oracle 9i 性能调优5
来源:互联网 发布:华东交大软件加背景 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/30 04:09
14、 Using Oracle Data Storage Structure Efficiently ---有效使用Oracle数据存储结构
1、创建cluster
SQL> create cluster mycluster (deptno number(2)) size 1024;
Cluster created.
SQL> create index my_idx on cluster mycluster;
Index created.
SQL> create table dept
2 (deptid number(2) primary key,
3 dname varchar2(20),
4 loc varchar2(30)
5 )
6 cluster mycluster(deptid);
Table created.
SQL> create table emp
2 (empid number primary key,
3 ename varchar2(20),
4 sal number,
5 deptno number(2) references dept(deptid)
6 )
7 cluster mycluster(deptno);
Table created.
SQL> create cluster hc(hk number) hashkeys 1000 size 8192;
Cluster created.
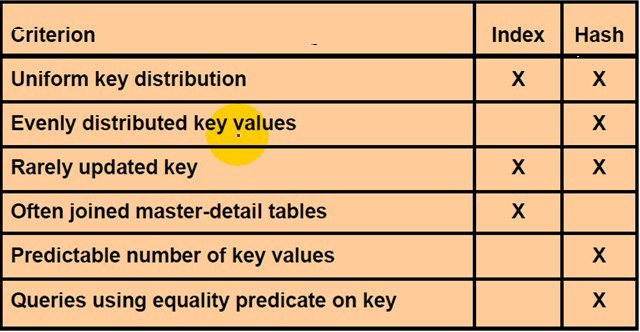
2、When to Use Cluster
3、Partitioning Methods
Range
Hash
List
Composite
4、Range Partitioning
SQL> create table range1
2 ( rk date,
3 data varchar2(20)
4 )
5 partition by range(rk)
6 (
7 partition p1 values less than (to_date('01/01/2009','dd/mm/yyyy')) tablespace ts0,
8* partition p2 values less than (to_date('01/01/2010','dd/mm/yyyy')) tablespace ts1)
SQL> /
Table created.
select segment_name,partition_name,segment_type from user_segments
select * from range1 partition(p1);
SQL> alter table range1
2 add partition
3 p3 values less than (maxvalue) tablespace ts2;
Table altered.
5、Hash Partitioning
2 ( empno int,
3 ename varchar2(20)
4 )
5 partition by hash(empno)
6 (
7 partition part1 tablespace ts1,
8 partition part2 tablespace ts2
9 )
10 /
Table created.
SQL> insert into emp1 select empno,ename from scott.emp;
14 rows created.
1* select * from emp1 partition(part1)
SQL> /
EMPNO ENAME
---------- --------------------
7369 SMITH
7499 ALLEN
7654 MARTIN
7698 BLAKE
7782 CLARK
7839 KING
7876 ADAMS
7934 MILLER
8 rows selected
5、List Partitioning
SQL> create table list1
2 (stateid varchar2(2),
3 data varchar2(100)
4 )
5 partition by list(stateid)
6 (
7 partition p1 values('TX','MA','NY') tablespace ts0,
8 partition p2 values('CA','PA') tablespace ts1,
9 partition p3 values(default) tablespace ts2
10 )
11 /
Table created.
6、Composite Partitioning
1 create table composite1
2 (range_key date,
3 hash_key int,
4 data varchar2(20)
5 )
6 partition by range(range_key)
7 subpartition by hash(hash_key) subpartitions 2
8 (
9 partition part1 values less than(to_date('01/01/2008','dd/mm/yyyy'))
10 ( subpartition h1,
11 subpartition h2
12 ),
13 partition part2 values less than(to_date('01/01/2009','dd/mm/yyyy'))
14 ( subpartition h12,
15 subpartition h22
16 )
17* )
SQL> /
Table created.
7、Partitioned Indexes
SQL> create index local_idx1 on range1(rk,data) local; ---local partition index
Index created.
SQL> select object_name,object_type from user_objects;
OBJECT_NAME OBJECT_TYPE
------------------------------ -------------------
LOCAL_IDX1 INDEX PARTITION
LOCAL_IDX1 INDEX PARTITION
LOCAL_IDX1 INDEX PARTITION
Index created.
十五、Application Tuning --应用调优
- oracle 9i 性能调优5
- oracle 9i 性能调优1
- oracle 9i 性能调优2
- oracle 9i 性能调优3
- oracle 9i 性能调优4
- oracle 9i 性能调优 1、Overview
- Oracle 9i 性能调优系列培训
- 小布老师oracle 9i性能调优
- Oracle 9i在AIX上的性能调整-性能调优
- 小布作品:Oracle 9i 性能调优系列培训(全71讲)
- 略读《Oracle 9i性能调整》
- Oracle 9i&10g编程艺术 性能测试
- Oracle性能调优
- [Oracle]性能调优
- Oracle性能调优
- oracle 性能调优
- oracle性能调优
- Oracle性能调优
- CUDA
- #pragma once 与 #ifndef 区别
- java中类的生命周期
- 一些常用而且必须记住的公共JS函数
- 国外人工智能牛人主页
- oracle 9i 性能调优5
- 利用VBSript 在 PowerDesigner中实现数据库建模操作批量化
- C++与QML文档之间传复杂数据结构(如结构体)
- 用POI HSSF处理EXCEL表格
- hdu 3517 Adopt or not
- SAP系统内的发票校验
- 【图像】矩阵 plot()函数
- Java Card Technology for Smart Card's Architecture and Programmer's Guide (Zhiqun Chen)翻译版(PART 6)
- windows与Linux的网卡MAC修改


