LRU Cache 实现
来源:互联网 发布:手机全透明软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/05/23 01:13
LRU Cache实现
LeetCode上有着样一道题目:
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the following operations: get and set.
get(key) - Get the value (will always be positive) of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.set(key, value) - Set or insert the value if the key is not already present. When the cache reached its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting a new item.
先来从实现的角度简单复习一下操作系统中的LRU算法吧:
原理
LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高”。
实现
最常见的实现是使用一个链表保存缓存数据,详细算法实现如下:
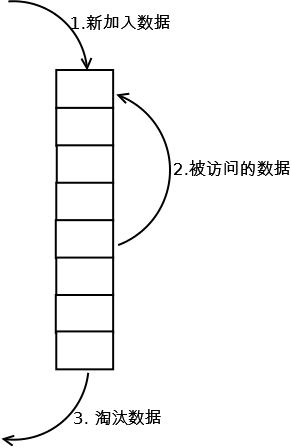
1. 新数据插入到链表头部;
2. 每当缓存命中(即缓存数据被访问),则将数据移到链表头部;
3. 当链表满的时候,将链表尾部的数据丢弃。
分析
【命中率】
当存在热点数据时,LRU的效率很好,但偶发性的、周期性的批量操作会导致LRU命中率急剧下降,缓存污染情况比较严重。
【复杂度】
实现简单。
【代价】
命中时需要遍历链表,找到命中的数据块索引,然后需要将数据移到头部。
LRU-K
原理
LRU-K中的K代表最近使用的次数,因此LRU可以认为是LRU-1。LRU-K的主要目的是为了解决LRU算法“缓存污染”的问题,其核心思想是将“最近使用过1次”的判断标准扩展为“最近使用过K次”。
实现
相比LRU,LRU-K需要多维护一个队列,用于记录所有缓存数据被访问的历史。只有当数据的访问次数达到K次的时候,才将数据放入缓存。当需要淘汰数据时,LRU-K会淘汰第K次访问时间距当前时间最大的数据。详细实现如下:
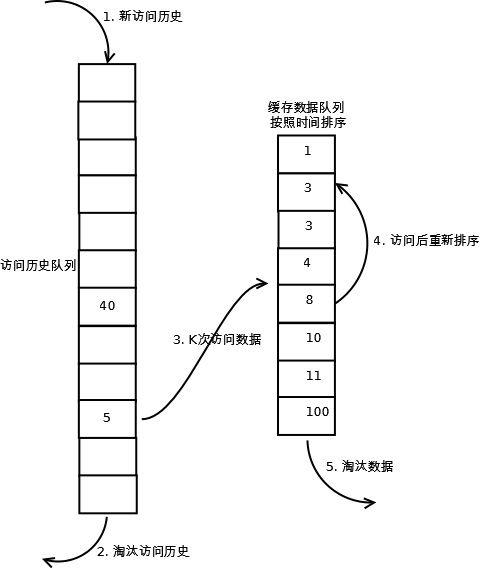
1. 数据第一次被访问,加入到访问历史列表;
2. 如果数据在访问历史列表里后没有达到K次访问,则按照一定规则(FIFO,LRU)淘汰;
3. 当访问历史队列中的数据访问次数达到K次后,将数据索引从历史队列删除,将数据移到缓存队列中,并缓存此数据,缓存队列重新按照时间排序;
4. 缓存数据队列中被再次访问后,重新排序;
5. 需要淘汰数据时,淘汰缓存队列中排在末尾的数据,即:淘汰“倒数第K次访问离现在最久”的数据。
OK,针对本题目,我们给出一段简单的实现代码,在下面的代码中我们使用map+list的方式来实现,其复杂度是O(logN)
其实,也就是使用红黑树+双向链表的方式来实现,map相当于一个红黑树,用来负责查找一块Cashe是否已经在内存中,
而list相当于一个双向链表,能够方便地插入和删除某个元素。我们可以发现,map的查找效率是O(logN),list插入删除的
效率是O(1),因此总体的复杂度是O(logN). 好了下面上代码:
通过LeetCode, 如有错误之处还请大家指正,从通学习进步:
#include <iostream>#include <map>#include <list>#include <utility>using namespace std;class LRUCache{public:LRUCache(int capacity) {m_capacity = capacity ;}int get(int key) {int retValue = -1 ;map<int, list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator> ::iterator it = cachesMap.find(key) ; //如果在Cashe中,将记录移动到链表的最前端if (it != cachesMap.end()){retValue = it ->second->second ;//移动到最前端list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator ptrPair = it -> second ;pair<int, int> tmpPair = *ptrPair ;caches.erase(ptrPair) ;caches.push_front(tmpPair) ;//修改map中的值cachesMap[key] = caches.begin() ;}return retValue ;}void set(int key, int value) {map<int, list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator> ::iterator it = cachesMap.find(key) ;if (it != cachesMap.end()) //已经存在其中{ list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator ptrPait = it ->second ;ptrPait->second = value ;//移动到最前面pair<int , int > tmpPair = *ptrPait ;caches.erase(ptrPait) ;caches.push_front(tmpPair) ;//更新mapcachesMap[key] = caches.begin() ;}else //不存在其中{pair<int , int > tmpPair = make_pair(key, value) ;if (m_capacity == caches.size()) //已经满{int delKey = caches.back().first ;caches.pop_back() ; //删除最后一个//删除在map中的相应项map<int, list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator> ::iterator delIt = cachesMap.find(delKey) ;cachesMap.erase(delIt) ;}caches.push_front(tmpPair) ;cachesMap[key] = caches.begin() ; //更新map}}private:int m_capacity ;//cashe的大小list<pair<int, int> > caches ;//用一个双链表存储cashe的内容map< int, list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator> cachesMap ;//使用map加快查找的速度};int main(int argc, char **argv){LRUCache s(2) ;s.set(2, 1) ;s.set(1, 1) ;cout << s.get(2) << endl;s.set(4, 1) ;cout << s.get(1) << endl;cout << s.get(2) << endl;return 0 ;}其实,我们可以发现,主要的耗时操作就是查找,因此,我们可以使用hash_map来代替map,因此时间复杂度可以降低到O(1),
下面是我在VS2008上编译通过的代码,但由于LeetCode后台是G++的缘故,没有提交成功,不过我个人感觉把代码贴上还是很有帮助的:
如有不妥之处,还请大家批评指正,共同学习进步:
#include <iostream>#include <hash_map>#include <list>#include <utility>using namespace std;using namespace stdext;class LRUCache{public:LRUCache(int capacity) {m_capacity = capacity ;}int get(int key) {int retValue = -1 ;hash_map<int, list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator> ::iterator it = cachesMap.find(key) ;//如果在Cashe中,将记录移动到链表的最前端if (it != cachesMap.end()){retValue = it ->second->second ;//移动到最前端list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator ptrPair = it -> second ;pair<int, int> tmpPair = *ptrPair ;caches.erase(ptrPair) ;caches.push_front(tmpPair) ;//修改map中的值cachesMap[key] = caches.begin() ;}return retValue ;}void set(int key, int value) {hash_map<int, list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator> ::iterator it = cachesMap.find(key) ;if (it != cachesMap.end()) //已经存在其中{list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator ptrPait = it ->second ;ptrPait->second = value ;//移动到最前面pair<int , int > tmpPair = *ptrPait ;caches.erase(ptrPait) ;caches.push_front(tmpPair) ;//更新mapcachesMap[key] = caches.begin() ;}else //不存在其中{pair<int , int > tmpPair = make_pair(key, value) ;if (m_capacity == caches.size()) //已经满{int delKey = caches.back().first ;caches.pop_back() ; //删除最后一个//删除在map中的相应项hash_map<int, list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator> ::iterator delIt = cachesMap.find(delKey) ;cachesMap.erase(delIt) ;}caches.push_front(tmpPair) ;cachesMap[key] = caches.begin() ; //更新map}}private:int m_capacity ;//cashe的大小list<pair<int, int> > caches ;//用一个双链表存储cashe的内容hash_map< int, list<pair<int, int> > :: iterator> cachesMap ;//使用map加快查找的速度};int main(int argc, char **argv){LRUCache s(2) ;s.set(2, 1) ;s.set(1, 1) ;cout << s.get(2) << endl;s.set(4, 1) ;cout << s.get(1) << endl;cout << s.get(2) << endl;return 0 ;}- LRU cache的实现
- LRU cache实现 (Java)
- [Google] LRU cache实现
- 实现LRU Cache
- 如何实现 LRU Cache?
- LRU Cache实现
- LRU Cache的实现
- LRU Cache 实现
- 简单LRU cache 实现
- LRU cache实现
- LRU cache实现 (Java)
- LRU cache实现
- LRU Cache的实现
- 如何实现 LRU Cache
- LRU Cache的实现
- LRU cache实现
- Python 实现LRU Cache
- 【链表】实现LRU缓存策略LRU Cache
- 为什么王兴雷军他们能二次创业成功
- js不支持重载的解决方案
- 哈希表
- 蜗牛—ORACLE基础之学习(一)
- CF Round #240 (Div. 2) C
- LRU Cache 实现
- android的自定义camera竖屏时,摄像头自动旋转90度的解决方案
- iOS多线程编程之NSThread的使用
- 黑马程序员-适配器模式
- SVN使用
- 2014微软编程一小时 题目1 : Arithmetic Expression Java实现
- PAT 1003
- 苹果新专利!红外光谱感应助力触控新技术
- Reorder List


