Bash Prompt -Linux 终端提示符
来源:互联网 发布:ubuntu 终端输入中文 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/01 00:06
Task: Display current BASH prompt (PS1)
Use the echo command to display current BASH prompt:$ echo $PS1
Sample outputs:
[\\u@\h \\W]\\$
Here is another output from my Debian based system:$ echo $PS1
Sample outputs:
\[\e]0;\u@\h: \w\a\]${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$By default the command prompt is set to [\u@\h \W]\$. The backslash-escaped special characters are decoded as follows:
- \u: Display the current username .
- \h: Display the hostname
- \W: Print the base of current working directory.
- \$: Display # (indicates root user) if the effective UID is 0, otherwise display a $.
Task: Modify current BASH prompt
Use the export command to setup a new shell prompt:$ export PS1="[\\u@\\H \\W \\@]\\$"
Sample outputs:
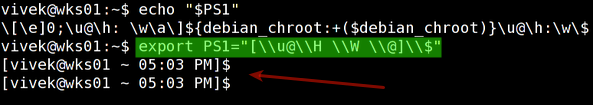
Fig.01: New prompt in action
Where,
- \H: Display FQDN hostname.
- \@: Display current time in 12-hour am/pm format
Task: Add colors to the prompt
To add colors to the shell prompt use the following export command syntax:
'\e[x;ym $PS1 \e[m'
Where,
- \e[ : Start color scheme.
- x;y : Color pair to use (x;y)
- $PS1 : Your shell prompt variable.
- \e[m : Stop color scheme.
To set a red color prompt, type the following command:$ export PS1="\e[0;31m[\u@\h \W]\$ \e[m "
Sample outputs:
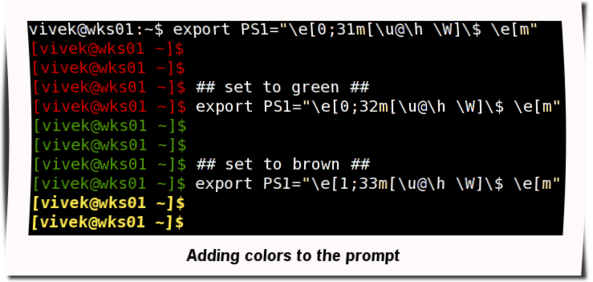
Fig.02: Adding the colors to the prompt
A list of color codes
ColorCodeBlack0;30Blue0;34Green0;32Cyan0;36Red0;31Purple0;35Brown0;33Blue0;34Green0;32Cyan0;36Red0;31Purple0;35Brown0;33Note: You need to replace digit 0 with 1 to get light color version.
Task: How do I make the prompt setting permanent?
Your new shell prompt setting set by $PS1 is temporary i.e. when you logout setting will be lost. To have it set every time you login to your workstation add above export command to your$HOME/.bash_profile file or $HOME/.bashrc file.$ cd
$ vi .bash_profile
OR$ vi $HOME/.bashrc
Append the following line:export PS1="\e[0;31m[\u@\h \W]\$ \e[m"
Save and close the file.
Say hello to tput command
You can also use tput command to set terminal and modify the prompt settings. For example, to display RED color prompt using a tput:export PS1="\[$(tput setaf 1)\]\u@\h:\w $ \[$(tput sgr0)\]"
A list of handy tput command line options
- tput bold - Bold effect
- tput rev - Display inverse colors
- tput sgr0 - Reset everything
- tput setaf {CODE}- Set foreground color, see color {CODE} table below for more information.
- tput setab {CODE}- Set background color, see color {CODE} table below for more information.
Various color codes for the tput command
Color {code}Color0Black1Red2Green3Yellow4Blue5Magenta6Cyan7WhiteRecommend readings
Bash allows these prompt strings to be customized by inserting a number of backslash-escaped special characters that are decoded as follows:
- \a : an ASCII bell character (07)
- \d : the date in "Weekday Month Date" format (e.g., "Tue May 26")
- \D{format} : the format is passed to strftime(3) and the result is inserted into the prompt string; an empty format results in a locale-specific time representation. The braces are required
- \e : an ASCII escape character (033)
- \h : the hostname up to the first '.'
- \H : the hostname
- \j : the number of jobs currently managed by the shell
- \l : the basename of the shell’s terminal device name
- \n : newline
- \r : carriage return
- \s : the name of the shell, the basename of $0 (the portion following the final slash)
- \t : the current time in 24-hour HH:MM:SS format
- \T : the current time in 12-hour HH:MM:SS format
- \@ : the current time in 12-hour am/pm format
- \A : the current time in 24-hour HH:MM format
- \u : the username of the current user
- \v : the version of bash (e.g., 2.00)
- \V : the release of bash, version + patch level (e.g., 2.00.0)
- \w : the current working directory, with $HOME abbreviated with a tilde
- \W : the basename of the current working directory, with $HOME abbreviated with a tilde
- \! : the history number of this command
- \# : the command number of this command
- \$ : if the effective UID is 0, a #, otherwise a $
- \nnn : the character corresponding to the octal number nnn
- \\ : a backslash
- \[ : begin a sequence of non-printing characters, which could be used to embed a terminal control sequence into the prompt
- \] : end a sequence of non-printing characters
- Bash Prompt -Linux 终端提示符
- linux 命令终端提示符显示-bash-4.1#
- 自定义bash终端提示符
- 自定义bash提示符 -- Bash prompt basics
- linux 命令终端提示符显示-bash-4.1#解决方法
- linux 命令终端提示符显示-bash-4.2#解决方法
- linux 命令终端提示符显示-bash-4.2#解决方法
- linux 命令终端提示符显示-bash-4.2#解决方法
- linux 命令终端提示符显示-bash-4.1#解决方法
- linux 命令终端提示符显示-bash-4.2#解决方法
- linux 命令终端提示符显示-bash-4.2#解决方法
- 设置bash终端提示符(PS1)
- Linux 终端提示符设置
- 定制Bash Shell的提示符(prompt string)
- Linux/Unix中的命令提示符prompt
- Linux/Unix中的命令提示符prompt
- Linux/Unix中的命令提示符prompt
- Linux修改BASH命令提示符
- poj 2060
- forecast过期问题
- 程序 'jps' 已包含在下列软件包中
- Google Chrome Extensions 最新精彩插件推荐
- 第002课 进制的算术运算(1)
- Bash Prompt -Linux 终端提示符
- javascript与c#之间的调用
- PHP数组的“自然”排序
- java异常
- 手动修改spfile.ora文件导致oracle启动不了的解决办法 .
- 温度场有限容积法程序入门之五:展望及问题
- 泛泰SKYA850救砖原理与分区表解析[2013.6.3更新]
- 兼容性窗口 --显示流程
- live555对于实时音视频的支持


