Codeforces Round #240 (Div. 1) 前3题 解题报告
来源:互联网 发布:科比詹姆斯知乎 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/05 11:40
第一次变紫色后打Div1,A两题,被虐回Div2了……
It's holiday. Mashmokh and his boss, Bimokh, are playing a game invented by Mashmokh.
In this game Mashmokh writes sequence of n distinct integers on the board. Then Bimokh makes several (possibly zero) moves. On the first move he removes the first and the second integer from from the board, on the second move he removes the first and the second integer of the remaining sequence from the board, and so on. Bimokh stops when the board contains less than two numbers. When Bimokh removes numbers x and y from the board, he gets gcd(x, y) points. At the beginning of the game Bimokh has zero points.
Mashmokh wants to win in the game. For this reason he wants his boss to get exactly k points in total. But the guy doesn't know how choose the initial sequence in the right way.
Please, help him. Find n distinct integers a1, a2, ..., an such that his boss will score exactly k points. Also Mashmokh can't memorize too huge numbers. Therefore each of these integers must be at most 109.
The first line of input contains two space-separated integers n, k (1 ≤ n ≤ 105; 0 ≤ k ≤ 108).
If such sequence doesn't exist output -1 otherwise output n distinct space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
5 2
1 2 3 4 5
5 3
2 4 3 7 1
7 2
-1
gcd(x, y) is greatest common divisor of x and y.
解题报告: 给定gcd的和,求任意符合该和的数列。做法是前面所有的数对的gcd为1,使最后一对数的gcd加上前面的所有1满足条件。
代码如下:
#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;void work(int n, int k){ int p = n/2; if(n==1 && k==0) { puts("1"); return; } else if(n==1) { puts("-1"); return; } if(k<p) { puts("-1"); return; } int t=2; for(int i=1;i<p;i++,t+=2) printf("%d %d ", t, t+1),k--; if(t<k) t=k; else if(t%k) t=t/k*k+k; printf("%d %d", t, t+k); if(n&1) printf(" 1\n"); else puts("");}int main(){ int n, k; while(~scanf("%d%d", &n, &k)) work(n, k);}Mashmokh's boss, Bimokh, didn't like Mashmokh. So he fired him. Mashmokh decided to go to university and participate in ACM instead of finding a new job. He wants to become a member of Bamokh's team. In order to join he was given some programming tasks and one week to solve them. Mashmokh is not a very experienced programmer. Actually he is not a programmer at all. So he wasn't able to solve them. That's why he asked you to help him with these tasks. One of these tasks is the following.
A sequence of l integers b1, b2, ..., bl (1 ≤ b1 ≤ b2 ≤ ... ≤ bl ≤ n) is called good if each number divides (without a remainder) by the next number in the sequence. More formally 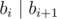 for all i (1 ≤ i ≤ l - 1).
for all i (1 ≤ i ≤ l - 1).
Given n and k find the number of good sequences of length k. As the answer can be rather large print it modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
The first line of input contains two space-separated integers n, k (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 2000).
Output a single integer — the number of good sequences of length k modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
3 2
5
6 4
39
2 1
2
In the first sample the good sequences are: [1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3], [1, 2], [1, 3].
解题报告:直接DP即可。代码如下:
#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;const int mod = 1000000007;typedef long long LL;int dp[2222][2222];void init(){ for(int i=1;i<=2000;i++) dp[i][1] = 1; for(int i=1;i<=2000;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=2000;j++) { int t=j; while(t<=2000) { dp[t][i+1]=((LL)dp[t][i+1]+dp[j][i])%mod; t+=j; } } }}void work(int n, int k){ int ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) ans=((LL)ans+dp[i][k])%mod; printf("%d\n", ans);}int main(){ init(); int n, k; while(~scanf("%d%d", &n ,&k)) work(n, k);}Mashmokh's boss, Bimokh, didn't like Mashmokh. So he fired him. Mashmokh decided to go to university and participate in ACM instead of finding a new job. He wants to become a member of Bamokh's team. In order to join he was given some programming tasks and one week to solve them. Mashmokh is not a very experienced programmer. Actually he is not a programmer at all. So he wasn't able to solve them. That's why he asked you to help him with these tasks. One of these tasks is the following.
You have an array a of length 2n and m queries on it. The i-th query is described by an integer qi. In order to perform the i-th query you must:
- split the array into 2n - qi parts, where each part is a subarray consisting of 2qi numbers; the j-th subarray (1 ≤ j ≤ 2n - qi) should contain the elements a[(j - 1)·2qi + 1], a[(j - 1)·2qi + 2], ..., a[(j - 1)·2qi + 2qi];
- reverse each of the subarrays;
- join them into a single array in the same order (this array becomes new array a);
- output the number of inversions in the new a.
Given initial array a and all the queries. Answer all the queries. Please, note that the changes from some query is saved for further queries.
The first line of input contains a single integer n (0 ≤ n ≤ 20).
The second line of input contains 2n space-separated integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[2n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109), the initial array.
The third line of input contains a single integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 106).
The fourth line of input contains m space-separated integers q1, q2, ..., qm (0 ≤ qi ≤ n), the queries.
Note: since the size of the input and output could be very large, don't use slow output techniques in your language. For example, do not use input and output streams (cin, cout) in C++.
Output m lines. In the i-th line print the answer (the number of inversions) for the i-th query.
22 1 4 341 2 0 2
0660
11 230 1 1
010
If we reverse an array x[1], x[2], ..., x[n] it becomes new array y[1], y[2], ..., y[n], where y[i] = x[n - i + 1] for each i.
The number of inversions of an array x[1], x[2], ..., x[n] is the number of pairs of indices i, j such that: i < j and x[i] > x[j].
解题报告:那天没做出来,今天看了别人的代码……
简单来说就是将所有的数建成一棵树,每个节点保存左子树中大于右子树的对数,小于右子树的对数。因为做分段,逆向操作时,大于和小于都是交换,所有每层的节点可以合并。复杂度就可以大大降低。代码如下:
#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;int a[(1<<20)+10];LL big[22], small[22];void divide(int l, int r, int dep){ if(l==r) return ; int m = (l+r)/2; divide(l, m, dep+1); divide(m+1, r, dep+1); for(int i=l;i<=m;i++) { big[dep]+=lower_bound(a+m+1, a+r+1, a[i])-(a+m+1); small[dep]+=(r-m)-(upper_bound(a+m+1, a+r+1, a[i])-(a+m+1)); } sort(a+l, a+r+1);}void work(int n){ for(int i=0;i<(1<<n);i++) scanf("%d", a+i); memset(big, 0, sizeof(big)); memset(small, 0, sizeof(small)); divide(0, (1<<n)-1, 0); int m; scanf("%d", &m); while(m--) { int t; scanf("%d", &t); for(int i=(n-t);i<n;i++) swap(big[i], small[i]); LL ans=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) ans+=big[i]; printf("%I64d\n", ans); }}int main(){ int n; while(~scanf("%d", &n)) work(n);}- Codeforces Round #240 (Div. 1) 前3题 解题报告
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div.1) 解题报告
- Codeforces Round #327 (Div. 1) 解题报告
- Codeforces Round #326 (Div. 1) 解题报告
- Codeforces Round #325 (Div. 1) 解题报告
- Codeforces Round #240 (Div. 2)(前三题解题报告)
- Codeforces Round #238 (Div. 2)前3题解题报告
- Codeforces Round #240 (Div. 2) ABCD简单解题报告
- Codeforces Round #278 (Div. 1) 解题报告 A.B.
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 1)解题报告A.B.C.
- Codeforces Round #290 (Div. 1) 解题报告(A B)
- Codeforces Round #299 (Div. 1) 解题报告 (AB)
- Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 1) A.B.C 解题报告
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 1)解题报告A.B.C.
- [Updating]Codeforces Round #402 (Div. 1)解题报告
- Codeforces Round #453 (Div. 1)解题报告(ABCD)
- Codeforces Round #149 (Div. 2)解题报告
- Codeforces Round #180 (Div. 2) 解题报告
- 按位与、或、异或等运算方法
- hibernate加载映射文件浅析
- getopt()
- 设计模式之桥接模式
- 数据结构-二叉树
- Codeforces Round #240 (Div. 1) 前3题 解题报告
- 设计模式之工厂模式
- xmind 安装及破解
- 称重传感器常用技术参数
- Android下PinnedHeaderListView使用
- BigDecimal的用法
- keystore 介绍
- VA、VAO和VBO API备忘
- 请求筛选模块被配置为拒绝包含 hiddenSegment 节的 URL 中的路径。


