nginx location的管理以及查找
来源:互联网 发布:433m模块stc单片机解码 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 16:57
【原文链接】 http://blog.csdn.net/fengmo_q/article/details/6683377
关于nginx代码解析,我师兄雕梁的博客(http://simohayha.javaeye.com)有一系列的文章可以阅读。我这里将只介绍他博客里没有关注到的或者讲述不详细的,但是我个人又认为是nginx里面比较重要的东西。在这一篇文章里,我将介绍nginx关于location的处理,大家都知道Nginx配置文件里面会有很多的location,nginx的配置指令的作用域可以分为 main,server,location这3个种,实际上这3者不是依次包含的关系,而是相互独立的关系,比如一个只具有main级别作用域的指令,是不能写在某个server或者location内的,模块的某个指令可以同时具有main,server,location这3种作用域,另外每个模块有 main,srv,loc这3个级别的配置,一个模块的main级别的配置对所有的server和location都是共享的,srv级别的配置对所有 location都是共享的,location只有自己独立的loc级别的配置,这就是为什么一个模块的srv和loc级别的配置需要merge,而 main级别的配置不需要merge的原因。这里看起来有点绕,区分一下main,server,location分别作为一种作用域级别和一个主体,类似于形容词和名字的区别,nginx的配置关系还是不难理解的。
一般来说一个请求url过来,nginx会将它解析到某一个location来处理。这个解析的过程实际上根据location的配置基本可以分为字符串匹配和正则表达式匹配这2种。对于location的组织方式,最简单的就是直接将它们保存为一个链表,解析url的时候一个一个遍历即可找到相应location,但是这样效率太低,对像nginx这种高性能的服务器来说是完全不可取的,nginx将字符串匹配的location组织成了一个三叉的字符串排序树,而且建立的时候也考虑了树的平衡性。文章后面我讲详细介绍源码的实现。
首先我来大概的介绍一下location的种类和匹配规则,以nginx wiki(http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpCoreModule#location)的例子做说明:
- location = / {
- # matches the query / only.
- [ configuration A ]
- }
- location / {
- # matches any query, since all queries begin with /, but regular
- # expressions and any longer conventional blocks will be
- # matched first.
- [ configuration B ]
- }
- location ^~ /images/ {
- # matches any query beginning with /images/ and halts searching,
- # so regular expressions will not be checked.
- [ configuration C ]
- }
- location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
- # matches any request ending in gif, jpg, or jpeg. However, all
- # requests to the /images/ directory will be handled by
- # Configuration C.
- [ configuration D ]
- }
- location @named {
- # Such locations are not used during normal processing of requests,
- # they are intended only to process internally redirected requests (for example error_page, try_files).
- [ configuration E ]
- }
可以看到上面的例子中有5种不同类型的location,其中第4个带 “~” 号前缀的为需要正则匹配的location,nginx在进行url解析时对这5种不同类型的location具有不同的优先级规则,大致的规则如下:
1,字符串精确匹配到一个带 “=” 号前缀的location,则停止,且使用这个location的配置;
2,字符串匹配剩下的非正则和非特殊location,如果匹配到某个带 "^~" 前缀的location,则停止;
3,正则匹配,匹配顺序为location在配置文件中出现的顺序。如果匹配到某个正则location,则停止,并使用这个location的配置;否则,使用步骤2中得到的具有最大字符串匹配的location配置。
例如,对下面的请求有:
1, / -> 精确匹配到第1个location,匹配停止,使用configuration A
2,/some/other/url -> 首先前缀部分字符串匹配到了第2个location,然后进行正则匹配,显然没有匹配上,则使用第2个location的配置configurationB
3,/images /1.jpg -> 首先前缀部分字符串匹配到了第2个location,但是接着对第3个location也前缀匹配上了,而且这时已经是配置文件里面对这个url的最大字符串匹配了,并且location带有 "^~" 前缀,则不再进行正则匹配,最终使用configuration C
4,/some/other/path/to/1.jpg -> 首先前缀部分同样字符串匹配到了第2个location,然后进行正则匹配,这时正则匹配成功,则使用congifuration D
nginx的url匹配规则实际上有点不妥,大部分情况下一个url必须先进行字符串匹配,然后再做正则匹配,但是实际上如果先做正则匹配,没有匹配上再 做字符串匹配,在很多情况下可以节省掉做字符串匹配的时间。不管怎样,先来看一下nginx源码里面的实现,在介绍匹配location过程之前,先来介 绍一下nginx里面对location的组织方式,实际上在配置解析阶段,nginx将字符串匹配的location和正则匹配的location分别 存储在http core模块的loc配置ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t结构的下面2个字段:
- ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *static_locations;
- (NGX_PCRE)
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **regex_locations;
- if
- /* create location trees */
- for (s = 0; s < cmcf->servers.nelts; s++) {
- clcf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
- if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, cscfp[s], clcf) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
- }
- if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
- }
- }
- static ngx_int_t
- ngx_http_init_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t *cscf,
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
- {
- ...
- locations = pclcf->locations;
- ...
- /* 按照类型排序location,排序完后的队列: (exact_match 或 inclusive) (排序好的,如果某个exact_match名字和inclusive location相同,exact_match排在前面)
- | regex(未排序)| named(排序好的) | noname(未排序)*/
- ngx_queue_sort(locations, ngx_http_cmp_locations);
- named = NULL;
- n = 0;
- #if (NGX_PCRE)
- regex = NULL;
- r = 0;
- #endif
- for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
- q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
- q = ngx_queue_next(q))
- {
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
- /* 由于可能存在nested location,也就是location里面嵌套的location,这里需要递归的处理一下当前location下面的nested location */
- if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, NULL, clcf) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- #if (NGX_PCRE)
- if (clcf->regex) {
- r++;
- if (regex == NULL) {
- regex = q;
- }
- continue;
- }
- #endif
- if (clcf->named) {
- n++;
- if (named == NULL) {
- named = q;
- }
- continue;
- }
- if (clcf->noname) {
- break;
- }
- }
- if (q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations)) {
- ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
- }
- /* 如果有named location,将它们保存在所属server的named_locations数组中 */
- if (named) {
- clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
- (n + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
- if (clcfp == NULL) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- cscf->named_locations = clcfp;
- for (q = named;
- q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
- q = ngx_queue_next(q))
- {
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- *(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
- }
- *clcfp = NULL;
- ngx_queue_split(locations, named, &tail);
- }
- #if (NGX_PCRE)
- /* 如果有正则匹配location,将它们保存在所属server的http core模块的loc配置的regex_locations 数组中,
- 这里和named location保存位置不同的原因是由于named location只能存在server里面,而regex location可以作为nested location */
- if (regex) {
- clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
- (r + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
- if (clcfp == NULL) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- pclcf->regex_locations = clcfp;
- for (q = regex;
- q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
- q = ngx_queue_next(q))
- {
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- *(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
- }
- *clcfp = NULL;
- ngx_queue_split(locations, regex, &tail);
- }
- #endif
- return NGX_OK;
- }
- static ngx_int_t
- ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(ngx_conf_t *cf,
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
- {
- ngx_queue_t *q, *locations;
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
- ngx_http_location_queue_t *lq;
- locations = pclcf->locations;
- if (locations == NULL) {
- return NGX_OK;
- }
- if (ngx_queue_empty(locations)) {
- return NGX_OK;
- }
- /* 这里也是由于nested location,需要递归一下 */
- for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
- q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
- q = ngx_queue_next(q))
- {
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
- if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- }
- /* join队列中名字相同的inclusive和exact类型location,也就是如果某个exact_match的location名字和普通字符串匹配的location名字相同的话,
- 就将它们合到一个节点中,分别保存在节点的exact和inclusive下,这一步的目的实际是去重,为后面的建立排序树做准备 */
- if (ngx_http_join_exact_locations(cf, locations) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- /* 递归每个location节点,得到当前节点的名字为其前缀的location的列表,保存在当前节点的list字段下 */
- ngx_http_create_locations_list(locations, ngx_queue_head(locations));
- /* 递归建立location三叉排序树 */
- pclcf->static_locations = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, 0);
- if (pclcf->static_locations == NULL) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- return NGX_OK;
- }
- location /xyz {
- }
- location = /xyz {
- }
- location /xyza {
- }
- location /xyzab {
- }
- location /xyzb {
- }
- location /abc {
- }
- location /efg {
- }
- location /efgaa {
- }
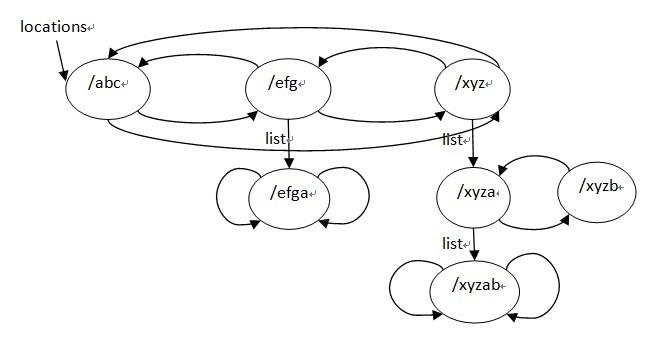
最后,来看下ngx_http_create_locations_tree函数:
- static ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *
- ngx_http_create_locations_tree(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_queue_t *locations,
- size_t prefix)
- {
- ...
- /* 根节点为locations队列的中间节点 */
- q = ngx_queue_middle(locations);
- lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
- len = lq->name->len - prefix;
- node = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
- offsetof(ngx_http_location_tree_node_t, name) + len);
- if (node == NULL) {
- return NULL;
- }
- node->left = NULL;
- node->right = NULL;
- node->tree = NULL;
- node->exact = lq->exact;
- node->inclusive = lq->inclusive;
- node->auto_redirect = (u_char) ((lq->exact && lq->exact->auto_redirect)
- || (lq->inclusive && lq->inclusive->auto_redirect));
- node->len = (u_char) len;
- ngx_memcpy(node->name, &lq->name->data[prefix], len);
- /* 从中间节点开始断开 */
- ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
- if (ngx_queue_empty(locations)) {
- /*
- * ngx_queue_split() insures that if left part is empty,
- * then right one is empty too
- */
- goto inclusive;
- }
- /* 从locations左半部分得到左子树 */
- node->left = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, prefix);
- if (node->left == NULL) {
- return NULL;
- }
- ngx_queue_remove(q);
- if (ngx_queue_empty(&tail)) {
- goto inclusive;
- }
- /* 从locations右半部分得到右子树 */
- node->right = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &tail, prefix);
- if (node->right == NULL) {
- return NULL;
- }
- inclusive:
- if (ngx_queue_empty(&lq->list)) {
- return node;
- }
- /* 从list队列得到tree子树 */
- node->tree = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &lq->list, prefix + len);
- if (node->tree == NULL) {
- return NULL;
- }
- return node;
- }
- struct ngx_http_location_tree_node_s {
- ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *left;
- ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *right;
- ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *tree;
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *exact;
- ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *inclusive;
- u_char auto_redirect;
- u_char len;
- u_char name[1];
- };
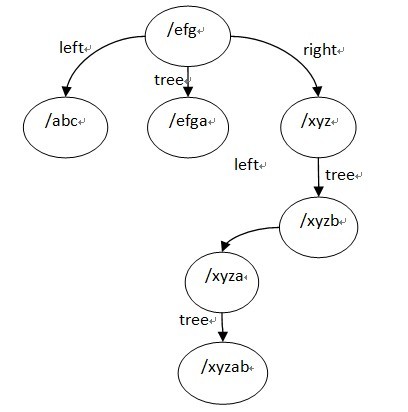
location tree结构用到的是left,right,tree 这3个字段, location tree实际上是一个三叉的字符串排序树,而且这里如果某个节点只考虑左,右子树,它是一颗平衡树,它的建立过程有点类似于一颗平衡排序二叉树的建立过程,先排序再用二分查找找到的节点顺序插入,ngx_http_location_tree_node_s的tree节点也是一颗平衡排序树,它是用该节点由ngx_http_create_locations_list()得到的list建立的,也就是该节点的名字是它的tree子树里面的所有节点名字的前缀,所以tree子树里面的所有节点的名字不用保存公共前缀,而且查找的时候,如果是转向tree节点的话,也是不需要再比较父节点的那段字符串了。
ngx_http_create_locations_tree()函数写的很清晰,它有一个参数是队列locations,它返回一颗三叉树,根节点为locations的中间节点,其左子树为locations队列的左半部分建立的location tree,右子树为location队列的右半部分建立的tree,tree节点为该根节点的list队列建立的tree。
最终建立的location tree如下(为了方便阅读,图中列出了tree节点的完整名字):
- nginx location的管理以及查找
- nginx location的管理以及查找
- nginx location的管理以及查找
- Nginx location的管理以及查找
- Nginx的location配置
- nginx的location匹配
- Nginx的location配置
- nginx的location用法
- nginx的location配置
- nginx location的配置
- nginx location的配置
- nginx构建static location tree和查找
- nginx 的location 的用法
- Nginx location 的选择规则
- nginx的location配置详解
- 关于nginx的location匹配
- nginx的location配置详解
- Nginx的location匹配问题
- python_udp数据报传输的实现
- win7 32 安装oracle server 10.2.0.1.0
- s3c2440定时器简介
- 使用jQuery实现鼠标悬浮图片轮换效果
- hibernate 多对一映射 many-to-one
- nginx location的管理以及查找
- objective 消息中心的处理
- python时间函数
- 移动视频分享应用Klip获Benchmark领投800万B轮融资
- vim自动补全功能
- 找出两个已经排好序的数组的中位数
- hibernate criteria查询
- C#Socket 通信
- 【产品经理】谁是产品经理,产品经理到底要做什么?


