LDD3源码分析之简单休眠
来源:互联网 发布:农村淘宝网彩票站 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/16 05:37
作者:刘昊昱
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/liuhaoyutz
编译环境:Ubuntu 10.10
内核版本:2.6.32-38-generic-pae
LDD3源码路径:examples/misc-modules/sleepy.c
本文分析LDD3第六章中关于简单休眠的示例代码sleepy.c。
首先列出sleepy.c的完整代码:
1/* 2 * sleepy.c -- the writers awake the readers 3 * 4 * Copyright (C) 2001 Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet 5 * Copyright (C) 2001 O'Reilly & Associates 6 * 7 * The source code in this file can be freely used, adapted, 8 * and redistributed in source or binary form, so long as an 9 * acknowledgment appears in derived source files. The citation10 * should list that the code comes from the book "Linux Device11 * Drivers" by Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet, published12 * by O'Reilly & Associates. No warranty is attached;13 * we cannot take responsibility for errors or fitness for use.14 *15 * $Id: sleepy.c,v 1.7 2004/09/26 07:02:43 gregkh Exp $16 */1718#include <linux/module.h>19#include <linux/init.h>2021#include <linux/sched.h> /* current and everything */22#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk() */23#include <linux/fs.h> /* everything... */24#include <linux/types.h> /* size_t */25#include <linux/wait.h>2627MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");2829static int sleepy_major = 0;3031static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(wq);32static int flag = 0;3334ssize_t sleepy_read (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)35{36 printk(KERN_DEBUG "process %i (%s) going to sleep\n",37 current->pid, current->comm);38 wait_event_interruptible(wq, flag != 0);39 flag = 0;40 printk(KERN_DEBUG "awoken %i (%s)\n", current->pid, current->comm);41 return 0; /* EOF */42}4344ssize_t sleepy_write (struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count,45 loff_t *pos)46{47 printk(KERN_DEBUG "process %i (%s) awakening the readers...\n",48 current->pid, current->comm);49 flag = 1;50 wake_up_interruptible(&wq);51 return count; /* succeed, to avoid retrial */52}535455struct file_operations sleepy_fops = {56 .owner = THIS_MODULE,57 .read = sleepy_read,58 .write = sleepy_write,59};606162int sleepy_init(void)63{64 int result;6566 /*67 * Register your major, and accept a dynamic number68 */69 result = register_chrdev(sleepy_major, "sleepy", &sleepy_fops);70 if (result < 0)71 return result;72 if (sleepy_major == 0)73 sleepy_major = result; /* dynamic */74 return 0;75}7677void sleepy_cleanup(void)78{79 unregister_chrdev(sleepy_major, "sleepy");80}8182module_init(sleepy_init);83module_exit(sleepy_cleanup);在模块初始化函数中,注册字符设备”sleepy”时,指定了该设备的读写函数分别是sleepy_read和sleepy_write。当某个进程对sleepy执行读操作时,会进入休眠。当某个进程对sleepy执行写操作时,会唤醒相应等待队列中的所有休眠进程。
为了管理休眠进程,需要建立等待队列,等待队列就是一个进程链表,其中包含等待某个特定事件的所有进程。等待队列通过“等待队列头”来管理,等待队列头是一个类型为wait_queue_head_t的结构体。可以静态初始化一个等待队列头:
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(name);
也可以动态初始化一个等待队列头:
wait_queue_head_t my_queue;
init_waitqueue_head(&my_queue);
一个进程要进入休眠,最常用的函数是:
wait_event_interruptible(queue, condition);
queue是等待队列头,condition是一个条件表达式,进程进入休眠前和被唤醒后,都会检查condition的值是否为真,如果不为真,则进程会进入休眠。
对应wait_event_interruptible的唤醒函数是:
wake_up_interruptible(wait_queue_head_t *queue)
sleepy.c第31行定义了等待队列头wq:
31static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(wq);
在sleepy_read函数中,38行调用wait_event_interruptible(wq, flag != 0)进入休眠。所以只要有进程对sleepy执行读操作,就会进入休眠。
在sleepy_write函数中,49行将flag设置为1,然后调用wake_up_interruptible(&wq)将等待在wq上的进程唤醒。
注意,因为在sleepy_read函数中,休眠进程被唤醒后,会把flag重新设置为0,所以虽然全部休眠进程都会被唤醒,但一次只有一个进程能真正继续执行,其它进程会重新休眠。但是为简单起见,这里没考虑并发处理等问题。
要测试sleepy模块,我们先创建sleepy_load和sleepy_unload脚本。
sleepy_load脚本的内容如下:
#!/bin/sh# $Id: complete_load,v 1.4 2004/11/03 06:19:49 rubini Exp $module="sleepy"device="sleepy"mode="666"# Group: since distributions do it differently, look for wheel or use staffif grep -q '^staff:' /etc/group; then group="staff"else group="wheel"fi# invoke insmod with all arguments we got# and use a pathname, as insmod doesn't look in . by default/sbin/insmod ./$module.ko $* || exit 1# retrieve major numbermajor=$(awk "\$2==\"$module\" {print \$1}" /proc/devices)# Remove stale nodes and replace them, then give gid and perms# Usually the script is shorter, it's scull that has several devices in it.rm -f /dev/${device}mknod /dev/${device} c $major 0chgrp $group /dev/${device} chmod $mode /dev/${device}sleepy_unload脚本的内容如下:
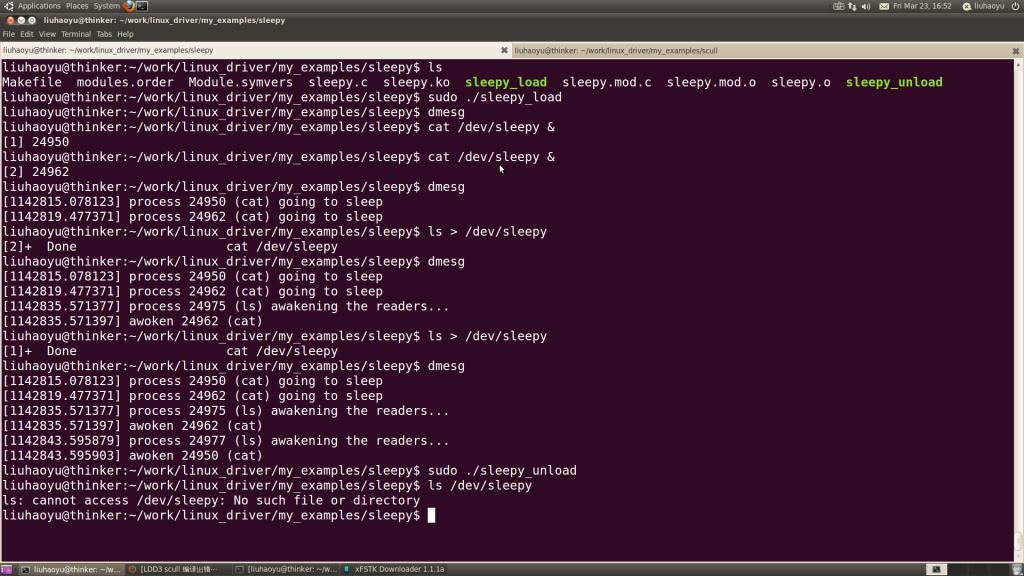
#!/bin/shmodule="sleepy"device="sleepy"# invoke rmmod with all arguments we got/sbin/rmmod $module $* || exit 1# Remove stale nodesrm -f /dev/${device}sleepy模块的测试过程如下图所示:
- LDD3源码分析之简单休眠
- LDD3源码分析之简单休眠
- LDD3源码分析之简单休眠
- LDD3源码分析之简单休眠
- LDD3源码分析之vmalloc
- LDD3源码分析之vmalloc
- LDD3源码分析之vmalloc
- LDD3源码分析之vmalloc
- LDD3源码分析之poll分析
- LDD3源码分析之llseek分析
- LDD3源码分析之poll分析
- LDD3源码分析之llseek分析
- LDD3源码分析之poll分析
- LDD3源码分析之llseek分析
- LDD3源码分析之llseek分析
- LDD3源码分析之llseek分析(二)
- LDD3源码分析之poll分析
- LDD3源码分析之poll分析
- 01背包(转)
- 随记
- Mac OSX 系统常用快捷键整理
- jquery-ui 手风琴组件Accordion学习(可全部折叠)
- gcc生成静态库和动态库
- LDD3源码分析之简单休眠
- JAVA 的checked异常和unchecked异常
- 使用ViewPager实现高仿launcher拖动效果
- 汇编语言超浓缩教程
- VC 调用 图片查看器
- 程序员
- Android Tombstone/Crash的log分析和定位
- 将Tomcat配置成服务启动
- 教你如何迅速秒杀99%的海量数据处理面试题


