Android-socket的基本使用,发送文字和图片以及心跳
来源:互联网 发布:ppt转pdf软件在线 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 15:51
项目需求收集通过Socket向服务器发送图片,之前没搞过,网上搜搜写了下面的例子,勉强解决了需求。
为了测试切换着方便,所以方法写的有点碎了。。。
原文地址 http://blog.csdn.net/qq_25806863/article/details/75533109
要求发送的消息的格式是,8个字节的消息长度+消息体
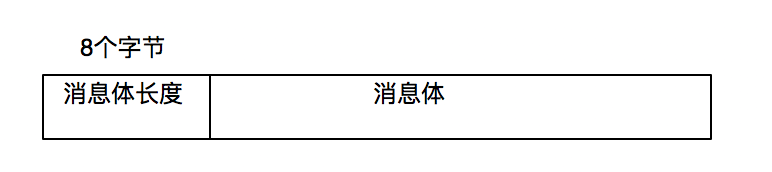
因为需要8个字节,所以消息长度决定用long
如果需要4个字节,可以用int。
手机客户端接收服务器的文字消息
服务端
服务端定义好端口号,开启以一个ServerSocket,写入文字消息:
public class Service { private static Socket socket; //定义端口号 private static final int POST = 30000; public static void main(String[] args) { try { //发送的内容 sendMsg("来自服务器的问候"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void sendMsg(String msg) throws IOException { System.out.println("开始连接"); //创建socket服务端口是30000,并等待连接 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(POST); Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); //获取输出流 DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); sendTextMsg(out, msg); out.close(); socket.close(); serverSocket.close(); System.out.println("通讯结束"); } public static void sendTextMsg(DataOutputStream out, String msg) throws IOException { //先写长度,就是消息体的字节数,long刚好8个字节 out.writeLong(msg.getBytes().length); //写入消息 out.write(msg.getBytes()); }}客户端,接收消息
客户端首先要跟服务器进行连接,然后才能进行通讯。
Socket连接需要网络权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>因为属于网络通讯,所以socket连接也不能放在主线程中,否则会报错

添加按钮
在布局中加一个按钮,点击方法是receive
<Button android:text="接收" android:layout_marginTop="50dp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:onClick="receive"/>定义方法
在Activity中定义方法
因为不能再主线程中访问,所以需要子线程。这里直接new了、、
public void receive(View view){ new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Socket socket; try { //这里进行连接服务器, //host是服务器ip地址,如“192.168.2.12” //post是端口,上面的服务端提供的端口号是30000 socket = new Socket(host, post); //获取输入流 DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); //读取长度,也即是消息头, long len = input.readLong(); //创建这个长度的字节数组 byte[] bytes = new byte[(int)len]; //再读取这个长度的字节数,也就是真正的消息体 input.read(bytes); //将字节数组转为String String s = new String(bytes); Log.i("accept", "len: "+len); Log.i("accept", "msg: "+s); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start();}
运行测试
先运行服务端,会发现程序没有一次执行完,在阻塞着等待连接
这时点击app中的接收按钮,日志中会打印接收到的信息
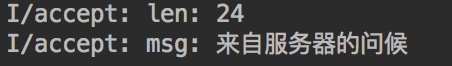
长度为24,消息内容为“来自服务器的问候”。
因为在utf-8中一个汉字是3个字节,所以8个汉字的消息长度是24字节。
这是看服务器端的打印:
发现服务端也正常执行完毕了。
手机客户端向服务端发送文字消息
服务端接收消息
public class Service { private static Socket socket; //定义端口号 private static final int POST = 30000; public static void main(String[] args) { try { //接收消息 getMsg(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void getMsg() throws IOException { System.out.println("开始连接"); ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(POST); Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); //获取输入流,通过这个流来读取消息 DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); //接收文字消息 getTextMsg(input); input.close(); socket.close(); serverSocket.close(); System.out.println("通讯结束"); } public static String getTextMsg(DataInputStream input) throws IOException { //一样先读长度,再根据长度读消息 long len = input.readLong(); System.out.println("len = " + len); byte[] bytes = new byte[(int) len]; input.read(bytes); String msg = new String(bytes); System.out.println("msd = " + msg); return msg; }}客户端发送消息
- 增加一个发送的按钮:
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="发送!" android:onClick="send"/>- 定义方法
public void send(View view) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Socket socket; try { //建立连接 socket = new Socket(host, post); //获取输出流,通过这个流发送消息 DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); //发送文字消息 sendTextMsg(out,"来自手机客户端的消息"); out.close(); socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); }public void sendTextMsg(DataOutputStream out, String msg) throws IOException { byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes(); long len = bytes.length; //先发送长度,在发送内容 out.writeLong(len); out.write(bytes); }运行测试
先运行服务端,也会停留着这个界面等待连接:

然后点击客户端的发送按钮,这是服务端会变成下面这样,完成这次消息的通讯

手机客户端想服务端发送图片
服务端接收图片,并保存到本地
在上面的getMsg()方法中,将getTextMsg(input);改为getImgMsg(input);
下面是getImgMsg(input);方法:
public static void getImgMsg(DataInputStream input) throws IOException { //同样是先读长度 long len = input.readLong(); System.out.println("len = " + len); byte[] bytes = new byte[(int) len]; //然后在读这个长度的字节到字节数组 input.readFully(bytes); //将独到的内容保存为文件到本地 File file = new File("/Users/xxx/" + len + ".png"); FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file); fileOutputStream.write(bytes); System.out.println("ok");}客户端发送图片
- 增加一个按钮:
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="200dp" android:onClick="sendImg" android:text="发送图片" />定义方法
public void sendImgMsg(DataOutputStream out ) throws IOException {//发送的图片为图标,就是安卓机器人,将bitmap转为字节数组 Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),R.mipmap.ic_launcher_round); ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); bitmap.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.PNG,100,bout);//写入字节的长度,再写入图片的字节 long len = bout.size();//这里打印一下发送的长度 Log.i("sendImgMsg", "len: "+len); out.writeLong(len); out.write(bout.toByteArray());}
运行测试
还是先开启服务端,服务器变成:

然后点击app的发送图片按钮,app中打印日志:

说明发送的图片的长度是11418个字节,大致换算大小是11k。
然后看服务端的日志:
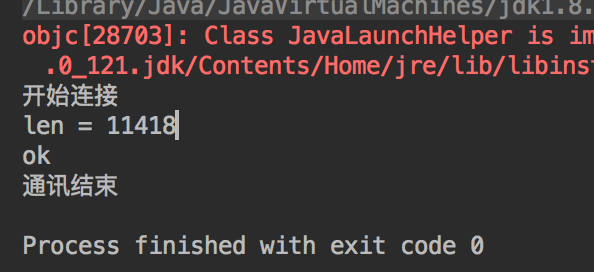
接收到的长度也是11418,并且保存到了文件,

关于心跳包
上面的例子中,每发送一次之后就把链接关闭了:
out.close();socket.close();serverSocket.close();心跳其实就是定期向服务端发送一个小数据,比如0.
让服务器知道这个链接还有用,不用关闭。
简单实现起来就是客户端通过一个无限循环,不停地向服务端发送消息,服务端通过一个无限循环不停地接收消息,都不关闭这个链接就行了。
服务端
public static void main(String[] args) { try { System.out.println("开始接收信息"); ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(POST); socket = serverSocket.accept(); DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true) { try { long len = 0; len = dataInputStream.readLong(); System.out.println("len = " + len); byte[] bytes = new byte[(int) len]; dataInputStream.readFully(bytes); String s = new String(bytes); System.out.println("data = " + s); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); isConnect = false; } } } }).start(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }客户端,一秒发送一次消息
try { //建立一次链接 socket = new Socket(host,post); outputStream = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); inputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();}Log.i(TAG, "run: 开始循环发送发送心跳");//一秒发送一个0,while (true){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Log.i(TAG, "run: 发送心跳0"); try { outputStream.writeLong("0".getBytes().length); outputStream.write("0".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); isConnect = false; }}运行测试
先运行服务端:

然后点击发送心跳的按钮,app的日志中打印:

在服务端的日志中可以看到:
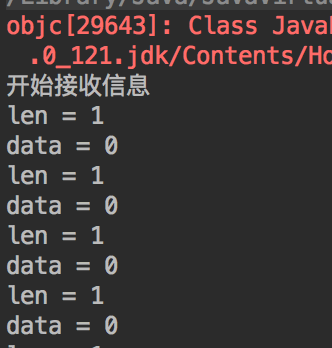
一秒一次

- Android-socket的基本使用,发送文字和图片以及心跳
- android socket发送图片
- 在Android上面如何使用带有心跳检测的Socket
- 在Android上面如何使用带有心跳检测的Socket
- 在Android上面如何使用带有心跳检测的Socket
- java之socket的OOBInline和UrgentData和发送心跳包研究
- java之socket的OOBInline和UrgentData和发送心跳包研究
- Socket多人聊天(文字+图片+多文件发送和接收)
- 使用第三方授权登录以及分享文字和图片
- Glide Android图片加载的利器---基本介绍和使用
- 判断Socket连接失效,发送心跳包
- java android Socket通信 发送以及接受
- UITextField(限制文字输入,调整光标,内容,占位文字显示的位置,以及基本使用)
- android socket 实现心跳包
- Android的socket通信的长连接,有心跳检测
- Android中使用webSocket实现文字及单张图片发送聊天功能
- Flex拖拽的基本实现,以及图片代理的创建和使用
- Android Socket连接(模拟心跳包,断线重连,发送数据等)
- 指针与数组名之间的区别
- cocos项目打包成安装后显示中文名的apk文件
- Android Studio Debug调试技巧集合
- centos7下php安装Redis扩展
- arttemplate 函数使用有感
- Android-socket的基本使用,发送文字和图片以及心跳
- Linux基础(一)(1)
- python中的selenium中的鼠标悬停事件!
- 实现一个Min栈——题集(六)
- Android 多个listview监听item的点击事件
- Hbase安装
- 小米手机的坑
- 如何巧用Android多进程,你不知道的点全总结!微信,微博等主流App都在用
- 主流开源深度学习框架对比分析


