Java服务定位器模式
来源:互联网 发布:曼彻斯特城市大学 知乎 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/23 23:36
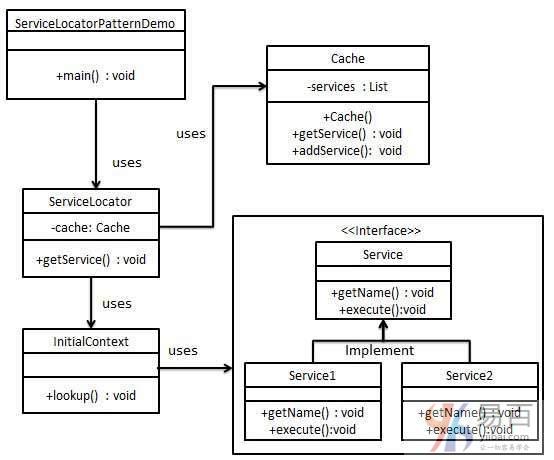
当我们想要使用JNDI查找来定位各种服务时,使用服务定位器设计模式。 考虑到为服务查找JNDI的高成本,所以在服务定位器模式使用缓存技术。 首次需要服务时,服务定位器在JNDI中查找并缓存服务对象。 通过服务定位器进一步查找或相同的服务在其缓存中完成,这在很大程度上提高了应用的性能。 以下是这种类型的设计模式的实体。
- 服务 - 将处理请求的实际服务。 将在JNDI服务器中查找此类服务的引用。
- 上下文/初始上下文 - JNDI上下文携带对用于查找目的的服务的引用。
- 服务定位器 - 服务定位器是通过JNDI查找缓存服务获得服务的单一联系点。
- 缓存 - 用于存储服务的引用以重用它们的缓存。
- 客户端 - 客户端是通过
ServiceLocator调用服务的对象。
实现实例
在这个实现的实例中,将创建一个ServiceLocator,InitialContext,Cache,Service作为表示实体的各种对象。Service1和Service2用来表示具体服务。
ServiceLocatorPatternDemo是一个演示类,在这里充当客户端,将使用ServiceLocator演示服务定位器设计模式。
服务定位器模式示例的结构如下图所示 -
第1步
创建一个名为 Service 的接口,其代码如下 -
Service.java
public interface Service { public String getName(); public void execute();}第2步
创建具体的服务类,其代码如下 -
Service1.java
public class Service1 implements Service { public void execute(){ System.out.println("Executing Service1"); } @Override public String getName() { return "Service1"; }}Service2.java
public class Service2 implements Service { public void execute(){ System.out.println("Executing Service2"); } @Override public String getName() { return "Service2"; }}第3步
为JNDI查找创建InitialContext 类,其代码如下 -
InitialContext.java
public class InitialContext { public Object lookup(String jndiName){ if(jndiName.equalsIgnoreCase("SERVICE1")){ System.out.println("Looking up and creating a new Service1 object"); return new Service1(); } else if (jndiName.equalsIgnoreCase("SERVICE2")){ System.out.println("Looking up and creating a new Service2 object"); return new Service2(); } return null; }}第4步
创建缓存类,其代码如下 -
Cache.java
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class Cache { private List<Service> services; public Cache(){ services = new ArrayList<Service>(); } public Service getService(String serviceName){ for (Service service : services) { if(service.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(serviceName)){ System.out.println("Returning cached " + serviceName + " object"); return service; } } return null; } public void addService(Service newService){ boolean exists = false; for (Service service : services) { if(service.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(newService.getName())){ exists = true; } } if(!exists){ services.add(newService); } }}第5步
创建服务定位器,其代码如下 -
ServiceLocator.java
public class ServiceLocator { private static Cache cache; static { cache = new Cache(); } public static Service getService(String jndiName){ Service service = cache.getService(jndiName); if(service != null){ return service; } InitialContext context = new InitialContext(); Service service1 = (Service)context.lookup(jndiName); cache.addService(service1); return service1; }}第6步
使用ServiceLocator类来演示服务定位器设计模式。
ServiceLocatorPatternDemo.java
public class ServiceLocatorPatternDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Service service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service1"); service.execute(); service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service2"); service.execute(); service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service1"); service.execute(); service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service2"); service.execute(); }}第7步
验证输出,执行上面的代码得到以下结果 -
Looking up and creating a new Service1 objectExecuting Service1Looking up and creating a new Service2 objectExecuting Service2Returning cached Service1 objectExecuting Service1Returning cached Service2 objectExecuting Service2阅读全文
0 0
- Java服务定位器模式
- Java服务定位器模式
- 服务定位器模式(service locator)
- 解耦模式--服务定位器
- 设计模式之服务定位器模式
- 设计模式学习笔记--服务定位器模式
- 服务定位器模式(C++实现)
- 服务定位器
- 【设计模式】服务定位器模式(Service Locator Pattern)
- 深度剖析Byteart Retail案例【服务定位器模式】
- Service Locator服务定位器
- J2EE业务层模式:服务门面,应用服务,以及业务委托,服务定位器
- (服务定位器)Service Locator
- 服务定位器模式(Service Locator Pattern)详解和代码示范
- 定位器
- 依赖注入 控制反转 服务定位器 模式 Dependency Injection Inversion of Control Service Locator Patterns | 超级经典
- 依赖注入 控制反转 服务定位器 模式 Dependency Injection Inversion of Control Service Locator Patterns | 超级经典
- 基于ACE的服务定位器(图失效)
- Java一些基础概念总结(面试可能会用到)
- java中奇偶数的判断
- C++中的cin.get()和C中的getchar()要注意的一点
- 报错
- 持续更新
- Java服务定位器模式
- Docker跨主机网络通信方案
- C#命名空间
- 希腊字母小计
- KNN算法
- c# datarow[] 转换成 datatable
- eclipse/myeclipse离线安装SVN插件
- 【10月23日】机器学习实战(一)KNN算法:手写识别系统
- 邮件系统部分内容(不完整)


