called from this script are identical to the original MUMmer release back in 1999. Even though it is an outdated program, it still has some advantages over the newer alignment scripts (nucmer, promer, run-mummer3). Like all of the alignment scripts, run-mummer1 is a three step process - matching, clustering and extension. However, unlike the newer alignment scripts, run-mummer1 uses the gaps program for its clustering step. The gaps program does not allow for rearrangements like mgaps, instead if finds the single longest increasing subset of matches across the full length of both sequences. This makes it well suited for SNP and small indel identification between small (< 10 Mbp), very similar sequences with few to no rearrangements.
run-mummer1来自于原来的MUMmer1.0版本。它已被更新,以利用3.0版的新后缀树的代码,然而,从该脚本调用的所有其他程序与1999年的原始MUMmer版本相同。即使它是一个过时的程序,它仍然比较新的对齐脚本(nucmer,promer,run-mummer3)有一些优点。像所有的对齐脚本,run-mummer1有三个步骤-匹配,集群和延伸。但是,与较新的对齐脚本不同,run-mummer1使用gaps程序进行聚类步骤。该gaps程序不像mgaps允许重排,取而代之的是找到在两个序列的全长上匹配的单个最长的子集。这使得非常适合用于小的(<10 Mbp),很少深圳至没有重排的非常相似的序列之间的SNP和小INDEL的鉴定。
Command line syntax
run-mummer1 <reference file> <query file> <prefix> [-r]The reference and query files must both be in FastA format and contain only one sequence. Memory usage will be dependent on the size of the reference sequence, so it may be advisable to make the smaller of the input files the reference to assure the program does not exhaust your computer’s memory resources. run-mummer1 uses a simplified scoring function that does not recognize masking characters, so it is not recommended to perform any masking on the input sequences. The value will be prefixed to the names of the resulting output files. The -r is optional and tells the script to reverse complement the query input sequence, thus all output coordinates will reference the reverse complement of the query. If the -r option is omitted, all matching will be limited to the forward strand of each sequence; if it is included, all matching will be limited to the forward strand of the reference and the reverse strand of the query.
参考和查询文件都必须是FASTA格式,并只包含有一个序列。内存使用将取决于参考序列的大小,因此可能建议使较小的输入文件为参考,以确保程序不会耗尽计算机的内存资源。run-mummer1使用不识别缺字字符的简化计分函数,所以并不建议对输入序列进行任何掩蔽。该值将作为前缀生成的输出文件的名称。-r是可选的,告诉脚本反向互补查询输入序列,从而所有输出坐标将参考该查询的反向互补。如果省略了-r选项,所有匹配将被限制在每个序列的正向链; 如果包括它,所有的匹配将被限制为基准的正向链及查询的反向链。
Program options
There are no available command line options for run-mummer1. Instead, the user must directly edit the csh script to alter the command line values passed to the individual pipeline programs. The only available tweak is changing the minimum match length value for mummer, set with the -l option within the script. Decreasing this value may increase the sensitivity of the script, but may drastically increase the resulting runtime.
run-mummer1没有可用的命令行选项。 相反,用户必须直接编辑csh脚本来更改传递给各个管道程序的命令行值。 唯一可用的调整是更改mummer的最小匹配长度值,并使用脚本中的-l选项进行设置。 降低此值可能会增加脚本的灵敏度,但可能会大大增加生成的运行时间。
Output format
There are four output files generated with each call of run-mummer1, and each of these files is prefixed with the value set on the command line. Each of these files will be referred to by its file extension (out, gaps, errorsgaps, align), and are described below.
每次调用run-mummer1生成四个输出文件,并且这些文件中的每个都以在命令行上设置的值作为前缀。 这些文件将由其文件扩展名(out,gap,errorsgaps,align)引用,并在下面进行描述。
The “out” file format
The standard output of the mummer program with it’s header information stripped, see the mummer output section for more information. Just a simple three column list, noting the position and length of every maximal exact match. Note that for reverse complement matches (produced with the -r option), the query start positions will reference the reverse complement of the query input sequence.
mummer程序的标准输出与标题信息被剥离,有关详细信息,请参阅mummer输出部分。 只是一个简单的三列列表,注意每个最大精确匹配的位置和长度。 请注意,对于反向互补匹配(由-r选项生成),查询开始位置将引用查询输入序列的反向补码。
The “gaps” file format
The standard output of the gaps program, see the gaps output section for more information.
gaps程序的标准输出,详见gaps输出部分。
The “errorsgaps” file format
An annotated version of the gaps format, with an extra column listing the number of errors counted in each gap. This is perhaps the most useful output file produced by run-mummer1 as it is easy to parse and identify SNPs, which appear as a ‘1’ in the final column. A ‘-’ character in the final column means the alignment was too large to compute. Example slice from an errorsgaps file:
gaps格式的注释版本,另附一列列出每个差距中计数的错误数。 这可能是由run-mummer1生成的最有用的输出文件,因为它很容易解析和识别在最后一列中显示为“1”的SNP。 最后一列中的’ - ‘字符意味着对齐太大而无法计算。 来自errorsgaps文件的部分示例:
403382 356512 77 none 1 1 -403466 356595 56 none 7 6 4403542 356670 81 none 20 19 2403626 356756 75 none 3 5 4The “align” file format
The align file is difficult to parse, but contains some useful visual information. It intersperses the gaps output file with the actual pair-wise alignment of each gap. Each alignment follows the listing of the two involved matches and uses a ‘^’ character to identify the non-identities. If an alignment was too large to process in memory a tag reading “*** Too long ***” will be listed in its place. Example align file:
align file很难解析,但包含一些有用的可视化信息。 它将gaps输出文件与每个gap的实际对齐排列插入。 每个对齐遵循两个相关匹配的列表,并使用“^”字符来标识非身份。 如果对齐太大无法被内存处理,则会将其标签“***太长***”列在其位置。 示例对齐文件:
> /home/aphillip/data/mgen.seq reverse Consistent matches 170273 729167 158 none 8 8 170433 729327 34 none 2 2 Errors = 2T: gaaggtctttttgattgtaaagS: gaaggtctttaagattgtaaag ^^ 170501 729395 155 none 34 34 Errors = 4T: aagaatgactctagcaggcaatggctggagtttgactgtaccactttgaataagS: aagaatgactttagcaggtaatggctagagtttgactgtaccattttgaataag ^ ^ ^ ^ 170659 729553 187 none 3 3 Errors = 2T: tggaaactatcagtctagagtgtS: tggaaactattaatctagagtgt ^ ^ 170856 729750 281 none 10 10 Errors = 2T: tagctgtcggagcgatcccttcggtagtgaS: tagctgtcggggcgatcccctcggtagtga ^ ^ (output continues ...)Each alignment region is padded with 10bp of the exact match surrounding it on either side.
5.3.4. run-mummer3
run-mummer3 is the simplest pipeline of the latest MUMmer3.0 programs. It runs the same matching and clustering algorithm as nucmer and promer, however it uses a different extension technique and does not perform the important pre- and post-processing steps of NUC/PROmer. Because of its simplistic form, run-mummer3 can only handle a single reference sequence, but like run-mummer1 its error-focused output makes it a handy tool for detecting SNPs and other small errors. The only major difference between run-mummer3 and run-mummer1 is the new version’s ability to handle multiple query sequences and its tolerance of large rearrangements. This makes run-mummer3 well suited for error detection between highly similar sequences that may have large rearrangements, inversions etc. Edit the script by adding the -D option to the combineMUMs command line to output a format designed for SNP identification. Still, run-mummer3 provides few advantages of the more user friendly nucmer program, and should be avoided where possible.
run-mummer3是最新MUMmer3.0程序的最简单的管道。它运行与nucmer和promer相同的匹配和聚类算法,但是它使用不同的扩展技术,并且不执行NUC / PROmer重要的前处理和后处理步骤。由于其简单的形式,run-mummer3只能处理单个参考序列,而且像run-mummer1一样,其以错误为中心的输出使其成为检测SNP和其他小错误的便利工具。 run-mummer3和run-mummer1之间的唯一主要区别是新版本处理多个查询序列的能力及其对大型重排的容限。这使得run-mummer3非常适合于可能具有大的重排,反转等的高度相似的序列之间的错误检测。通过将-D选项添加到combineMUMs命令行来输出用于SNP标识的格式来编辑脚本。run-mummer3提供了比nucmer程序更加友好的优点。
Command line syntax
run-mummer3 <reference file> <query file> <prefix>The reference and query files should both be FastA format. The reference file may only have a single sequence, but there is no limit on the number of sequences the query file may contain. It is very important that the reference file only contain one sequence, because the script will give you no indication something went wrong and there will just be empty output files. run-mummer3 uses a simplified scoring function that does not recognize masking characters, so it is not recommended to perform any masking on the input sequences. The value will be prefixed to the names of the resulting output files. Both forward and reverse complement matches will be found by default; to change this behavior or change any parameters, requires requires hand editing the script.
引用和查询文件都应该是FastA格式。 参考文件可能只有一个序列,但查询文件可能包含的序列数量没有限制。 引用文件只包含一个序列是非常重要的,因为脚本不会给你任何错误提示,只有空的输出文件。 run-mummer3使用不识别掩码字符的简化评分函数,因此不建议对输入序列执行任何屏蔽。 前缀值将作为结果输出文件的名称前缀。 默认情况下会发现前向和后向补码匹配; 要更改此行为或更改任何参数,需要手动编辑脚本。
Program options
There are no available command line options for run-mummer3. Instead, the user must directly edit the csh script to alter the command line values passed to the individual pipeline programs. Altering these parameters is suggested for most applications, as the default values may not always produce the best output. Parameter values may be added or changed for mummer, mgaps and combineMUMs. Run these programs with the -help option for a list of available options, or refer to this manual for more information on mummer or mgaps. Note that the -c option cannot be used for mummer in this script, or mgaps will fail to cluster the reverse complement matches.
run-mummer3没有可用的命令行选项。 相应的,用户必须直接编辑csh脚本来更改传递给各个管道程序的命令行值。 对于大多数应用程序,建议更改这些参数,因为默认值可能并不总是产生最佳输出。 参数值可以添加或更改为mummer,mgaps和combineMUM。 使用-help选项运行这些程序以获取可用选项的列表,或者参考本手册获取有关mummer或mgaps的更多信息。 请注意,mummer中的-c选项不能用于此脚本中,否则mgaps将无法对反向补码进行聚类。
Output format
Like run-mummer1, run-mummer3 produces four output files prefixed with the value set on the command line. Each of these files will be referred to by its file extension (out, gaps, errorsgaps, align), and are described below.
像run-mummer1一样,run-mummer3生成四个输出文件,前缀是在命令行上设置的值。 这些文件将由其文件扩展名(out,gap,errorsgaps,align)引用,并在下面进行描述。
The “out” file format
Pure, unadulterated mummer output. See the mummer output section for more information. Just a simple three column list, noting the position and length of every maximal exact match. Note that for reverse complement matches, the query start positions will reference the reverse complement of the query input sequence.
纯净,无掺杂的MUMmer输出。 有关详细信息,请参阅“mummer输出”部分。 只是一个简单的三列列表,注意每个最大精确匹配的位置和长度。 注意,对于反向补码匹配,查询开始位置将引用查询输入序列的反向补码。
The “gaps” file format
The standard output of the mgaps program, see the mgaps output section for more information.
mgaps程序的标准输出,有关更多信息,请参阅mgaps输出部分。
The “errorsgaps” file format
An annotated version of the gaps format, with an extra column listing the number of errors counted in each gap. This is perhaps the most useful output file produced by run-mummer1 as it is easy to parse and identify SNPs, which appear as a ‘1’ in the final column. A ‘-’ character in the final column means the alignment was too large to compute. Example slice from an errorsgaps file:
gaps格式的注释版本,另附一列列出每个差距中计数的错误数。 这可能是由run-mummer1生成的最有用的输出文件,因为它很容易解析和识别在最后一列中显示为“1”的SNP。 最后一列中的’ - ‘字符意味着对齐太大而无法计算。 来自errorsgaps文件的示例切片:
403382 356512 77 none 1 1 - 403466 356595 56 none 7 6 4 403542 356670 81 none 20 19 2 403626 356756 75 none 3 5 4The “align” file format
The align file is difficult to parse, but contains some useful visual information. It intersperses the mgaps output file with the actual pair-wise alignment of each gap. Each alignment follows the listing of the two involved matches and uses a ‘^’ character to identify the non-identities and a ‘=’ character to identify the MUM portion. The gap alignment is also padded with 10bp of the exact match surrounding it on either side. Example align file:
align file很难解析,但包含一些有用的可视信息。 它将Mgaps输出文件以每个间隙的实际对齐方式散置。 每个对齐遵循两个相关匹配的列表,并使用“^”字符来标识非身份和用于标识MUM部分的’=’字符。 gap比对也用10bp填充,其两侧都包围它。 示例对齐文件:
(... output continues)> ID21 3944620 24 983 none - - 3945604 1008 22 none 1 1 Errors = 1A: agactctttctttggttgattB: agactctttccttggttgatt ==========^========== 3945655 1059 26 none 29 29 Errors = 3A: cttgcgattgtctttgcatttgtctttgtttctttttcttcatgctgctB: cttgcgattggctttgcatttggctttgtttctttttcctcatgctgct ==========^ ^ ^========== 3945684 1088 29 none 3 3 Errors = 2A: ttacttttttctc-cattatagtaB: ttactttttt-tctcattatagta ==========^ ^==========Region: 3944620 .. 3945743 24 .. 1146 8 / 1124 0.71%> ID21 Reverse> ID22> ID22 Reverse 5183942 8 31 none - - 5183980 47 4221 none 7 8 Errors = 3A: cccagaaaac-accacctccggccagtaB: cccagaaaaccaccactcccggccagta ==========^ ^^========== 5188202 4269 314 none 1 1 Errors = 1A: tgcaccagaacgtaataatccB: tgcaccagaaagtaataatcc ==========^==========Region: 5183942 .. 5188515 4578 .. 4 4 / 4575 0.09%(output continues ...)After each cluster, the align file prints a line beginning with the Region keyword that shows the start and stop of the alignment in the reference and the start and stop of the alignment in the query respectively. The query coordinates in the region line will reference the forward strand of the query, while the lines taken from the gaps file will still reference the reverse strand of the query. The region line also shows and error ratio and the error percentage.
每个聚类之后,对齐文件打印一个以Region关键字开头的行,它们分别显示了引用中对齐的开始和停止以及查询中对齐的开始和停止。 区域行中的查询坐标将引用查询的正向链,而从间隙文件获取的行仍将引用查询的反向链。 区域线也显示和错误率和误差百分比。
5.4. Utilities
MUMmer includes a few utility programs intended to parse the delta encoded alignment files and output their contents to the user. The majority of these programs will only operate on the delta file output of NUCmer or PROmer, however the generalized visualization tool, mummerplot
, will function on a variety of input.
MUMmer包括一些实用程序,旨在解析delta编码的对齐文件,并将其内容输出给用户。 大多数这些程序只能在NUCmer或PROmer的delta文件输出上运行,然而通用的可视化工具mummerplot可以在各种输入上运行。
5.4.1. delta-filter
delta-filter is a utility program for the manipulation of the delta encoded alignment files output by the NUCmer and PROmer pipelines. It takes a delta file as input and filters the information based on the various command line switches, outputting only the desired alignments to stdout. Options to filter by alignment length, identity, uniqueness and consistency are provided. Certain combinations of these options can greatly reduce the number of unwanted alignments in the delta file, thus making the output of programs such as show-coords more comprehendible.
delta-filter是用于操纵由NUCmer和PROmer管道输出的delta编码对齐文件的实用程序。 它需要一个delta文件作为输入,并根据各种命令行开关对信息进行过滤,仅将期望的对齐方式输出到stdout。 提供了通过对齐长度,身份,唯一性和一致性进行过滤的选项。 这些选项的某些组合可以大大减少delta文件中的不需要的对齐数量,从而使诸如show-coords之类的程序的输出更易于理解。
Command line syntax
delta-filter [options] <delta file> > <filtered delta file>The may represent either NUCmer of PROmer data. The will be the filtered down version of the input. Output will be to stdout. delta-filter run with no options is the identity function.
可以表示PROmer或NUCmer的数据。 将是输入的过滤版本。 输出将是stdout。 不带选项的delta-filter运行是身份功能。
Program options
-g Global alignment using length*identity weighted LIS (longest increasing subset). For every reference-query pair, leave only the alignments which form the longest mutually consistent set使用长度*身份加权LIS(最长增加子集)的全局对齐。 对于每个参考查询对,只留下形成最长相互一致集合的对齐-h Print the help information and exit打印帮助信息并退出-i float Set the minimum alignment identity [0, 100], (default 0)设置最小对齐标识[0,100],(默认为0)-l int Set the minimum alignment length (default 0)设置最小对齐长度(默认为0)-q Query alignment using length*identity weighted LIS. For each query, leave only the alignments which form the longest consistent set for the query使用长度*身份加权LIS查询对齐。 对于每个查询,只留下形成查询最长一致集合的对齐方式-r Reference alignment using length*identity weighted LIS. For each reference, leave only the alignments which form the longest consistent set for the reference.使用长度*身份加权LIS的参考对齐。 对于每个参考,只留下形成参考的最长一致集合的对齐。-u float Set the minimum alignment uniqueness, i.e. percent of the alignment matching to unique reference AND query sequence [0, 100], (default 0)设置最小对齐唯一性,即对齐匹配的百分比与唯一引用AND查询序列[0,100],(默认为0)-o float Set the maximum alignment overlap for -r and -q options as a percent of the alignment length [0, 100], (default 75)将-r和-q选项的最大对齐重叠设置为对齐长度的百分比[0,100],(默认为75)The -g
option simulates the behavior of MUMmer1 by performing a similar algorithm to determine the longest mutually consistent set of matches, while the -r
and -q
option only require the match set to be consistent with respect to either the reference or query respectively. The difference being, the -g
option does not allow for inversions, translocations, etc. while the -r
and -q
options do. However, none of these options (-g -r -q
) allow for the inclusion of multiple repeat copies. Use -g
when aligning two sequences which are globally consistent, use -r
for determining the best mapping of a reference to a query (one-to-many), use -q
for determining the best mapping of a query to a reference (many-to-one), and use -r
and -q
in conjunction for a one-to-one mapping of reference to query. The -u
option is handy for keeping only those alignments which are anchored in unique sequence. The -o
option sets the alignment overlap tolerance for the -r
and -q
options, i.e. the amount two adjacent alignments included by -r
or -q
are allowed to overlap.
-g选项通过执行类似的算法来模拟MUMmer1的行为,以确定最长的相互一致的匹配集合,而-r和-q选项只要求匹配集相对于引用或查询分别保持一致。区别在于-g选项不允许在-r和-q选项中进行反转,移动等操作。但是,这些选项(-g -r -q)都不允许包含多个重复的副本。使用-g对齐两个全局一致的序列,使用-r来确定对查询(一对多)的引用的最佳映射,使用-q确定查询到引用的最佳映射(多对一),并且使用-r和-q来结合对查询引用的一对一映射。 -u选项可用于仅保留以唯一序列为基础的对齐。 -o选项设置-r和-q选项的对齐重叠限度,即由-r或-q包含的两个相邻对齐的量允许重叠。
Output format
Output format is the same as the input format. See the NUCmer Output format section for more details.
输出格式与输入格式相同。 有关详细信息,请参阅NUCmer输出格式部分。
5.4.2. mapview
mapview
is a utility script for displaying sequence alignments as provided by NUCmer or PROmer. It takes the output from show-coords
or mgaps
and converts it to a FIG, PDF or PS image file. By default, it produces FIG files which can be viewed with the common system utility xfig
or converted to PDF or PS with the fig2dev
utility (neither programs are included with MUMmer). mapview
is useful for mapping multiple query contigs (e.g. from a draft sequencing project) against an annotated reference sequence. Exons and other features can also be plotted with the NUCmer or PROmer alignments, aiding in exon refinement and analysis. Individual MUMmer hits are plotted according to their percent identity, making regions of high or low similarity easily distinguishable.
mapview是一个用于显示NUCmer或PROmer提供的序列比对的实用程序脚本。 它需要来自show-coords或mgaps的输出,并将其转换为FIG,PDF或PS映像文件。 默认情况下,它生成可以使用公共系统实用程序xfig查看的FIG文件,或者使用fig2dev实用程序将其转换为PDF或PS(两个程序都不包含在MUMmer中)。 mapview对于将多个查询contigs映射(例如,来自一个draft sequencing project)与注释的引用序列进行映射是有用的。 外显子和其他特征也可以用NUCmer或PROmer对齐来绘图,从而帮助外显子细化和分析。 个别MUMmer命中根据其百分比身份绘制,使相似度高或低的区域容易区分。
Command line syntax
mapview [options] <coords file> [UTR coords] [CDS coords]The
must be produced with the show-coords
program run with the -r
-l
options (see show-coords section), or the mgaps
program. This coords file may represent either NUCmer or PROmer data, and it is recommended that it be generated with the -k
option (or run on a filtered delta file) to reduce redundancy in the PROmer output, however this option does not always select the proper reading frame. The optional UTR and CDS coordinate files which refer to the reference sequence, should be in GFF format. These contain the coordinates of coding sequences and untranslated regions for genes on the reference genome and will be displayed graphically if provided.
必须使用-r -l选项(请参阅show-coords部分)或mgaps程序运行的show-coords程序来生成。 此coords file可能表示NUCmer或PROmer数据,建议使用-k选项生成(或在已过滤的delta文件上运行),以减少PROmer输出中的冗余,但是,此选项并不总是选择正确的阅读框。 参考参考序列的可选的UTR和CDS坐标文件应为GFF格式。 它们包含参考基因组上基因的编码序列和非翻译区的坐标,如果提供,将以图形显示。
Program options
-d int--maxdist Set the maximum distance, in base-pairs, between graphically linked matches (default 50000)以图形链接的匹配(默认为50000)设置基本对的最大距离-f string--format Set the output file format to 'fig', 'pdf' or 'ps' (default 'fig')格式将输出文件格式设置为'fig','pdf'或'ps'(默认'fig')-h--help Print help information and exit打印帮助信息并退出-m float--mag Set the magnification at which the figure is rendered, this option will be used when generating PDF or PS files (default 1.0)设置渲染图形的放大倍率,生成PDF或PS文件时使用此选项(默认值为1.0)-n int--num Set the number of output files used to partition the output, this is to avoid generating files that are too large to display (default 10)设置用于分区输出的输出文件的数量,这样做是为了避免生成太大而不能显示的文件(默认为10)-p string--prefix Set the output file prefix (default PROMER_graph or NUCMER_graph)设置输出文件前缀(默认为PROMER_graph或NUCMER_graph)-v--verbose Verbose logging of the processed files处理文件的详细日志记录-V--version Display the version information and exit显示版本信息并退出-x1 int Set the lower coordinate bound of the display window设置显示窗口的下坐标界限-x2 int Set the upper coordinate bound of the display window设置显示窗口的上坐标界限-g|ref If the input file is provided by 'mgaps', set the reference sequence ID (as it appears in the first column of the UTR/CDS coords file)如果输入文件由“mgaps”提供,请设置参考序列ID(如在UTR / CDS协调文件的第一列中显示的)-I Display the name of the query sequences显示查询序列的名称-Ir Display the name of the reference genes 显示参考基因的名称All matches from the same contig are linked by drawing lines between each successive pair of matches, if the matches occur too far apart, then this can get a little messy. The -d
option can help clean up the plots by limiting the distance a link can span. The -n
value can be increased or decreased if the resulting FIG files are either too big or too small respectively.
来自同一contig的所有匹配都通过在每个连续的匹配对之间绘制线条来进行链接,如果匹配发生的距离太远,那么这可能会有点凌乱。 -d选项可以通过限制链接可以跨越的距离来帮助清除绘图。 如果所得到的FIG文件太大或太小,-n值可以增加或减少。
Output format
The mapview
script produces FIG output files (or PDF or PS if requested) that graphically represent the alignment described in the input coords file. An example of the resulting figures can be seen below.
mapview脚本生成图形表示输入coords file中描述的对齐方式的图输出文件(或PDF或PS)。 所得的一个例子可以在下面看到。

The above MapView FIG shows a 220 kbp slice of D. melanogaster chromosome 2L and its alignment to D. pseudoobscura. The alignment, generated by PROmer, shows all regions of conserved amino acid sequence. The blue rectangle spanning the figure represents the reference (D. melanogaster), with annotated genes shown above it and the PROmer alignments shown below it. Alternative splice variants of the same gene are stacked vertically. Exons are shown as boxes, with intervening introns connecting them. The 5’ and 3’ UTRs are colored pink and blue to indicate the gene’s direction of translation. PROmer matches are shown twice, once just below the reference genome, where all matches are collapsed into red boxes, and in a larger display showing the separate matches within each contig, where the contigs are colored differently to indicate contig boundaries. The vertical position of the matches indicates their percent identity, ranging from 50% at the bottom of the display to 100% just below the red rectangles. Percent identity is of the amino acid translations used by PROmer. Matches from the same query sequence are connected by lines of the same color.
上述MapView FIG显示了黑腹果蝇染色体2L的220kbp片段及其与D.obobseudobscura的比对。由PROmer产生的比对显示保守氨基酸序列的所有区域。跨越图形的蓝色矩形表示参考序列(D. melanogaster),其上面显示了注释的基因,下面显示的PROmer比对。相同基因的可变剪接变体垂直堆叠。外显子显示为盒子,插入内含子连接它们。 5’和3’UTR是粉红色和蓝色的,表示基因的翻译方向。 PROmer匹配显示两次,一次在参考基因组下方,其中所有匹配被折叠成红色框,并且在更大的显示中显示每个重叠群内的单独匹配,其中重叠群的颜色不同以指示contig边界。匹配的垂直位置表示其 identity百分比,从显示屏底部的50%到正好低于红色矩形的100%。 identity百分比是PROmer使用的氨基酸翻译。来自相同查询序列的匹配通过相同颜色的行连接。
5.4.3. mummerplot
mummerplot
is a script utility that takes output from mummer
, nucmer
, promer
or show-tiling
, and converts it to a format suitable for plotting with gnuplot
. The primary plot type is an alignment dotplot where a sequence is laid out on each axis and a point is plotted at every position where the two sequences show similarity. As an extension to this plot style, mummerplot
is also able to offset multiple 1-vs-1 dotplots to form a multiplot where multiple sequences can be laid out on each axis. This plot style is especially handy for browsing an alignment of two contig sets. Identity plots are also possible by coloring each data point with a color gradient representing identity, or by collapsing the y-axis data onto a single line and then vertically offsetting the data points by their identities. In addition to producing the plot data, mummerplot
also generates a gnuplot
script that will be evaluated in order to generate the graph. Since mummerplot
simply generates gnuplot
input, gnuplot
must also be installed and accessible from the system path. Information about the free gnuplot
software is currently available at www.gnuplot.info.
mummerplot是一个脚本实用程序,从mummer,nucmer,promer或show-tiling中输出,并将其转换为适合于使用gnuplot绘制的格式。主绘图类型是对齐点图,其中在每个轴上布置序列,并且在两个序列显示相似性的每个位置处绘制点。作为这种绘图风格的扩展,* mummerplot*还能够抵消多个1对1点图形成多画面,其中可以在每个轴上布置多个序列。这种情节风格特别适用于浏览两个contig集的对齐。身份图也可以通过用表示身份的颜色渐变着色每个数据点,或者通过将y轴数据折叠到单个行上,然后通过其身份垂直地偏移数据点。除了生成绘图数据之外,mummerplot还会生成一个gnuplot脚本,以便生成图形。由于mummerplot只是生成gnuplot输入,gnuplot也必须从系统路径安装和访问。有关免费gnuplot软件的信息目前可在www.gnuplot.info上获得。
Command line syntax
mummerplot [options] <match file>The
can either be a three column match list from mummer
(either 3 or 4 column format), the delta file from nucmer
or promer
, or the default output from show-tiling
. mummerplot
will automatically detect the type of input file it is given, regardless of its file extension, or it will fail if the input file is of an unrecognized type. If the X11 terminal is selected for output (default behavior), an X11 window will be spawned and the plot will be drawn to the screen. If a terminal other than X11 is selected, an extra file will be output containing the plot graphic. The leftover .gp
script contains the commands necessary for generating the plot, and may be edited afterwards and rerun with gnuplot to change line thickness, labels, colors, etc.
可以是mummer(3或4列格式)的三列匹配列表,nucmer或promer的delta文件,或show-tiling的默认输出。 mummerplot会自动检测它所输入的输入文件的类型,无论其文件扩展名如何,输入文件是无法识别的类型就会失败。 如果X11端口被选择用于输出(默认行为),将产生X11窗口,并将绘图绘制到屏幕。 如果选择X11以外的终端,则会输出一个额外的文件,其中包含绘图图形。 剩下的<前缀> .gp脚本包含生成绘图所需的命令,并可以编辑,然后使用gnuplot重新运行以更改线条粗细,标签,颜色等。
Program options
-b int--breaklen Highlight alignments with a breakpoint further than the given distance from the nearest sequence end突出显示比较距离最近序列结束的给定距离的断点--[no]color Color plot lines with a percent similarity gradient or turn off all color (default color by match direction)具有百分比相似度梯度的颜色曲线或关闭所有颜色(默认颜色按照匹配方向)-c--coverage Generate a reference coverage plot, also known as a percent identity plot (default behavior for show-tiling input)生成参考覆盖图,也称为百分比图形(show-tiling输入的默认行为)--depend Print dependency information and exit打印依赖关系信息并退出-f--filter Only display alignments which represent the "best" one-to-one mapping of reference and query subsequences (requires delta formatted input)仅显示代表参考和查询子序列的“最佳”一对一映射的对齐(需要delta格式输入)-h--help Print help information and exit打印帮助信息并退出-l--layout Layout a multiplot by ordering and orienting sequences such that the largest hits cluster near the main diagonal (requires delta formatted input)通过排序和定向序列来布局多路径,使得主对角线附近的最大匹配簇(需要delta格式输入)-p string--prefix Set the output file prefix (default 'out')设置输出文件前缀(默认为'out')--rv Reverse video, swap the foreground and background colors for x11 plots (requires x11 terminal)反转视频,交换x11图的前景和背景颜色(需要x11终端)-r string--IdR Select a specific reference sequence for the x-axis选择x轴的特定参考序列-q string--IdQ Select a specific query sequence for the y-axis为y轴选择特定的查询序列-R string--Rfile Generate a multiplot by using the order and length information contained in this file, either a FastA file of the desired reference sequences or a tab-delimited list of sequence IDs, lengths and orientations [ +-]通过使用此文件中包含的顺序和长度信息生成多路径,所需参考序列的FastA文件或序列号,长度和方向[+ - ]的制表符分隔列表-Q string--Qfile Generate a multiplot by using the order and length information contained in this file, either a FastA file of the desired query sequences or a tab-delimited list of sequence IDs, lengths and orientations [ +-]通过使用此文件中包含的顺序和长度信息,即所需查询序列的FastA文件或序列ID,长度和方向[+ - ]的制表符分隔列表,生成多路径-s string--size Set the output size to small, medium or large将输出大小设置为小,中或大--small --medium --large (default 'small')-S--SNP Highlight SNP locations in the alignment突出显示对齐中的SNP位置-t string--terminal Set the output terminal to x11, postscript or png将输出端子设置为x11,postscript或png--x11 --postscript --png-x range--xrange Set the x-range for the plot in the form "[min,max]"以“[min,max]”的形式设置绘图的x范围-y range--yrangeSet the y-range for the plot in the form "[min,max]"以“[min,max]”的形式设置绘图的y范围-V--version Display version information and exit显示版本信息并退出The –breaklen
option is only useful for highlighting discrepancies between two near identical sequence sets. The –color
option looks best when plotted to a postscript terminal and looks worst when plotted to a png terminal. If the alignment is very sparse, many of the alignments will “disappear” because they are too small to be rendered. If this happens, try editing the gnuplot script to plot with “linespoints” instead of “lines”. The –coverage
option is sometimes the only sensible way to plot one vs. many comparisons if “many” is very large, and it is also a useful plot for finding gaps in the reference (e.g. physical gaps in a contig set). The –filter
option will throw away sometimes valuable repeat information, but is nonetheless very helpful in cleaning up an otherwise noisy plot. The –layout
feature is only meant to be used for multiplots where the two sequence sets are near identical, and even when this is true, the layout algorithm isn’t perfect. The -R -Q
options are necessary for any multiplot, otherwise the script won’t know how long the sequences are. The sequences will be laid out in the order found in these files and every sequence in –Rfile
and –Qfile
will be plotted even if no alignments exist. The –SNP
or –breaklen
options will change the plot colors so that green is normal and red is highlighted.
–breaklen选项仅用于突出显示两个近似相同序列集之间的差异。–color选项在绘制到postscript终端时看起来最好,绘制到png终端时看起来最差。如果对齐非常稀疏,许多对齐将“消失”,因为它们太小而无法渲染。如果发生这种情况,请尝试编辑gnuplot脚本以“linespoints”而不是“lines”进行绘图。 “–coverage”选项有时是唯一合理的方法来绘制一个比较多的比较,如果“很多”是非常大的,并且它也是寻找参考序列中的空白(例如重叠组中的物理间隙)的有用的图。 –filter选项将丢弃有时重要的重复信息,但是在清理其他噪音方面仍然是非常有帮助的。 –layout功能仅用于两个序列集接近相同的多路径,即使是这样,layout算法也不完美。 -R -Q选项对于任何多路径都是必需的,否则脚本将不知道序列的长度。序列将按照这些文件中的顺序排列,即使没有对齐方式,也将绘制-Rfile和-Qfile中的每个序列。 –SNP或–breaklen选项将更改图形颜色,使绿色为正常,并突出显示红色。
Output format
The mummerplot
script outputs three files, .gp .fplot .rplot
, when run with standard parameters. The first of which is the gnuplot script. This script contains the commands necessary to generate the plot, and refers to the two data files which contain the forward and reverse matches respectively. If the –filter
or –layout
option are specified, an additional .filter
file will be generated containing the filtered delta information. If the –breaklen
or –SNP
are included, an additional data file .hplot
will be created containing the highlight information. Finally, if a terminal other than X11 is specified, the plot graphic will saved to the file .ps
or .png
if the terminal is postscript of PNG respectively. Line thickness, color, and many other options can be added or removed from the plot by hand editing the gnuplot script. Examples of the two types of plots are displayed below, the dot plot first, followed by the coverage plot, and finnaly a couple multiplots.
当使用标准参数运行时,mummerplot脚本输出三个文件 .gp .fplot .rplot。第一个是gnuplot脚本。该脚本包含生成绘图所需的命令,并分别指向包含正向和反向匹配的两个数据文件。如果指定了–filter或–layout选项,将生成一个附加的 .filter文件,其中包含过滤的增量信息。如果包括–breaklen或–SNP,将创建一个附加数据文件 .hplot,其中包含高亮度信息。最后,如果指定了X11以外的终端,则如果终端分别是PNG的postscript,则图形将保存到文件 .ps或 .png。通过手动编辑gnuplot脚本,可以从绘图中添加或删除线条粗细,颜色和许多其他选项。下面显示了两种类型的绘图的例子,首先是点图,然后是覆盖图,并且显示了几个多边形。

For a dot plot, the reference sequence is laid across the x-axis, while the query sequence is on the y-axis. Wherever the two sequences agree, a colored line or dot is plotted. The forward matches are displayed in red, while the reverse matches are displayed in green. If the two sequences were perfectly identical, a single red line would go from the bottom left to the top right. However, two sequences rarely exhibit this behavior, and in the above plot, multiple gaps and inversions can be identified between these two strains of Helicobacter pylori. This plot was generated from nucmer output, however running mummerplot on a simple match list from mummer would produce similar results, but with more “noise”. In the newer versions, mummerplot plots points at the beginning and end of each line to avoid pixel resolution issues and also uses different plotting colors. Therefore, the output may look slightly different than displayed on these pages.
对于点图,参考序列跨越x轴,而查询序列在y轴上。 无论两个序列一致,绘制一条彩色线或点。 正向匹配显示为红色,而反向匹配显示为绿色。 如果两个序列完全相同,则一条红线将从左下角到右上角。 然而,两个序列很少表现出这种行为,并且在上述图中,可以在这两种幽门螺杆菌菌株之间鉴定出多个间隙和反转。 这个图是从nucmer输出生成的,然而在mummer上的一个简单的匹配列表上运行mummerplot会产生类似的结果,但是具有更多的“噪点”。 在较新的版本中,mummerplot绘制每行开始和结尾的点,以避免像素分辨率问题,并使用不同的绘图颜色。 因此,输出可能看起来与这些页面上显示的略有不同。

When there are many query sequences mapping to a single reference sequence, it is often helpful to use a coverage or percent identity plot. This type of plot lays out each of the alignment regions (or for show-tiling, the full contigs) according to their percent similarity and mapping location to the reference. For easier visualization of gaps, all of the alignments are also re-plotted at 10% similarity to normalize the y coordinates and produce a secondary 1D plot. Note that since mummer produces nothing but exact matches, only the normalized 1D plot will appear in the figure.
当有许多查询序列映射到单个参考序列时,通常使用覆盖率或百分比标识图。 这种情况根据它们的相似百分比和映射位置给出参考,绘制出每个对齐区域(或show-tiling,全部contigs)。 为了更容易观察到间隙,所有对齐线也以10%的相似度进行重绘,以标准化y坐标并产生二次1D图。 请注意,由于mummer只产生完全匹配,只有标准化的1D图将出现在图中。
A multiplot is a plot for multiple reference and query sequences where each reference/query pair is given its own grid box and their dotplot is drawn within the constraints of that box. Thus, every grid line represents the end of one sequence and the beginning of the next. This allows us to draw every dotplot for the two sequence sets at once, as displayed by the two contig sets in the above left image. With a little shuffling of the order and orientation of the sequences, a more pleasing layout can be obtained as show in the above right image. This is the same contig set as on the left, however the contigs have been reordered and oriented so that the major alignments cluster around the main diagonal of the plot. This allows for easier browsing of the plot by centralizing the important information, and also highlights contigs that have disagreeing sequences by breaking the diagonal. Currently a greedy approach is used to perform the layout, and while good at bringing alignments to the diagonal, it does not always produce the optimal ordering. Therefore, a break in the diagonal does not always signal a disagreement between the two sequence sets (see the mummerplot –breaklen
option for an easy way to highlight assembly discrepancies).
A quick reference guide for interpretting the dot plot is available here.
multiplot是多个参考和查询序列的图,其中每个引用/查询对被赋予其自己的网格框,并且它们的点图在该框的约束内绘制。因此,每个网格线表示一个序列的结尾和下一个序列的开始。这允许我们一次绘制两个序列集的每个点图,如上图左侧图像中的两个连字组所显示的。通过对序列的顺序和方向进行一点洗牌,可以获得更令人愉快的布局,如上图所示。这是与左边相同的contig,但是重新排列已被重新排列和定向,以便主要排列围绕着图的主对角线。这可以通过集中重要信息来更容易地浏览情节,并且通过打破对角线来突出显示具有不同意顺序的contigs。目前,采用贪婪方法来执行布局,并且在对齐线对齐的同时,并不总是产生最佳排序。因此,对角线的断裂并不总是表示两个序列集之间的分歧(参见mummerplot –breaklen选项用于突出显示装配差异的简单方法)。
这里提供了一个解释点图的快速参考指南。
5.4.4. show-aligns
show-aligns
parses the delta encoded alignment output of NUCmer and PROmer, and displays the pair-wise alignments from the two sequences specified on the command line. It is handy for identifying the exact location of errors and looking for SNPs between two sequences.
show-aligns解析NUCmer和PROmer对齐输出的delta编码,并从命令行上指定的两个序列显示成对的对齐。 识别错误的确切位置并寻找两个序列之间的SNP是非常方便的。
Command line syntax
show-aligns [options] <delta file> <IdR> <IdQ>The
is the delta output file of either nucmer
or promer
.
is the FastA header tag of the desired reference sequence, and
is the FastA header tag of the desired query sequence. All alignments between these two sequences will be displayed. Output will be to stdout.
是nucmer或promer的delta输出文件。 是所需参考序列的FastA头标签,是所需查询序列的FastA头标签。 将显示这两个序列之间的所有对齐。 输出将是stdout。
Program options
-h Print help information and exit打印帮助信息并退出-q Sort alignments by the query start coordinate按查询开始坐标排序对齐-r Sort alignments by the reference start coordinate通过引用开始坐标排序对齐-w int Set the screen width of the output (default 60)设置输出的屏幕宽度(默认为60)-x int The alignment matrix type, 1 [BLOSUM 45], 2 [BLOSUM 62] or 3 [BLOSUM 80] (default 2)对齐矩阵类型,1 [BLOSUM 45],2 [BLOSUM 62]或3 [BLOSUM 80](默认2)The -x
option applies to amino acid alignments (promer
output) and will only affect the error notations, not the alignment.
-x选项适用于氨基酸比对(promer输出),仅影响错误符号,而不影响对齐。
Output format
Output is to stdout
and is slightly different depending on the type of alignment, i.e. nucleotide or amino acid. Each alignment is preceded with a header containing the BEGIN
keyword, the frame/direction information and the start and end in the reference and query respectively. Each individual line of the alignment is prefixed with the position of the first base on that line, these positions reference the forward strand of the DNA sequence regardless of alignment type. Errors in nucleotide alignments are marked with a ‘^’
character below the two mismatching sequence bases. Errors in protein alignments are noted with a whitespace in between the two mismatching acids, while similarities (positive alignment scores) are marked with a ‘+’
and identities are noted with a copy of the matching acid. Each alignment is followed by a footer containing the END
keyword, the frame/direction information and the start and end in the reference and query respectively. Perhaps the best way to explain this format is by example, so snippets of the two types of alignments are given below.
根据比对的类型,即核苷酸或氨基酸,stdout略有不同。每个对齐前面都分别包含BEGIN关键字,帧/方向信息以及引用和查询中的开头和结尾的标题。对齐的每个单独的行以第一个碱基的位置为前缀,这些位置参照DNA序列的正向链,而不考虑对准类型。核苷酸比对中的错误在两个不匹配的序列碱基之下用’^’字符标记。蛋白质比对中的错误用两个不匹配的酸之间的空格进行记录,而相似性(阳性比对分数)用’+’标记,并且用匹配的酸的拷贝记录身份。每个对齐方式后跟一个包含END关键字,框架/方向信息以及参考和查询中的开始和结束的页脚。或许说明这种格式的最好办法就是举例说明,所以下面给出了两种类型对齐的代码段。
Nucleotide alignment output
/home/aphillip/data/GHP.1con /home/aphillip/data/GHPJ9.1con============================================================-- Alignments between Helicobacter_pylori_26695 and Helicobacter_pylori_strain_J99-- BEGIN alignment [ +1 4262 - 4316 | +1 4469 - 4522 ]4262 gatttgaacttccgtttccaccgtgaaagggtggtatccttggccacta4469 gatttgaacccctgtaaccaccgtgaaagggtggtatcc.taaccacta ^^ ^ ^^ ^ ^^ 4311 gatgaa4517 gatgaa -- END alignment [ +1 4262 - 4316 | +1 4469 - 4522 ]-- BEGIN alignment [ +1 5198 - 22885 | +1 5389 - 23089 ](output continues ...)Amino acid alignment output
/home/aphillip/data/mgen.seq /home/aphillip/data/ecoliO157.seq============================================================-- Alignments between mgen.seq and Escherichia_coli_O157:H7-- BEGIN alignment [ +1 31690 - 31995 | +3 3336375 - 3336680 ]31690 VSFSFYLVPNKRSPASPRPGIMYLLSFNFSSIAARNIST*GCIFSTLLI + F Y VP SPASPRPGIMY SF+ SI A ST GC FS+ I3336375 IIFILYFVPKILSPASPRPGIMYPCSFSP*SIDAVYSSTSGCAFSSAAI31837 PSGAATIAITLILIGLSSLIDLIAVNNVVPVASIGSRIITCESEMFSGI PSGAAT TL+L+ + + PVASIGS I S M 3336522 PSGAATSTRTLMLLQPAFFSRSMVAITEPPVASIGSTISAIRSSMLETS31984 FL*Y F Y3336669 FWKY-- END alignment [ +1 31690 - 31995 | +3 3336375 - 3336680 ]-- BEGIN alignment [ +2 50819 - 51220 | -1 3263900 - 3263499 ](output continues ...)5.4.5. show-coords
show-coords
parses the delta alignment output of NUCmer and PROmer, and displays summary information such as position, percent identity and so on, of each alignment. It is the most commonly used tool for analyzing the delta files.
show-coords解析NUCmer和PROmer的delta对齐输出,并显示每个对齐方式的摘要信息,如位置,百分比身份等。 它是分析delta文件最常用的工具。
Command line syntax
show-coords [options] <delta file>The
is the delta output file of either nucmer
or promer
.
是nucmer或promer的delta输出文件。
Program options
-b Brief output that only displays the non-redundant locations of aligning regions简单输出,仅显示对齐区域的非冗余位置-B Switch output to btab format将输出切换为btab格式-c Include percent coverage columns in the output在输出中包含百分比coverage列-d Include the alignment direction/reading frame in the output (default for promer)在输出中包括对齐方向/读框(默认为promer)-g Only display alignments included in the Longest Ascending Subset, i.e. the global alignment. Recommened to be used in conjunction with the -r or -q options. Does not support circular sequences仅显示最长升序子集中包括的对齐方式,即全局对齐。 建议与-r或-q选项配合使用。 不支持循环序列-h Print help information and exit打印帮助信息并退出-H Omit the output header省略输出标题-I float Set minimum percent identity to display设置要显示的最小百分比身份-k *PROMER ONLY* Knockout (do not display) alignments that overlap another alignment in a better reading frame在更好的阅读框架中,重新排列(不显示)与另一个对齐重叠的对齐-l Include sequence length columns in the output在输出中包含序列长度列-L int Set minimum alignment length to display设置要显示的最小对齐长度-o Annotate maximal alignments between two sequences, i.e. overlaps between reference and query sequences注释两个序列之间的最大比对,即参考和查询序列之间的重叠-q Sort output lines by query通过查询对输出行进行排序-r Sort output lines by reference通过引用对输出行进行排序-T Switch output to tab-delimited format将输出切换到制表符分隔的格式The -b
option alters the output table to only display the location of the aligning regions, not their identity, direction, frame, etc. Also, for protein data, the -b
option will collapse all overlapping frames, and list a single encompassing region. -B
switches the output format to “btab” (Blast tablature) which is a tab-delimited table with a different layout than the standard show-coords
format. The coverage information added with the -c
option is equal to the length of the alignment divided by the length of the sequence. The -k
option will select the “best” reading frame by choosing the alignment that is longest, or has the highest percent identity and is within 75% of the length of the longest alignment; only alignments that overlap each other by greater than 50% of their length will be considered for knockout. The -T
option is different than the -B
option because it retain the normal ordering of output columns. The output of the -d
option for NUCmer data will appear under the [FRM]
column, just like the reading frame info from PROmer data. The -o
annotations will appear in the final column of the output. The descriptions reference the reference sequence, e.g. [END]
means the overlap is on the end of the reference sequence and [CONTAINED]
means the reference sequence is contained by the query sequence.
-b选项更改输出表仅显示对齐区域的位置,而不是它们的身份,方向,框架等。此外,对于蛋白质数据,-b选项将折叠所有重叠的框架,并列出单个包围区域。 -B将输出格式切换为“btab”(Blast tablature),这是一个不同于标准show-coords格式布局的制表符分隔表。添加了-c选项的coverage信息等于对齐长度除以序列长度。 -k选项将通过选择最长的对齐方式或具有最高百分比的身份并且在最长对齐的长度的75%内选择“最佳”阅读框架。只有相互重叠的长度超过其长度的50%的比对将被考虑进行淘汰。 -T选项与-B选项不同,因为它保留了输出列的正常排序。 NUCmer数据的-d选项的输出将显示在[FRM]列下,就像来自PROmer数据的读取框信息一样。 -o注释将显示在输出的最后一列中。该描述参考参考序列,例如。 [END]表示重叠在参考序列的末尾,[CONTAINED]表示查询序列包含参考序列。
The -c
and -l
options are useful when comparing two sets of assembly contigs, in that these options help determine if an alignment spans an entire contig, or is just a partial hit to a different sequence. The -b
option is useful when the user wishes to identify syntenic regions between two genomes, but is not particularly interested in the actual alignment similarity or appearance. This option also disregards match orientation, so should not be used if this information is needed. The -g
option comes in handy when comparing sequences that share a linear alignment relationship, that is there are no rearrangements. Large nsertions, deletions and gaps can then be identified by the break between two adjacent alignments in the output. If there are more than one global alignment that share the same score, then one of them is picked at random to display. This is useful when mapping repetitive reads to a finished sequence.
当比较两组组装的contigs时,-c和-l选项很有用,因为这些选项有助于确定对齐是否跨越整个contig,或者仅仅是对不同序列的部分命中。 当用户希望识别两个基因组之间的合成区域时,-b选项非常有用,但对实际的比对相似性或外观并不特别感兴趣。 此选项也忽略了匹配方向,因此如果需要此信息,则不应使用。 当比较共线性对齐关系的序列时,-g选项很方便,即没有重新排列。 然后可以通过输出中两个相邻对齐线之间的断点来识别大的插入,删除和gaps。 如果有不止一个共享相同分数的全局比对,则随机挑选其中一个。 将重复读取映射到完成的序列时,这是有用的。
Output format
Output is to stdout
and is slightly different depending on the type of alignment, i.e. nucleotide or amino acid. Some of the described columns, such as percent similarity, will not appear for nucleotide comparisons. When run without the -H
or -B
options, show-coords
prints a header tag for each column; the descriptions of each tag follows. [S1]
start of the alignment region in the reference sequence [E1]
end of the alignment region in the reference sequence [S2]
start of the alignment region in the query sequence [E2]
end of the alignment region in the query sequence [LEN 1]
length of the alignment region in the reference sequence [LEN 2]
length of the alignment region in the query sequence [% IDY]
percent identity of the alignment [% SIM]
percent similarity of the alignment (as determined by the BLOSUM scoring matrix) [% STP]
percent of stop codons in the alignment [LEN R]
length of the reference sequence [LEN Q]
length of the query sequence [COV R]
percent alignment coverage in the reference sequence [COV Q]
percent alignment coverage in the query sequence [FRM]
reading frame for the reference and query sequence alignments respectively [TAGS]
the reference and query FastA IDs respectively. All output coordinates and lengths are relative to the forward strand of the reference DNA sequence.
根据比对的类型,即核苷酸或氨基酸,stdout输出略有不同。所描述的一些列,如百分比相似性,不会出现在用于核苷酸的比较中。当没有-H或-B选项运行时,show-coords会打印每个列的标题标签;每个标签的描述如下。 [S1]参考序列中比对区域的起始[E1]参考序列中比对区域的末尾[S2]查询序列中比对区域的起始[E2]查询序列中对齐区域的对齐区域的末尾[LEN 1]参考序列中比对区域的长度[LEN 2]查询序列中比对区域的长度[%IDY]比对的百分比同一性[%SIM]比对的百分比相似度(由BLOSUM评分矩阵确定)[%STP]比对中终止密码子的比例[LEN R]参考序列的长度 [LEN Q]查询序列长度[COV R]参考序列中的比对覆盖率[COV Q]查询序列的比对覆盖率[FRM]阅读框分别用于参考和查询序列比对[TAGS]参考和查询FastA ID。所有输出坐标和长度相对于参考DNA序列的正向链。
When run with the -B
option, output format will consist of 21 tab-delimited columns. These are as follows: [1]
query sequence ID [2]
date of alignment [3]
length of query sequence [4]
alignment type [5]
reference file [6]
reference sequence ID [7]
start of alignment in the query [8]
end of alignment in the query [9]
start of alignment in the reference [10]
end of alignment in the reference [11]
percent identity [12]
percent similarity [13]
length of alignment in the query [14]
0 for compatibility [15]
0 for compatibility [16]
NULL for compatibility [17]
0 for compatibility [18]
strand of the query [19]
length of the reference sequence [20]
0 for compatibility [21]
and 0 for compatibility.
当使用-B选项运行时,输出格式将由21个制表符分隔的列组成。 这些如下:[1]查询序列ID [2]对齐日期[3]查询序列长度[4]对齐类型[5]参考文件[6]参考序列ID [7]查询中对齐的开始[ 8]查询中的对齐结束[9]参考文献[10]中的比对开始参考文献[11]中的比对结果[11]百分比相似度[12]查询中的比对长度[14] 0 兼容性[15] 0用于兼容性[16] NULL用于兼容性[17] 0用于兼容性[18]查询链[19]参考序列长度[20] 0用于兼容性[21],0表示兼容性。
5.4.6. show-snps
show-snps
is a utility program for reporting polymorphisms contained in a delta encoded alignment file output by NUCmer or PROmer. It catalogs all of the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions/deletions within the delta file alignments. Polymorphisms are reported one per line, in a delimited fashion similar to show-coords
. Pairing this program with the appropriate MUMmer tools can create an easy to use SNP pipeline for the rapid identification of putative SNPs between any two sequence sets, as demonstrated in SNP detection section.
show-snps是用于报告由NUCmer或PROmer输出的delta编码对齐文件中包含的多态性的实用程序。 它将所有单核苷酸多态性(SNP)和插入/删除目录列入delta文件比对。 每一行报告多态,以类似于show-coords的分隔方式报告。 将该程序与适当的MUMmer工具配对可以创建一个易于使用的SNP流程,用于快速识别任何两个序列集之间的假定SNP,如SNP检测部分所示。
Command line syntax
show-snps [options] <delta file>The
is the delta output of either nucmer
or promer
. Output will be to stdout.
是nucmer或promer的delta输出。 输出将是stdout。
Program options
-C Do not report SNPs from alignments with an ambiguous mapping, i.e. only report SNPs where the [R] and [Q] columns equal 0 and do not output these columns不要使用模糊映射来报告SNP与对齐方式,即仅报告[R]和[Q]列等于0并且不输出这些列的SNP-h Print help information and exit打印帮助信息并退出-H Do not print the output header不要打印输出标题-I Do not report indels不报告indel-l Include sequence length information in the output在输出中包含序列长度信息-q Sort output lines by query IDs and SNP positions通过查询ID和SNP位置对输出行进行排序-r Sort output lines by reference IDs and SNP positions通过引用ID和SNP位置对输出行进行排序-S Specify which alignments to report by passing 'show-coords' lines to stdin通过将“show-coords”行传递给stdin来指定要报告的对齐方式-T Switch to tab-delimited format切换到制表符分隔的格式-x int Include x characters of surrounding SNP context in the output (default 0) 在输出中包含周围SNP上下文的x个字符(默认为0)The -C
option is a little confusing, but in simple terms it avoids calling SNPs from repetitive regions. “ambiguous mapping” refers to a position on the reference or query that is covered by more than one alignment. This can be caused by simple repeats, or overlapping alignments caused by tandem repeats that exist in different copy numbers. Either way, calling SNPs from these regions is questionable, and therefore the -C
option should be invoked in most instances. To generate output suitable for further parsing, use the -H -T
options. The [BUFF]
output column will refer to the sequence positions requested by the -r -q
options, so these options affect more than the order of the output. The -S
option will accept all forms of show-coords
output, so output can be piped into show-snps
or a simple cut/paste from one xterm to another should get the job done. This option is helpful when the user has a specific alignment they would like to see SNPs from. -x
does nothing other than print out the characters on either side of the listed position for both the reference and query. The ‘.’
character is used to represent indels, while ‘-’
represents end-of-sequence.
-C选项有点混乱,但简单来说,它避免了在重复区域调用SNP。 “模糊映射”是指由多个对齐所覆盖的引用或查询上的位置。这可能是由简单重复引起的,或由不同拷贝数存在的串联重复引起的重叠比对引起的。无论哪种方式,调用这些区域的SNP是有问题的,因此在大多数情况下应该调用-C选项。要生成适合进一步解析的输出,请使用-H -T选项。 [BUFF]输出列将引用由-r -q选项请求的序列位置,因此这些选项会影响输出顺序。 -S选项将接受所有形式的show-coords输出,因此输出可以被管道传输到show-snps,或者从一个xterm到另一个xterm的简单剪切/粘贴应该完成工作。当用户具有要查看SNP的特定对齐方式时,此选项很有用。 -x除了打印引用和查询的列表位置两边的字符之外什么都不做。 ‘.’字符用于表示indels,而’ - ‘表示序列结束。
Output format
Output is to stdout and is slightly different depending on which command switches are set. For instance, by default the output is arranged in a table style, however if the -T
option is active, the output will be tab-delimited. Also, the sequence files, alignment type and column headers are output by default, however if the -H
option is active, the headers will be stripped from the output. Other options like -l -C -x
will add or remove columns from the output. So, for description purposes, all possible column headers will be given and it is up to the user to pair the column header with the column number. The descriptions for each header tag follows. [P1]
position of the SNP in the reference sequence. For indels, this position refers to the 1-based position of the first character before the indel, e.g. for an indel at the very beginning of a sequence this would report 0. For indels on the reverse strand, this position refers to the forward-strand position of the first character before indel on the reverse-strand, e.g. for an indel at the very end of a reverse complemented sequence this would report 1. [SUB]
character or gap at this position in the reference [SUB]
character or gap at this position in the query [P2]
position of the SNP in the query sequence [BUFF]
distance from this SNP to the nearest mismatch (end of alignment, indel, SNP, etc) in the same alignment [DIST]
distance from this SNP to the nearest sequence end [R]
number of repeat alignments which cover this reference position [Q]
number of repeat alignments which cover this query position [LEN R]
length of the reference sequence [LEN Q]
length of the query sequence [CTX R]
surrounding reference context [CTX Q]
surrounding query context [FRM]
sequence direction (NUCmer) or reading frame (PROmer) [TAGS]
the reference and query FastA IDs respectively. All positions are relative to the forward strand of the DNA input sequence, while the [BUFF]
distance is relative to the sorted sequence.
输出为stdout,并且根据设置的命令开关稍有不同。例如,默认情况下,输出以表格样式排列,但如果-T选项处于活动状态,输出将以制表符分隔。此外,默认情况下会输出序列文件,对齐类型和列标题,但如果-H选项处于活动状态,则标题将从输出中删除。其他选项,如-l -C -x将会从输出中添加或删除列。因此,为了描述目的,将给出所有可能的列标题,由用户将列标题与列号配对。以下是每个标题标签的说明。[P1]参考序列中SNP的位置。对于indel,这个位置是指indel之前的第一个字符的基于1的位置,例如。对于在序列的最初的indel,这将报告0。对于反向链上的indel,该位置是指在反向链上的indel之前的第一个字符的前向链位置,例如。对于反向互补序列末尾的indel,这将报告1.[SUB]参考序列中此位置的字符或gap[SUB]查询序列中此位置的字符或gap[P2]SNP在查询序列中的位置[BUFF]在同一对齐中距离该SNP到最接近的失配(对齐结束,indel,SNP等)[DIST]从这个SNP到最近序列结束的距离[R]覆盖此参考位置的重复对齐数[Q]覆盖该查询位置的重复对齐次数[LEN R]参考序列长度[LEN Q]查询序列长度[CTX R]周围参考上下文[CTX Q]周围查询上下文[FRM]序列方向(NUC)或阅读框(PROmer)[TAGS]分别参考和查询FastA ID。所有位置都相对于DNA输入序列的正向链,而[BUFF]距离是相对于排序的序列。
5.4.7. show-tiling
show-tiling
attempts to construct a tiling path out of the query contigs as mapped to the reference sequences. Given the delta alignment information of a few long reference sequences and many small query contigs, show-tiling
will determine the best mapped location of each query contig. Note that each contig may only be tiled once, so repetitive regions may cause this program some difficulty. This program is useful for aiding in the scaffolding and closure of an unfinished set of contigs, if a suitable, high similarity reference genome is available. Or, if using PROmer, show-tiling
will help in the identification of syntenic regions and their contig’s mapping to the references.
This program is not suitable for “many vs. many” assembly comparisons, however a new tool based on the concepts of show-tiling
should be available in the near future that will facilitate the mapping of assembly contigs.
show-tiling尝试构建映射到参考序列的查询重叠群中的平铺路径。 给定几个长参考序列和许多小型查询重叠群的delta对齐信息,show-tiling将确定每个查询重叠群的最佳映射位置。 请注意,每个contig只能平铺一次,因此重复的区域可能会导致此程序的一些困难。 如果合适的高相似性参考基因组可用,该程序可用于帮助未完成的重叠群的支架和闭合。 或者,如果使用PROmer,show-tiling将有助于识别合成区域及其contig映射到参考序列。
该程序不适用于“多对多”组装比较,但是在不久的将来应该可以提供基于展示概念的新工具,这将有助于组装重叠群的映射。
Command line syntax
show-tiling [options]
The
is the delta output file of either nucmer
or promer
. Primary output will be to stdout.
是nucmer或promer的delta输出文件。 主要输出将是stdout。
Program options
-a Describe the tiling path by printing the tab-delimited alignment regions通过打印制表符分隔的对齐区域来描述平铺路径-c Assume the reference sequences are circular, and allow tiled contigs to span the origin假设参考序列是环形的,并且允许平铺的重叠群跨越原点-h Print help information and exit打印帮助信息并退出-g int Maximum gap between clustered alignments, where -1 will represent infinity (nucmer default 1000, promer default -1)聚集对齐之间的最大gap,其中-1表示无穷大(nucmer默认1000,promer默认值-1)-i float Minimum percent identity (nucmer default 90.0, promer default 55.0)最小百分比身份(nucmer默认为90.0,默认默认为55.0)-l int Minimum contig length (default 1)最小contig长度(默认为1)-p filename Output a pseudo molecule of the query contigs to file将查询重叠群的伪分子输出到文件-R Deal with repetitive contigs by randomly placing them in one of their copy locations (implies -V 0)通过随机将它们放在其中一个复制位置(implies -V 0)来处理重复的重叠群体-t filename Output a TIGR assembler style contig list of EVERY mapping contig to file输出每个EVERY映射contig到文件的TIGR汇编器样式contig列表-u filename Output the tab-delimited alignment regions of the unusable contigs to file将不可用的重叠群的制表符分隔的对齐区域输出到文件-v float Minimum contig alignment coverage (nucmer default 95.0, promer default 50.0)最小contig对齐覆盖(nucmer默认为95.0,promer默认为50.0)-V float Minimum contig coverage difference (nucmer default 10.0, promer default 30.0)最小contig覆盖差(nucmer default 10.0,promer default 30.0)-x Describe the tiling path by printing the XML contig linking information 通过打印XML contig链接信息来描述平铺路径 The -i
and -l
options filter out all contigs below these cutoffs. The -p
option creates a pseudo molecule from the query sequence, and arranges them as the map to the reference. The -v
option sets the minimum percent of the query contig that must be covered by aligning bases, while the -V
option sets the difference in percent coverage to determine one mapping is better than another. To include the most possible contigs in the tiling, set the -V
option to zero and lower the -i
and -v
options to reasonable values. For NUCmer data, percent coverage is the non-redundant number of aligning bases divided by the length of the query sequence, while for PROmer data, percent coverage is the extent of the syntenic region divided by the length of the query sequence. The difference being, show-tiling
does not penalize a PROmer mapping for having big gaps and small alignments. The -x
option output can be used as input to the TIGR scaffolder “Bambus”, for use as contig linking information. With the exception of the output generated by the -t
option, all tiling paths include the minimal number of contigs needed to generate the maximum reference coverage. This means that there may be other, smaller contigs that map to the reference, but because they are shadowed by larger contigs, they are not reported. The -R
option is very useful for maintaining uniform, ‘random’ coverage of reads when mapping to a reference.
-i和-l选项会过滤出所有这些截止值之下的所有contigs。 -p选项从查询序列创建一个伪分子,并将它们作为映射排列到reference。 -v选项设置必须通过对齐基础覆盖的查询连字符的最小百分比,而-V选项设置百分比覆盖率的差异,以确定一个映射比另一个更好。为了将最可能的重叠组包含在平铺中,请将-V选项设置为零,并将-i和-v选项降低为合理的值。对于NUCmer数据,百分比覆盖率是对齐基数的非冗余数除以查询序列的长度,而对于PROmer数据,百分比覆盖率是合成区域的范围除以查询序列的长度。不同之处在于,展示平铺不会对PROER映射造成很大的差距和小的排列。 -x选项输出可用作TIGR scaffolder“Bambus”的输入,用作contig链接信息。除了-t选项生成的输出之外,所有平铺路径都包含生成最大参考覆盖所需的最小数目的重叠组。这意味着可能有其他更小的重叠群映射到参考,但是由于它们被较大的重叠群遮蔽,所以它们不被报告。在映射到引用时,-R选项对于保持读取的统一的“随机”覆盖非常有用。
Output format
Output is to stdout
and differs depending on the command line options. Standard output has an 8 column list per mapped contig, separated by the FastA headers of each reference sequence. These columns are as follows: [1]
start in the reference [2]
end in the reference [3]
gap between this contig and the next [4]
length of this contig [5]
alignment coverage of this contig [6]
average percent identity of this contig [7]
contig orientation [8]
contig ID. Output of the -a
and -u
options have the same columns as show-coords
run with the -THcl
options. Output of the -x
option follows standard XML format. An example of the standard output of show-tiling
follows:
输出为stdout,并根据命令行选项而有所不同。 标准输出具有每个映射重叠组的8列列表,由每个引用序列的FastA头分隔。 这些列如下:[1]reference的起始[2]在reference的终止[3]一个contig和下一个contig间的gap[4]该contig长度[5]该contig的比对覆盖率[6]该contig的平均identity [7] contig方向[8] contig ID。 -a和-u选项的输出具有与-THcl选项一起运行的show-coord相同的列。 -x选项的输出遵循标准XML格式。 show-tiling的标准输出的例子如下:
>gba:6615 5227293 bases-10807 20017 105 30825 100.00 99.99 + 25320123 21388 42 1266 100.00 100.00 - 12121431 93545 37 72115 100.00 100.00 + 27293583 96184 -15 2602 100.00 100.00 + 5196170 98575 161 2406 100.00 99.96 - 9398737 100543 1072 1807 100.00 99.83 - 94101616 103405 3121 1790 100.00 99.89 + 1075215716 5216412 73 697 100.00 100.00 - 92(output continues ...)>gbx:17223 181677 bases-12269 43162 -258 55432 100.00 100.00 - 942905 49553 -106 6649 100.00 100.00 + 749448 112332 -659 62885 100.00 100.00 - 21111674 112935 -519 1262 100.00 100.00 + 22112417 116940 -201 4524 100.00 100.00 + 23116740 160401 -27 43662 100.00 100.00 + 10160375 167673 1734 7299 100.00 100.00 - 159>gbx:17224 94829 bases-89937 5606 54601 95544 100.00 99.99 - 16860208 61126 -56235 919 100.00 99.24 - 43 The negative start positions indicate contigs that are wrapping around the origin, since this output was generated with the -c
option.
负的起始位置指示围绕原点的contig,因为该输出是使用-c选项生成的。
5. Known problems
MUMmer’s modular design is very beneficial, however it has created a small set of inconveniences. Some modules like mummer
have been updated in the recent 3.0 release, while others like mgaps
have not. Since it is not always possible to update all modules at once, some legacy issues appear. For example, because mgaps
was originally written to cluster the output of a matching algorithm that could only handle one reference sequence, its input and output is constrained to handle only a single reference sequence. When mummer
was updated in the 3.0 release, it was modified to handle multiple reference sequences, but this causes a slight incompatibility as its output can no longer be fed into mgaps
when it contains multiple reference sequences. The same type of annoyance occurs between mummer
and gaps
, as gaps
was originally designed to handle only one reference and only one query sequence. Such incompatibilities can be inconvenient, but workarounds with stream editors and conversion scripts are common practice by those familiar with MUMmer. Learning more about the output of each program can lead to a better understanding of how the modules communicate with one another and make it possible to format the output of one module so that it can be understood by a legacy module.
nucmer
, promer
and run-mummer3
all have a difficult time with tandem repeats. If the two sequences contain a different number of copies of the same tandem repeat, these alignment routines will sometimes generate a cluster on either side of the tandem and extend alignments past one another, failing to join them into a single alignment region. This generates two overlapping alignments and makes it difficult to determine what caused this erratic behavior. In addition, the %identity for this region may appear artificially low as the alignment extension attempted to align sequence that was offset by the difference in length of the tandem repeats, instead of identifying the single large insertion. Any difference in the tandem between the reference and query can be calculated as the difference of the alignment overlap in each sequence. This bug is more of a nuisance than a critical problem, so a fix is being considered but no timeline has been set for its implementation.
The MUMmer programs do not perform validity checking on their inputs. If any part of the package appears to malfunction, please check that the input files are within the constraints of each program (i.e. number of sequences allowed, FastA format, memory usage, etc.).
This document will be under constant edit, so if you notice any errors please contact us.
MUMmer的模块化设计是非常有益的,但是它造成了一小部分的不便。在最近的3.0版本中,已经更新了一些类似mummer的模块,而另一些模块则没有。由于并不总是可以一次更新所有模块,因此会出现一些遗留问题。例如,因为最初写入的是一个匹配算法的输出,它只能处理一个引用序列,所以它的输入和输出被限制为只处理一个引用序列。当在3.0版本中更新了mummer时,它被修改为处理多个引用序列,但是这会导致轻微的不兼容性,因为它的输出在包含多个引用序列时不能再被馈送到mgaps。同样类型的烦恼发生在mummer和gaps之间,因为gaps最初被设计为仅处理一个参考和仅一个查询序列。这种不兼容性可能不方便,但使用流编辑器和转换脚本的解决方法是熟悉MUMmer的常见做法。更多地了解每个程序的输出可以更好地了解模块如何彼此通信,并且可以格式化一个模块的输出,以便可以通过遗留模块来理解。
nucmer,promer和run-mummer3遇到串联重复都有困难。如果两个序列包含相同串联重复的不同数目的拷贝,则这些对准例程有时会在串联的任一侧产生簇并且将对准彼此延伸,不能将它们连接到单个对齐区域中。这会产生两个重叠的对齐,并且使得难以确定导致这种不规则行为的原因。此外,该区域的%同一性可能会人为地低,因为对齐扩展试图对齐由串联重复的长度差异抵消的序列,而不是识别单个大插入。可以将参考和查询之间的串联的任何差异计算为每个序列中的对准重叠的差异。这个bug比一个关键的问题更麻烦,所以正在考虑一个修复,但没有为其实现设置时间表。
MUMmer程序不对其输入进行有效性检查。如果包装的任何部分出现故障,请检查输入文件是否在每个程序的限制内(即允许的序列数,FastA格式,内存使用量等)。
本文档将不断修改,所以如果您发现任何错误,请与我们联系。
6. Acknowledgements
The development of MUMmer is supported in part by the National Science Foundation under grants IIS-9902923 and IIS-9820497, and by the National Institutes of Health under grants R01-LM06845 and N01-AI-15447.
MUMmer3.0 is a joint development effort by Stefan Kurtz of the University of Hamburg and Adam Phillippy, Art Delcher and Steven Salzberg at TIGR. Stefan’s contribution of the new suffix tree code was essential to making MUMmer3.0 an open source project. Please see the ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS file in the distribution for an updated list of contributors.
7. Contact information
Please address questions and bug reports via Email to:
- Mummer文档翻译
- 翻译文档
- 文档翻译
- MongoDB文档翻译-引言-文档
- GSM0222 文档的翻译
- Tomcat文档翻译
- Tomcat文档翻译二
- OpenKM 文档翻译
- dhtmlxtree文档翻译
- NHibernate文档翻译
- dhtmlxtree文档翻译
- dhtmlxtree文档翻译(转)
- WinPcap文档翻译第一章
- 预备翻译C99文档
- Squirrel 文档翻译( Introduction )
- Squirrel 文档翻译( 目录)
- Squirrel 文档翻译(Statements)
- Squirrel 文档翻译( Class )
- 前端js再新窗口打开页面,以post传递参数方式
- 快速排序
- BLAST中的E值(E-value)
- eclipse在git提交时忽略不必要的文件
- 双目匹配与视差计算
- Mummer文档翻译
- linux中的信号3——alarm、pause函数
- INSTALL_FAILED_NO_MATCHING_ABIS 的解决办法
- [(可持久化)字典树 优化建图][2-SAT] LOJ#6036. && 雅礼集训 2017 Day4. 编码
- arcgis api for js入门开发系列十四最近设施点路径分析
- Struts2_文件上传
- Android Framework AIDL的使用
- Java Reflection(反射机制)详解
- java_DateUtil_篇1


