HDU4134:Sequence Folding
来源:互联网 发布:怎样在matlab2014编程 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 22:23
Problem Description
Alice and Bob are practicing hard for the new ICPC season. They hold many private contests where only the two of them compete against each other. They almost have identical knowledge and skills, the matter which results many times in ties in both the number of problems solved and in time penalty! To break the tie, Alice and Bob invented a tie breaker technique called sequence folding! The following are the steps of this technique:
1- Generate a random integer N >= 2.
2- Generate a sequence of N random integers.
3- If N = 2 go to step 6.
4- Fold the sequence by adding the Nth element to the first, the N-1th element to the second and so on, if N is odd then the middle element is added to itself, figure 1 illustrates the folding process.
5- Set N = ceil (N/2) and go to step 3.
6- The sequence now contains two numbers, if the first is greater than the second then Alice wins, otherwise Bob wins.
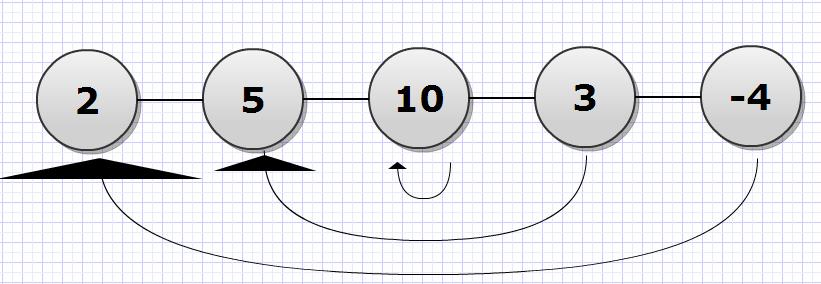
Figure 1.a Before Folding

Figure 1.b After one step of folding
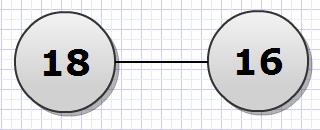
Figure 1.c After two steps of folding, Alice wins!
In this problem you’re given the sequence of N integers and are asked determine the contest winner using the sequence folding tie breaker technique.
1- Generate a random integer N >= 2.
2- Generate a sequence of N random integers.
3- If N = 2 go to step 6.
4- Fold the sequence by adding the Nth element to the first, the N-1th element to the second and so on, if N is odd then the middle element is added to itself, figure 1 illustrates the folding process.
5- Set N = ceil (N/2) and go to step 3.
6- The sequence now contains two numbers, if the first is greater than the second then Alice wins, otherwise Bob wins.



In this problem you’re given the sequence of N integers and are asked determine the contest winner using the sequence folding tie breaker technique.
Input
The first line contains T (1 <= T <= 100), the number of test cases. The first line of each test case contains an integer (2 <= N <= 100), the number of elements of the sequence. The next line contains N space separated integers. The sum of any subset of the numbers fit in a 32 bit signed integer.
Output
For each test case print the name of the winner. Follow the output format below.
Sample Input
252 5 10 3 -435 4 -3
Sample Output
Case #1: AliceCase #2: Bob
水题一道,按照题目的意思来就可以了
意思就是把一个序列对折,对应的数字相加
如果是奇数,那么对折后中间的数就自己加自己
最后只剩下两个
如果第一个比第二个打,那么就是Alice胜
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ int t,cas = 1; int a[105],i,n; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { scanf("%d",&n); for(i = 0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); while(n!=2) { for(i = 0;i<n;i++) a[i] = a[i]+a[n-i-1]; if(n%2) n = (n+1)/2; else n/=2; } printf("Case #%d: ",cas++); if(a[0]>a[1]) printf("Alice\n"); else printf("Bob\n"); } return 0;}
- HDU4134:Sequence Folding
- HDU--4134(Sequence Folding)
- Folding
- Folding@home
- poj2176 Folding
- Paper folding
- UVA1630 - Folding
- Area Folding
- Folding Gym
- Word Folding
- 计蒜客 folding
- Folding UVA
- UVa1630 Folding/poj 2176 Folding/zoj 1554 Folding
- ZOJ 1554 Folding
- zoj 1554 Folding
- POJ 2176 Folding (字符串)
- 常量折叠 Constant folding
- Timus 1238. Folding
- 还是动态规划。XDOJ Problem 1144
- 谈谈我的首个开源项目WeiboSpider(0)——WeiboSpider的总体架构
- C# using 三种使用方式
- Rsync源码——滚动校验
- 分治与递归
- HDU4134:Sequence Folding
- Rsync源码——md5
- mem_malloc:Unknown symbol kmalloc_caches
- 三个数找出大小为中间的数(Python)
- 实现了免费上网 - 室外工程级usb大功率无线网卡的应用(原创)
- vim基本命令
- block
- linux学习之linux百问2,不断更新
- apache2.4配置cgi和fastcgi


