Linux下生产者消费者问题详细分析(操作系统期中考试论文---并发程序的同步和互斥)
来源:互联网 发布:手持云台 知乎 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 12:10
海淘论坛,转运四方
这是操作系统期中考试时我写的小论文,想要文档及代码的点击下载。
要求如下:



本篇为了简洁,只贴有用的信息。
执行逻辑说明:
程序启动后首先初始化信号量集和循环缓冲队列。然后按照提示信息输入生产者数量和消费者数量。根据生产者和消费者数量创建相应的生产者线程和消费者线程。生产者线程执行生产者函数,向缓冲区放一个值,然后write指针加1。消费者执行消费者函数,从缓冲区读一个值,然后read指针加1。
源码如下:
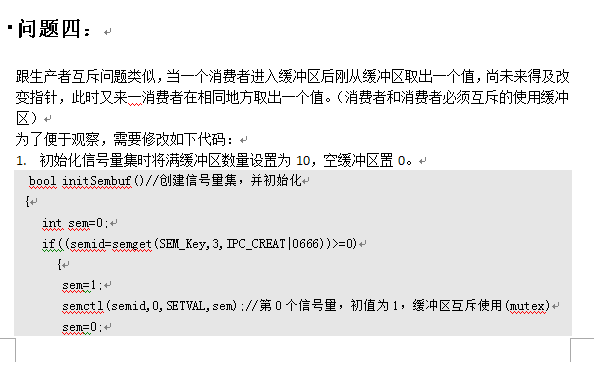
/* pc.c:Producer and Consumer Problem *author : houjialin *To compile: g++ pc.c -o pc -l pthread */#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>//exit#include<sys/types.h>#include<sys/ipc.h>#include<sys/sem.h>#include<pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>//sleep#include<signal.h>#define Maxbuf 10 //定义循环缓冲队列及对其的一组操作struct Circlebuf//循环缓冲队列结构{ int read;//读指针 int write;//写指针 int buf[Maxbuf];//缓冲区} circlebuf;void writeCirclebuf(Circlebuf *circlebuf,int *value)//向缓冲区中写一个值{ circlebuf->buf[circlebuf->write]=(*value); circlebuf->write=(circlebuf->write+1)%Maxbuf;//写过后指针+1 }int readCirclebuf(Circlebuf *circlebuf)//从当前指针读一个值,返回value{ int value=0; value=circlebuf->buf[circlebuf->read]; circlebuf->buf[circlebuf->read]=0; //读过后置0 circlebuf->read=(circlebuf->read+1)%Maxbuf;//读过后read+1 return value;}void OutCirclebuf(Circlebuf *circlebuf){ printf("Circlebuf value:"); for(int i=0;i<Maxbuf;i++) { printf("%d ", circlebuf->buf[i]); } printf("\n");}//定义信号量及对其的操作#define SEM_Key 4001 //信号量Key值 struct sembuf semaphore;//定义一个信号量int semid;//信号量IDbool initSembuf()//创建信号量集,并初始化{ int sem=0; if((semid=semget(SEM_Key,3,IPC_CREAT|0666))>=0) { sem=1; semctl(semid,0,SETVAL,sem);//第0个信号量,初值为1,缓冲区互斥使用(mutex) sem=10; semctl(semid,1,SETVAL,sem);//第1个信号量,初值为10,当前空缓冲区数(empty) sem=0; semctl(semid,2,SETVAL,sem);//第2个信号量,初值为0,当前满缓冲区数(full) return true; } else return false;}//对信号量的PV操作void Pmutex(){ semaphore.sem_num=0; semaphore.sem_op=-1; semaphore.sem_flg=SEM_UNDO; semop(semid,&semaphore,1);}void Vmutex(){ semaphore.sem_num=0; semaphore.sem_op=1; semaphore.sem_flg=SEM_UNDO; semop(semid,&semaphore,1);}void Pempty(){ semaphore.sem_num=1; semaphore.sem_op=-1; semaphore.sem_flg=SEM_UNDO; semop(semid,&semaphore,1);}void Vempty(){ semaphore.sem_num=1; semaphore.sem_op=1; semaphore.sem_flg=SEM_UNDO; semop(semid,&semaphore,1);}void Pfull(){ semaphore.sem_num=2; semaphore.sem_op=-1; semaphore.sem_flg=SEM_UNDO; semop(semid,&semaphore,1);}void Vfull(){ semaphore.sem_num=2; semaphore.sem_op=1; semaphore.sem_flg=SEM_UNDO; semop(semid,&semaphore,1);}void sigend(int sig) { semctl(semid, IPC_RMID, 0); exit(0); } void * productThread(void *i)//生产者线程{ int *n=(int *)i; while(true) { Pempty();//① Pmutex();//② writeCirclebuf(&circlebuf,n); printf("Producer %d succeeded put a value=%d into the circlebuf.\n",*n,*n); OutCirclebuf(&circlebuf); Vmutex();//③ Vfull();//④ }}void * consumerThread(void *i)//消费者{ int *n=(int *)i; int value=0;//消费品存放处 while(true) { Pfull();//⑤ Pmutex();//⑥ value=readCirclebuf(&circlebuf); printf("The consumer %d succeful consume .The value is %d \n",*n,value); Vmutex();//⑦ Vempty();//⑧ }}int main(){ While(! initSembuf());//初始化信号量集 signal(SIGINT, sigend); signal(SIGTERM, sigend); int ConsNum=0,ProdNum=0,ret;//初始化生产者消费者数量 pthread_t cpid,ppid;//线程ID //初始化循环缓冲队列 circlebuf.read=circlebuf.write=0; for(int i=0;i<Maxbuf;i++) { circlebuf.buf[i]=0; } printf("Please input the number of producter :"); scanf("%d",&ProdNum); int *pro=new int[ProdNum]; printf("Please input the number of consumer :"); scanf("%d",&ConsNum); int *con=new int[ConsNum]; for(int i=1;i<=ProdNum;i++)//启动生产者 { ppid=i+100;//为了和消费者线程ID区别,每个线程号都加100 pro[i-1]=i; ret=pthread_create(&ppid,NULL,productThread,(void *)&pro[i-1]);// if(ret!=0) { printf("Create thread error"); exit(1); } } for(int i=1;i<=ConsNum;i++)//启动消费者 { cpid=i; con[i-1]=i; ret=pthread_create(&cpid,NULL,consumerThread,(void *)&con[i-1]); if(ret!=0) { printf("Create thread error"); exit(1); } } sleep(100000);//不让main线程停止}编程平台说明:
操作系统:Ubuntu11.04
编译器: g++
同步机制:采用Linux下的信号量机制实现并发进程间的同步和互斥。源程序建立的信号量集中有三个信号量。第一信号量初值为1,缓冲区互斥时使用。第二个初值为10,相当于当前可用空缓冲区数量。第三个初值为0,表示当前已放入产品的缓冲区数量。
静态条件说明和执行结果分析:
(由于格式换着太麻烦了,这里直接上图片了。)
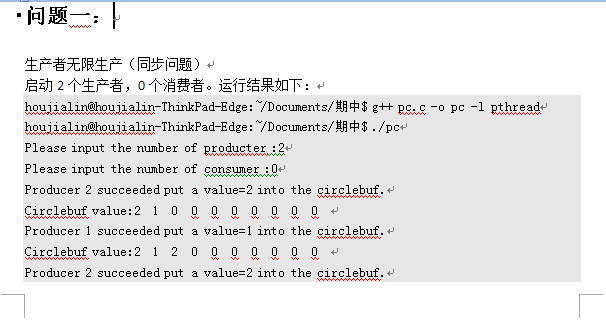
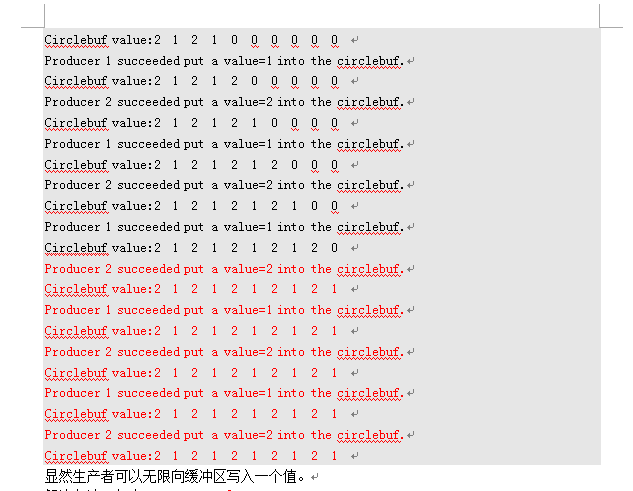

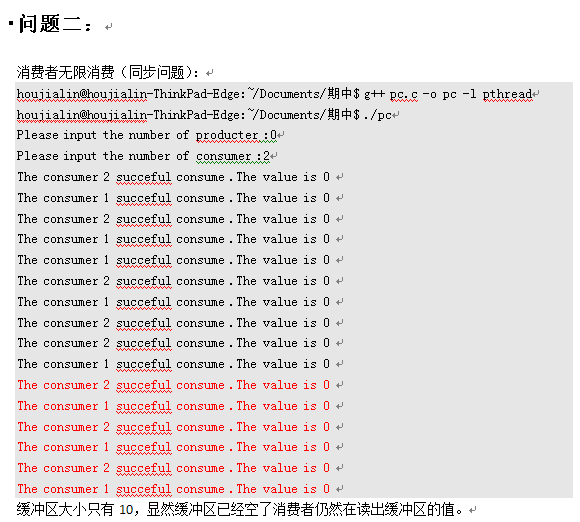


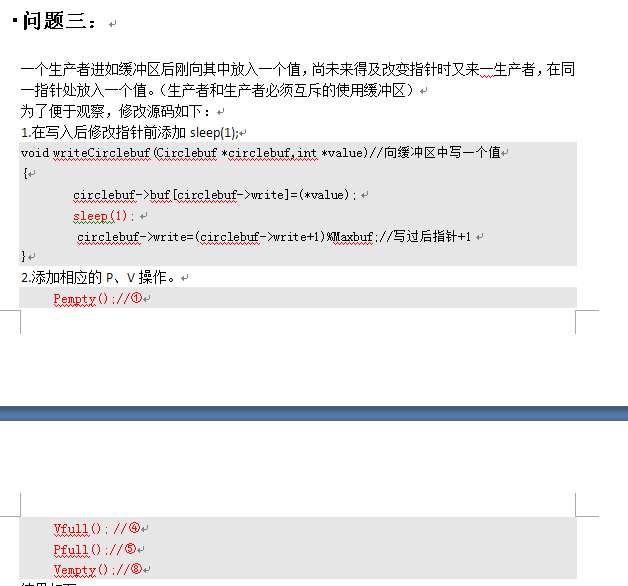




- Linux下生产者消费者问题详细分析(操作系统期中考试论文---并发程序的同步和互斥)
- 生产者-消费者问题实现 (linux下C同步信号量和互斥信号量的应用)
- linux中的生产者和消费者问题--信号量 互斥 同步
- linux同步和互斥综合使用---生产者和消费者
- 进程、线程知识点总结和同步(消费者生产者,读者写者三类问题)、互斥、异步、并发、并行、死锁、活锁的总结
- Linux下信号量实现进程同步、互斥(生产者消费者问题)
- 【操作系统】生产者消费者问题分析(线程同步)
- python 生产者,消费者的同步互斥问题
- 资源同步与互斥问题(生产者与消费者)
- Linux下进程的同步互斥实例——生产者消费者
- 利用线程的同步和互斥解决两个消费者两个生产者一个临界区问题
- 经典生产者与消费者问题(线程的同步与互斥)
- GNU/Linux中解决多线程互斥同步问题(生产者消费者同步问题)
- 操作系统同步生产者消费者问题
- Java---并发和同步(生产者--消费者)
- 三个同步与互斥问题之生产者与消费者
- 操作系统学习笔记-信号量及PV操作与进程互斥和消费者生产者问题
- linux操作系统之生产者与消费者同步问题
- comment on的重要意义
- linux tr
- 等值首尾和问题
- 怎样花两月时间去应聘互联网公司
- 数组全排列c语言实现
- Linux下生产者消费者问题详细分析(操作系统期中考试论文---并发程序的同步和互斥)
- jQuery 自定义函数方法
- 调查:你目前使用的QTP版本是多少?
- 黑马程序员—Java高新技术2
- 现代软件工程讲义 4 方法论 - 事后诸葛亮会议
- linux平台下 延迟工作队列实例
- zoj 2857 Image Transformation
- RHEL AS4 上oracle10gR2 静默安装
- 含有return 的try catch finally的执行顺序


