Color depth
来源:互联网 发布:ubuntu 虚拟机 wifi 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/04/30 12:44
Color depth, is the term used to refer to the number of bits used in a single pixel on a screen [1], it is also reffered to as bit depth or bits per pixel (bpp). The number of colors increase exponentially depending on the number of bits, eg. a 2-bit image will have 4 colors, an 8-bit image will have 256 colors and so on and so forth. Images displayed in 16-bits are known as hi-color images, and images of 24-bits (around 16.7 million colors) are usually reffered to as true-color display, due to the accuracy of the image to the human eye (which is said to only be able to differentiate between 10 million colors [2]). Images may be displayed in 32-bits but this will only be visible to experts [3]. It is important to note that the color depth is a setting that can be adjusted through the operating system, which indicates the maximum level of color depth a computer supports. Thus, if you send a 24-bit image to an 8-bit computer screen, you will view the image in 8-bits. The level of color depth depends on the video memory available [4]. Most computers support 24-bit displays. The colors we view on an HDMI display have 30-bits, 36 bits, and 40-bits [5].

1-bit image

2-bit image

8-bit image

24-bit image
Understanding Color in Computers
Colors on screen are represented differently than in pigment. In pigment the primary colors are red, blue and yellow, which when combined create the color black. This is known as subtractive color because colors are moving from white to black. Another subtractive color method often used in printing is CMYK (Ceylon, Magenta, Yellow, and Black).
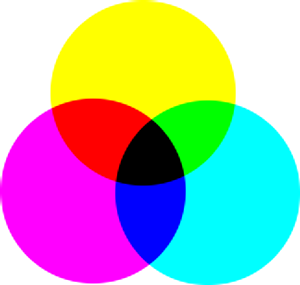
On a screen colors are represented by additive color, meaning the screen start black, and when the primary colors are mixed together we get white. The primary colors in additive color are red, blue, and green (RGB). This is particularly important in the fields of graphic design, and photography where they have to consider rendering images on screen for a final printed product.

The quality of an image usually depends on color depth and resolution (the number of pixels on a screen). Images with a large number of pixels, each having a high color depth allows for better looking images.
- Color depth
- Bit Depth、Color Depth
- Color depth (from Wiki)
- OpenNI- working with depth and color maps
- How does HDR relate to color space and bit depth?
- Depth
- Fusing time-of-flight depth and color for real-time segmentation and tracking
- 关于LCD Datesheet中 Color Depth的262K/65K的解释
- Unity 对Camera 属性Clear Flags 的SkyBox/Solid Color/Depth Only深度解析
- NOTE: Color Map Optimization for 3D Reconstruction with Consumer Depth Cameras
- Color Map Optimization for 3D Reconstruction with Consumer Depth Cameras
- color #
- color
- color
- Color
- color
- color
- color
- RHEL安装Hyper-V集成服务后无法使用光驱的解决方法
- nfs:server is not responding,still trying 解决
- awk实例
- 如何让eclipse和glassfish结合使用
- 很完整的2、8、10、16进制转换方法的进制的转化
- Color depth
- symantec NBU with status 59: access to the client was not allowed
- ABAP SCREEN 常用语句
- flash player 安装报错不是最新版本问题解决
- 动态规划:数字三角形
- jstl标签和EL表达式
- linux下错误bad interpreter: No such file or directory
- SSH xml配置文件及架构设计
- [linux安全] nmap扫描器的使用


